Geomancer
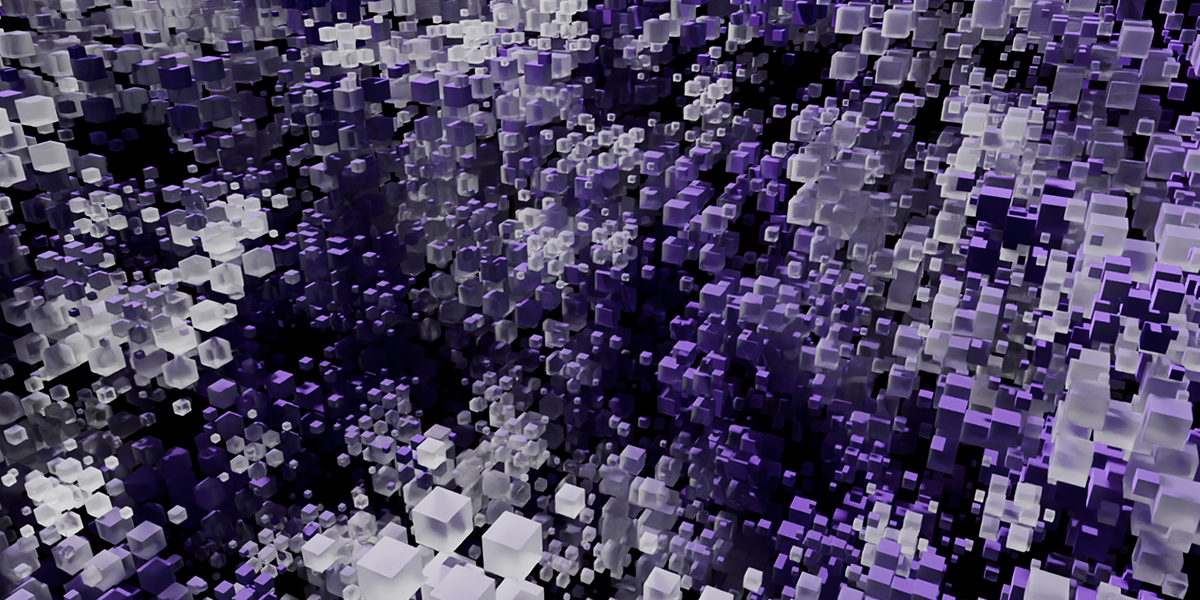

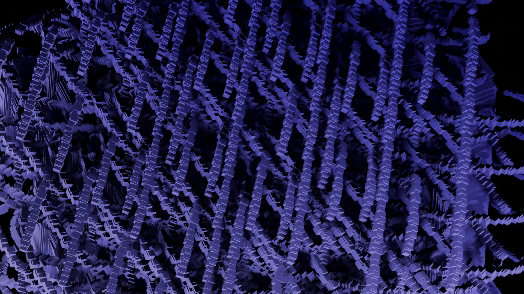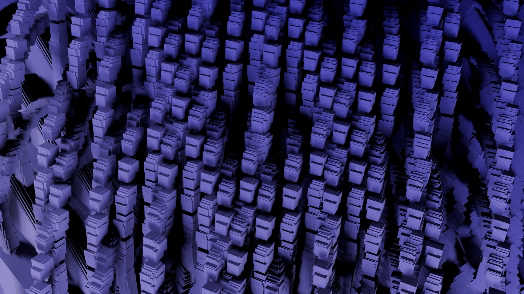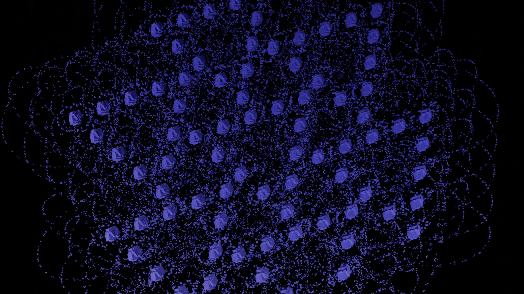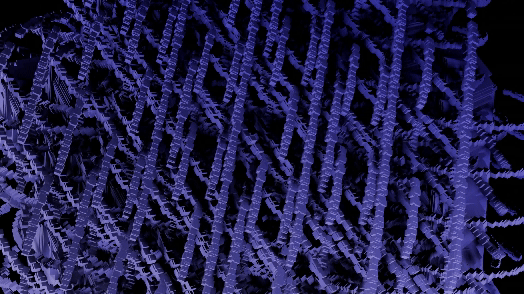
GeoMancer is a suite of geometry node setups that you can trigger at the press of a button. Each node setup has macro controls for easy to digest and manipulate or animate parameters. It is completely code driven, so no need to manage external project files. From the basics of instancing to complex mathematical methods and fractal distributions, GeoMancer aims to be a go-to resource those who like to build using geometry nodes. Stack them, modify them, animate them... see what you can do!
Features
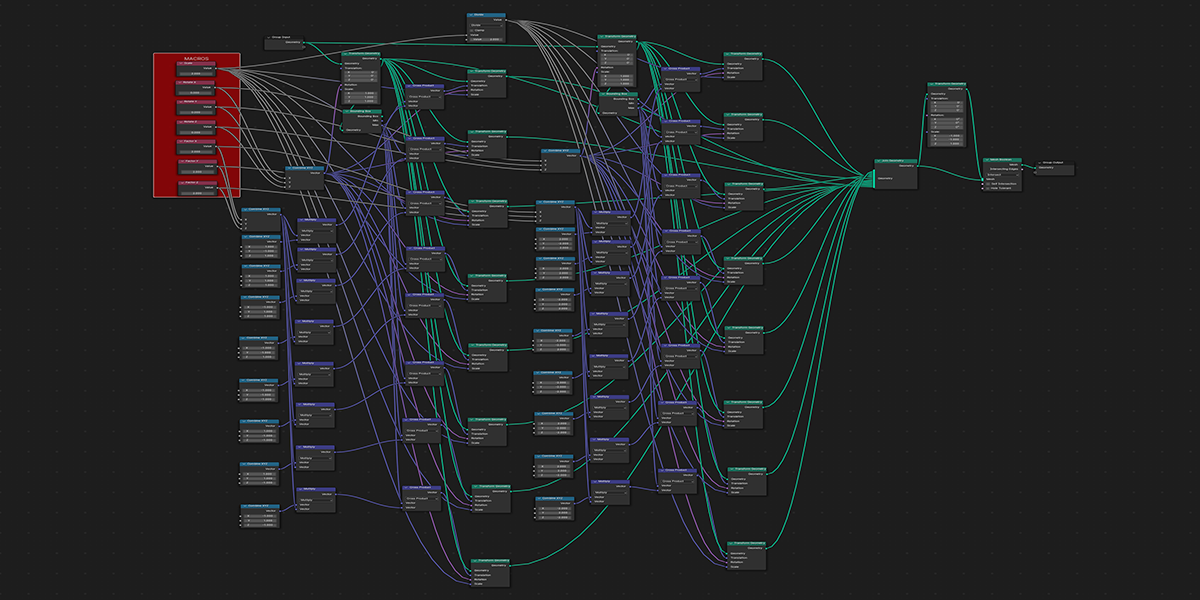
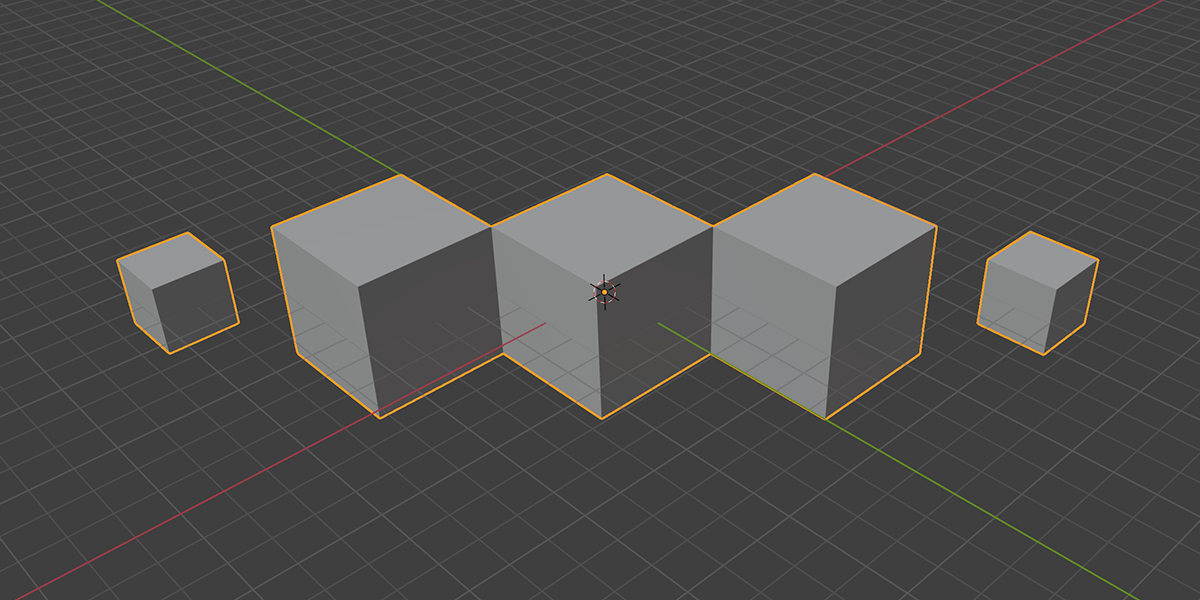
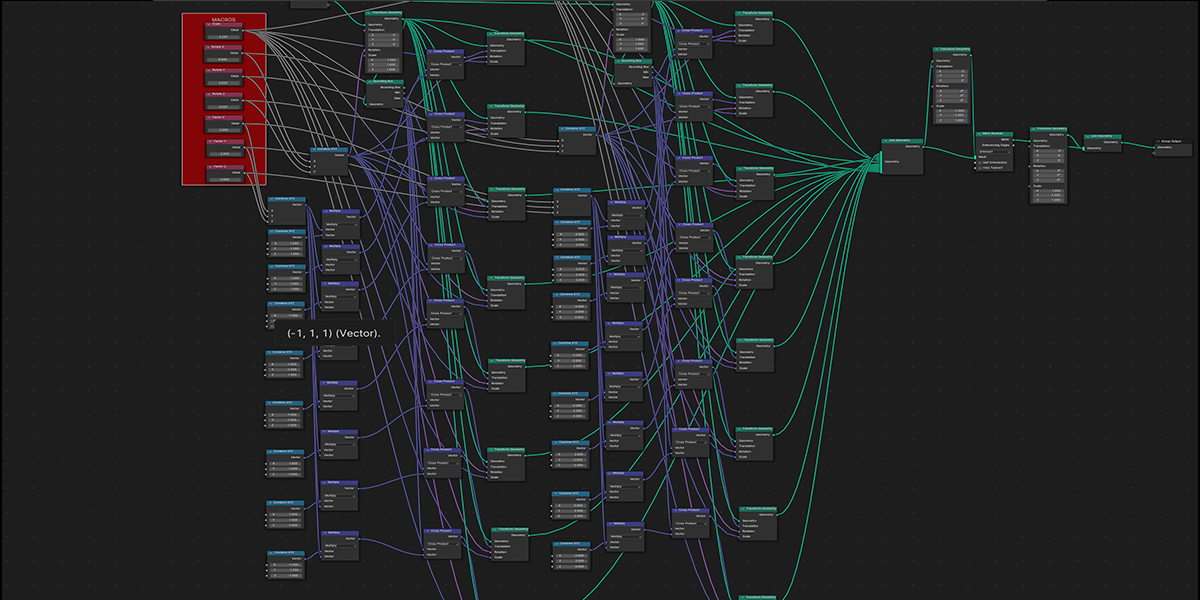
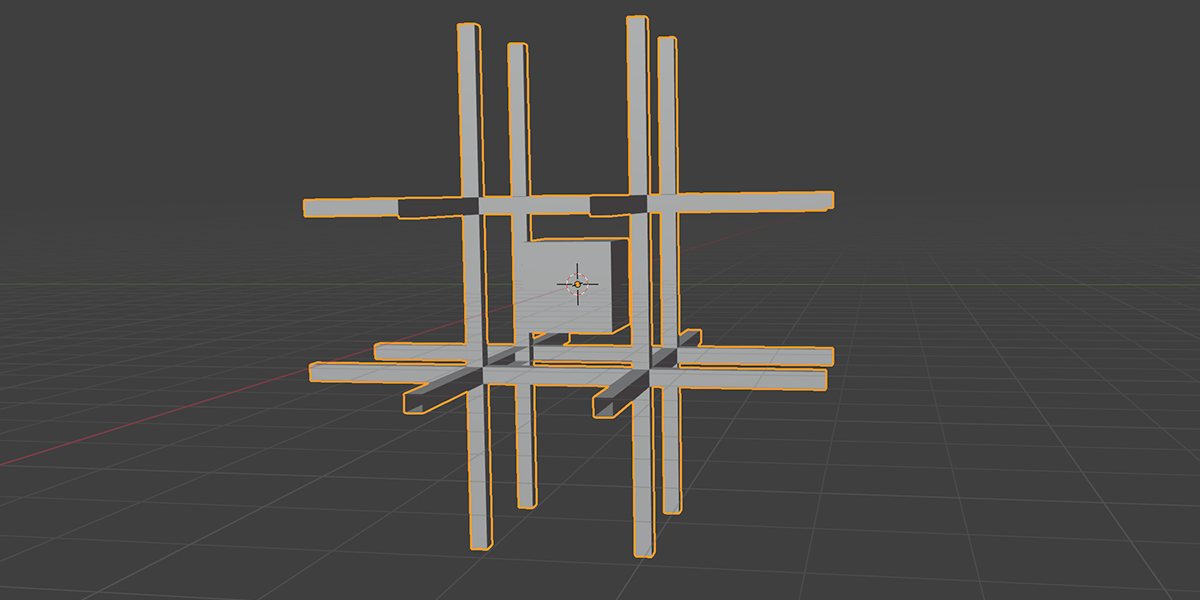
There are currently 21 primary node setups included in the add-on, with 3 variations for each, totally 63 node setups available. There is also a utility "Print Node Setup" operation at the top, which you can use to print any node setup you make if you wish to add your own presets or just get a code-version of your geometry node arrangement. Below we will look at each of the current operations. Each image shows the completed node tree as well as the three variations when applied to a basic default cube:
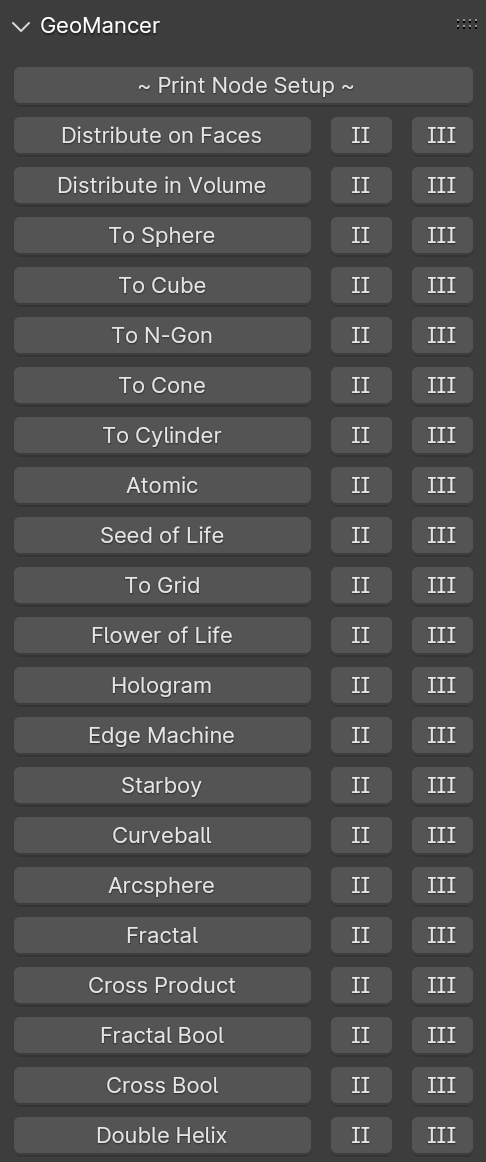
1) ~Print Node Setup~
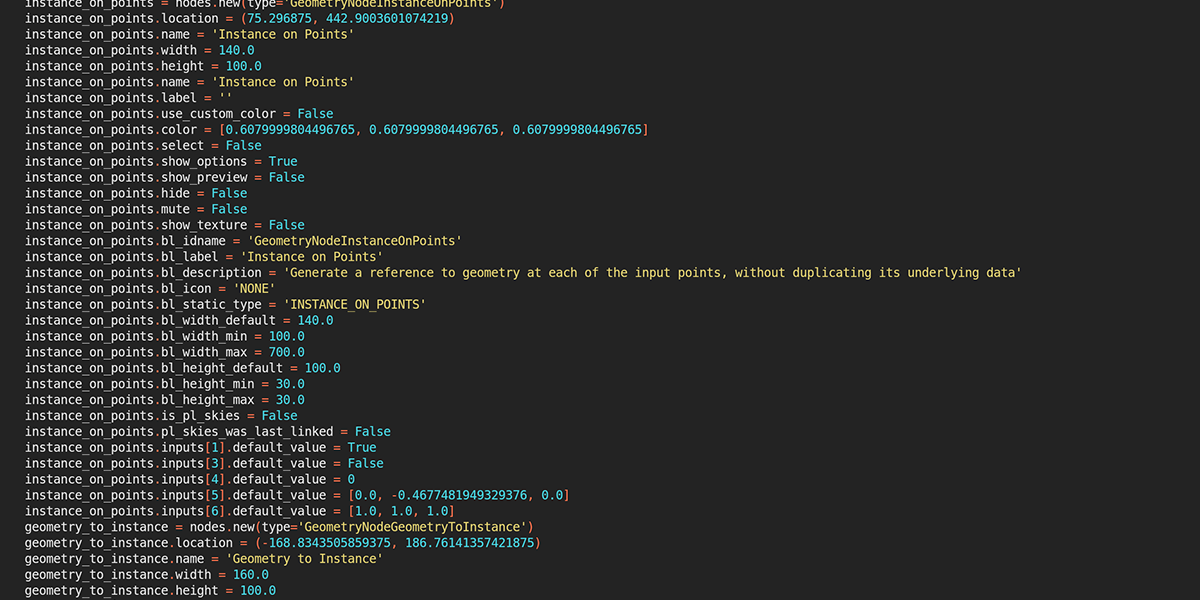
This button will print any selected Geometry Node setup to a python-formatted text document in Blender. This is a utility function that you can use to modify setups and create your own code-driven geometry nodes without a need to manage external projects or libraries. It is also useful for discovering callable functions or node indices if you want to dive into geometry nodes and python.
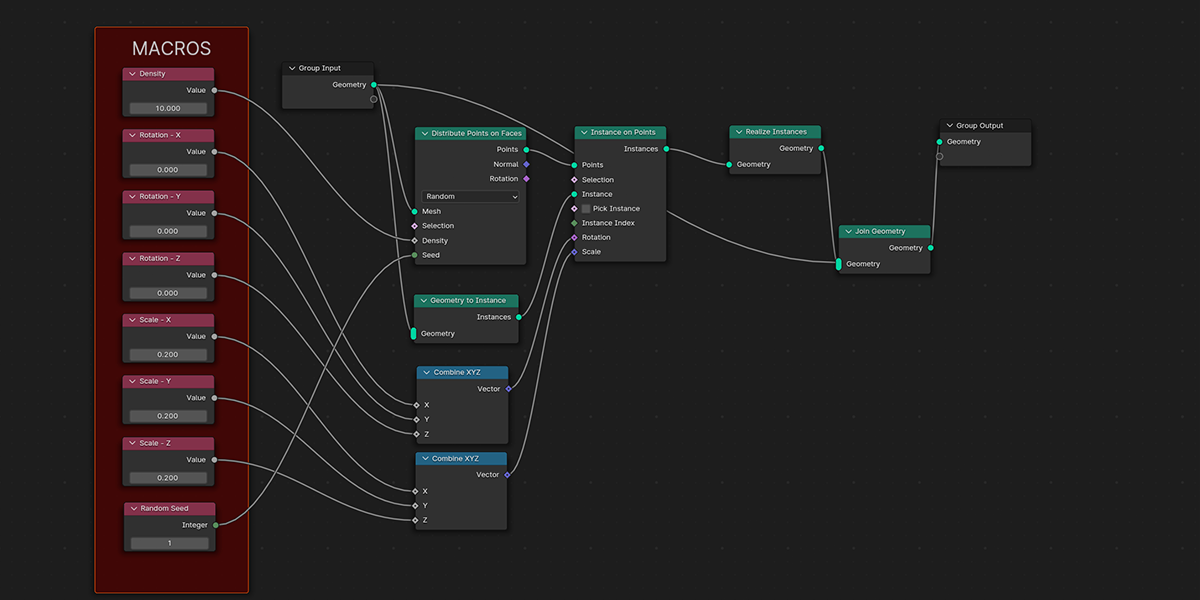
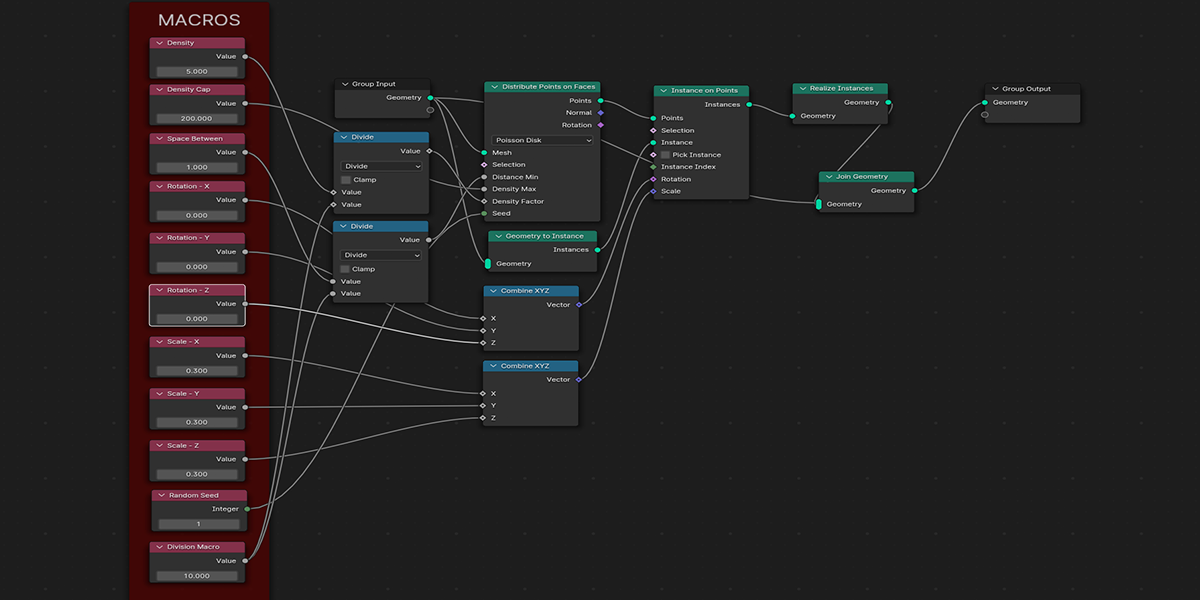
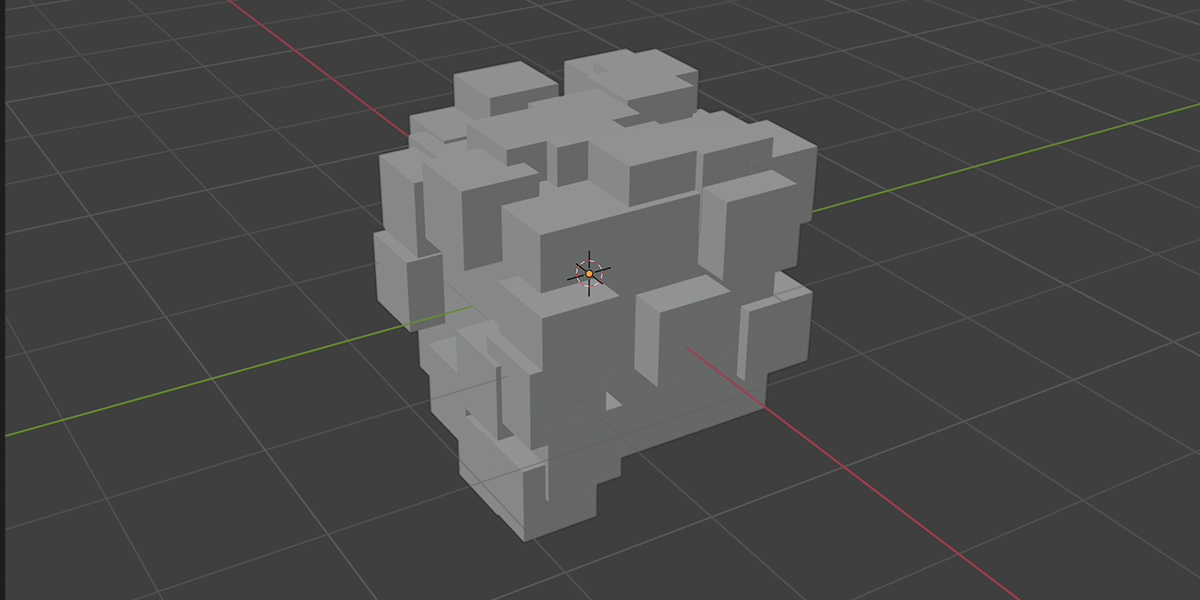
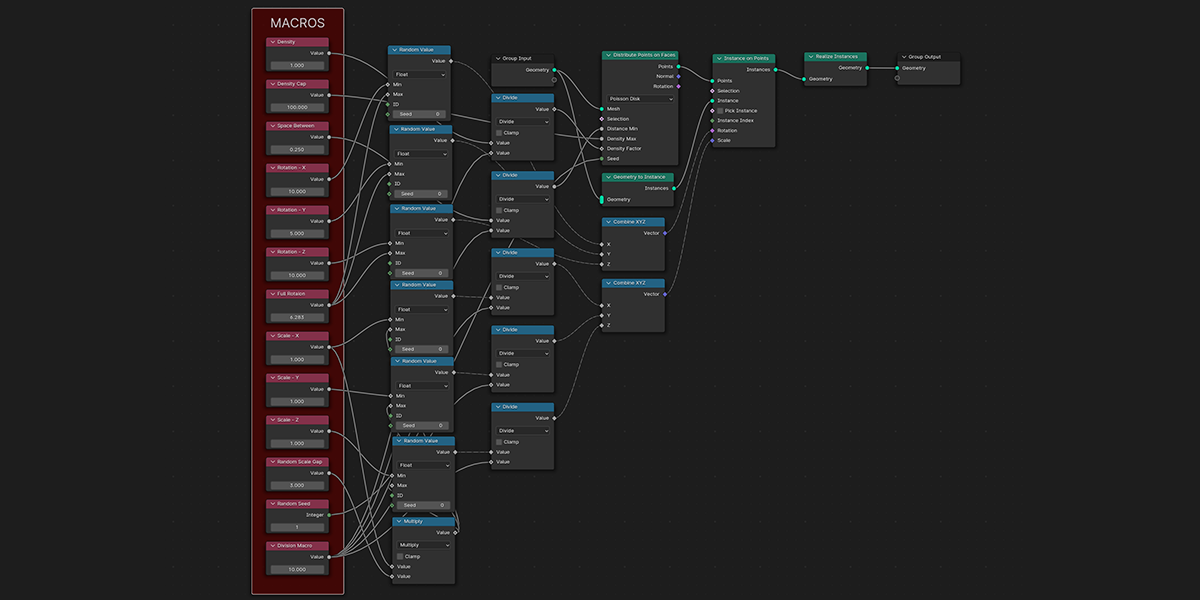
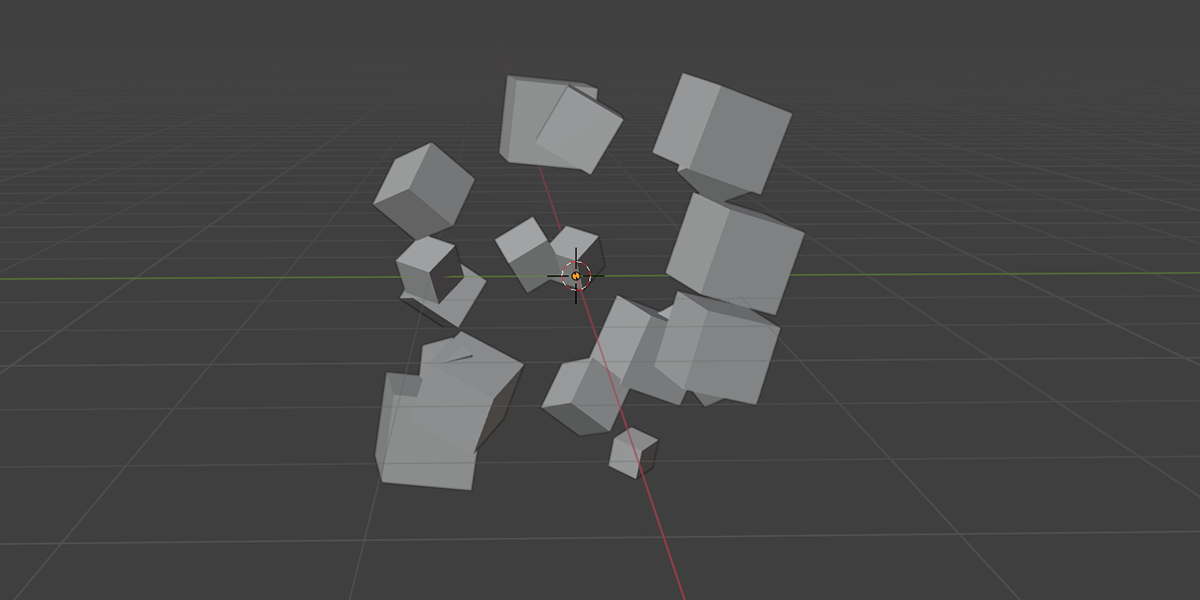
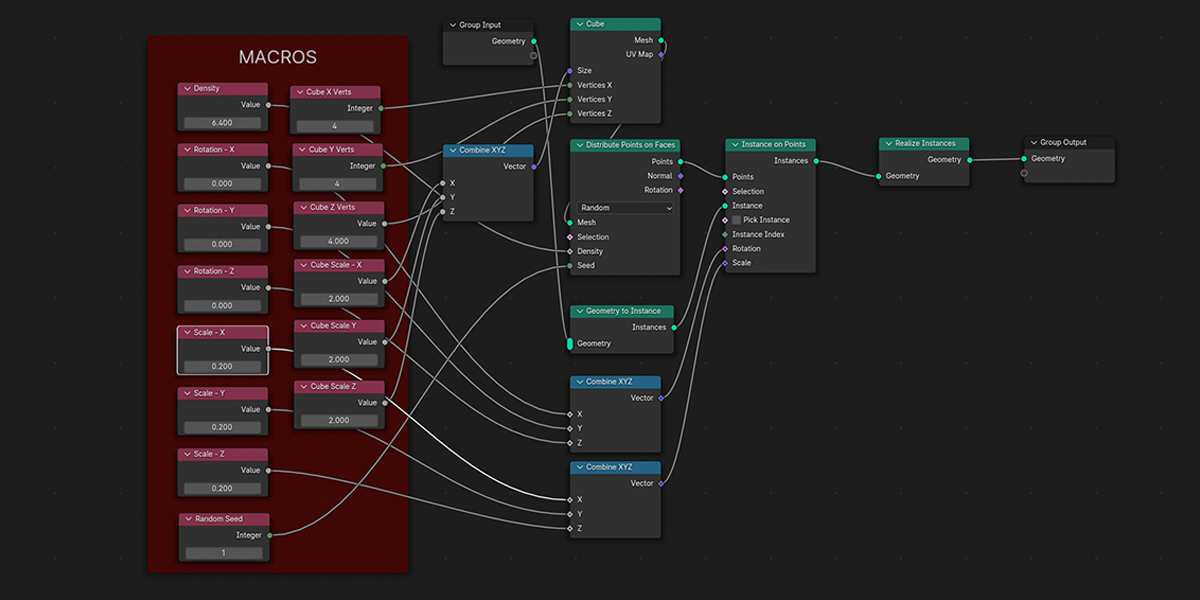
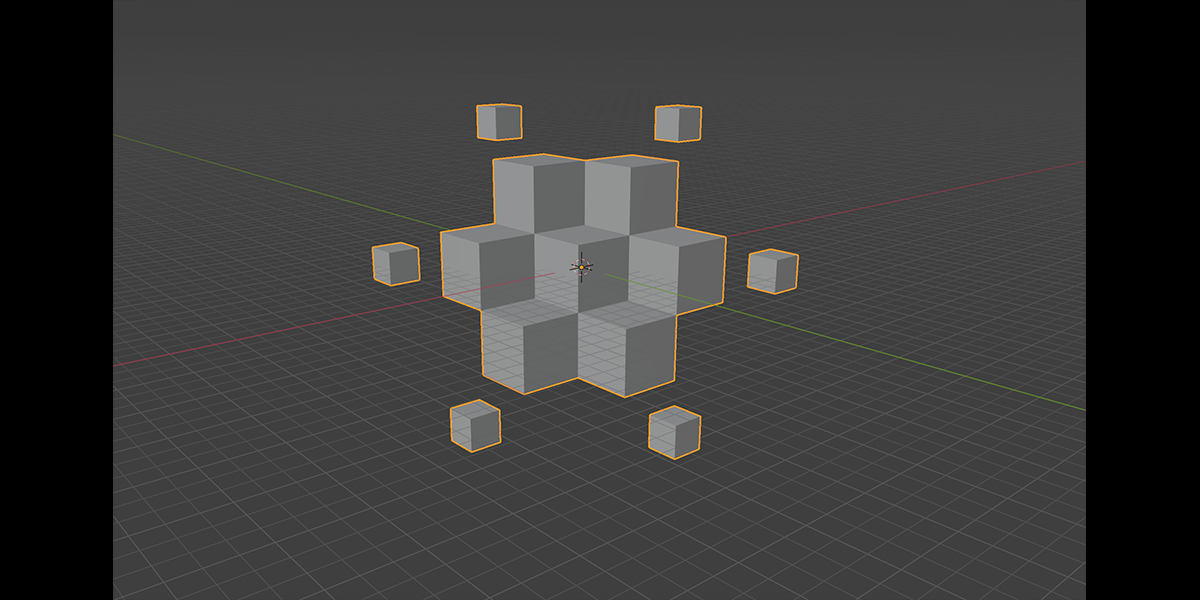
2) Distribute on Faces
A basic but commonly used geometry node setup, which will create instances of an object on the face of an object. The variations provide a combination of basic instancing, random rotation and scale
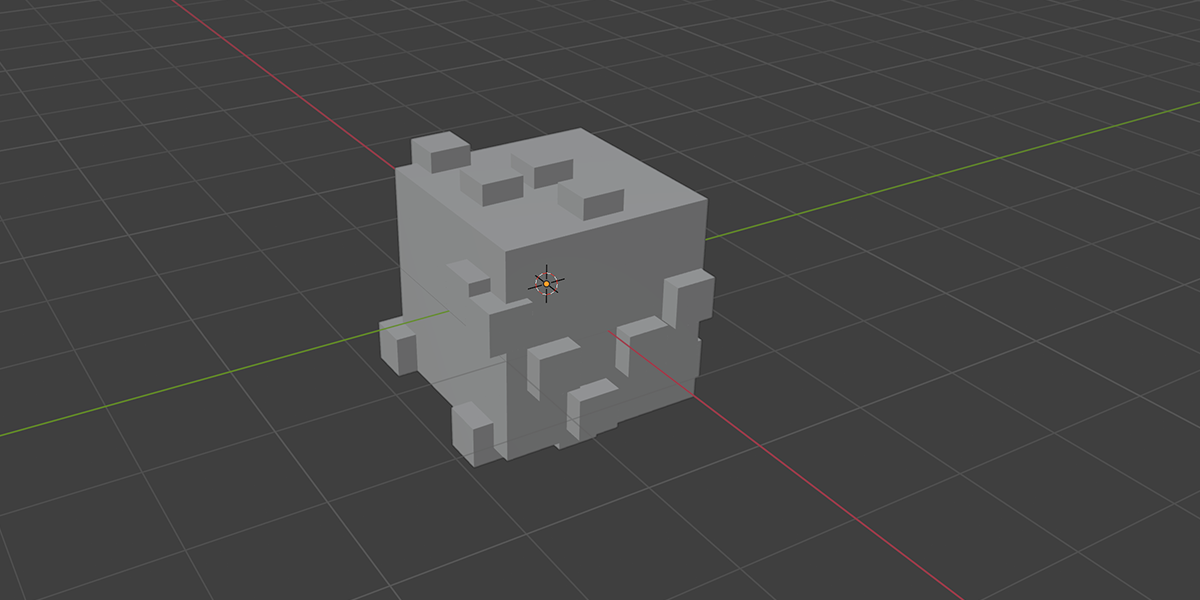
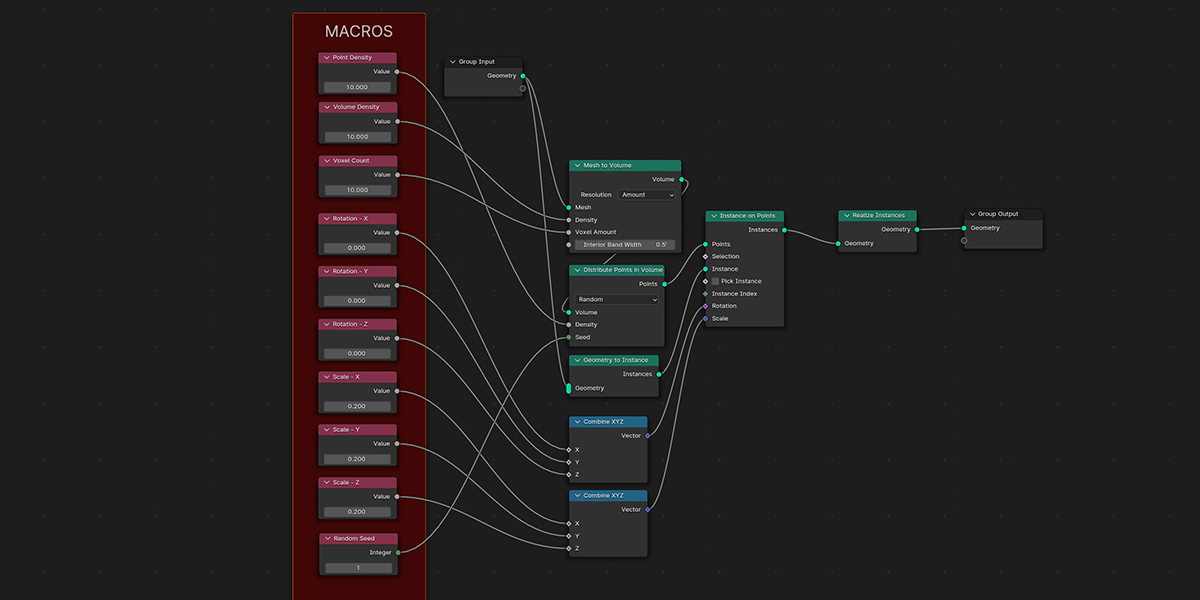
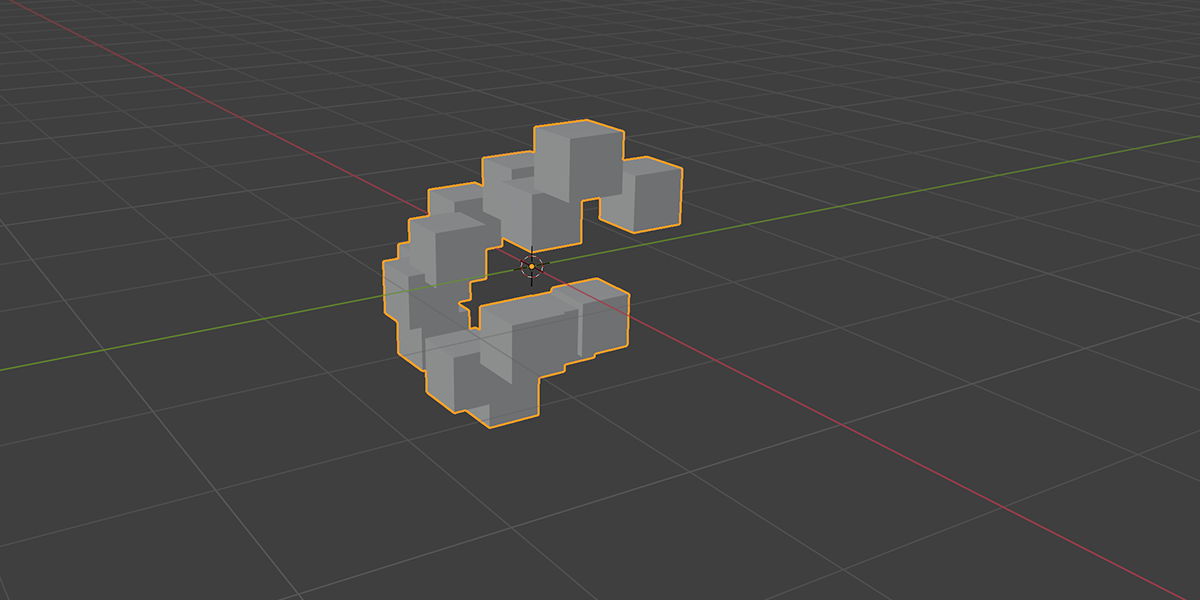
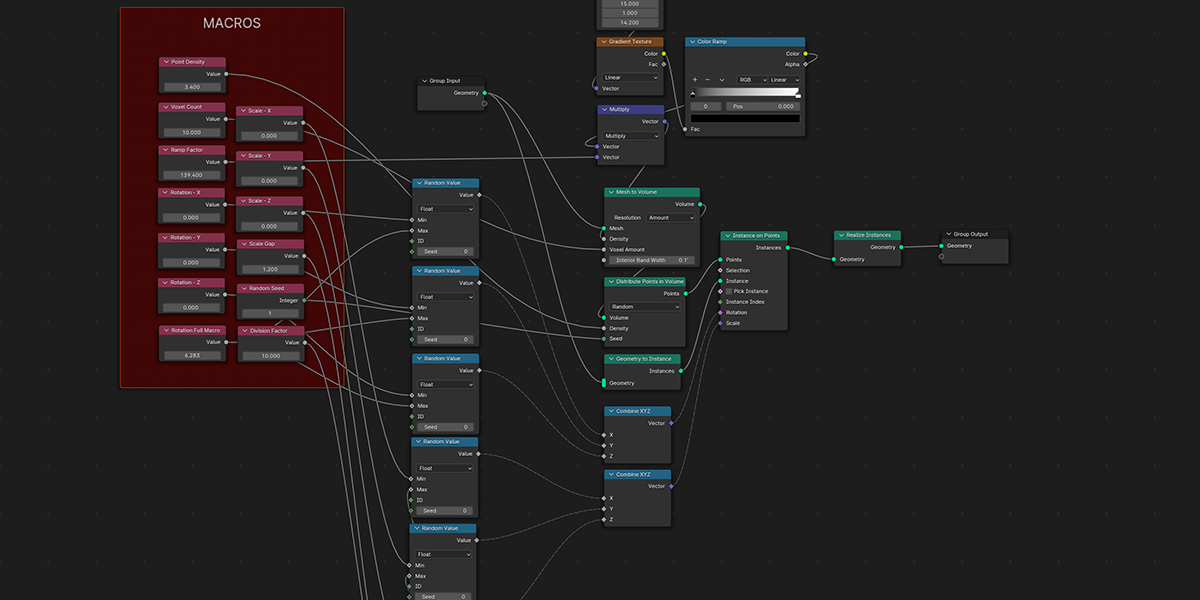
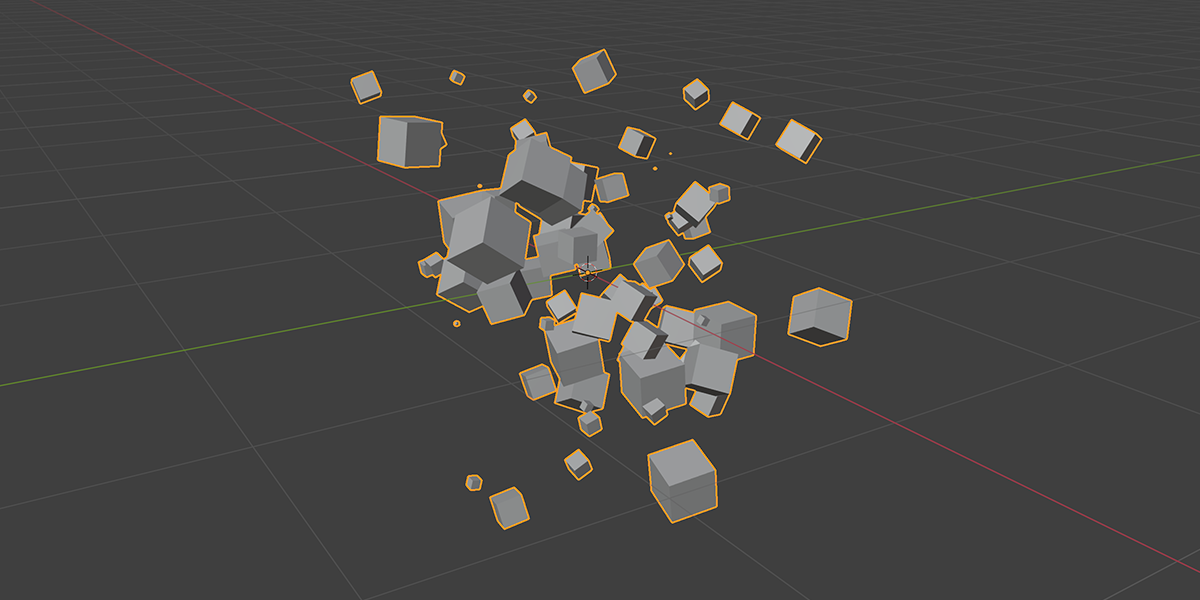
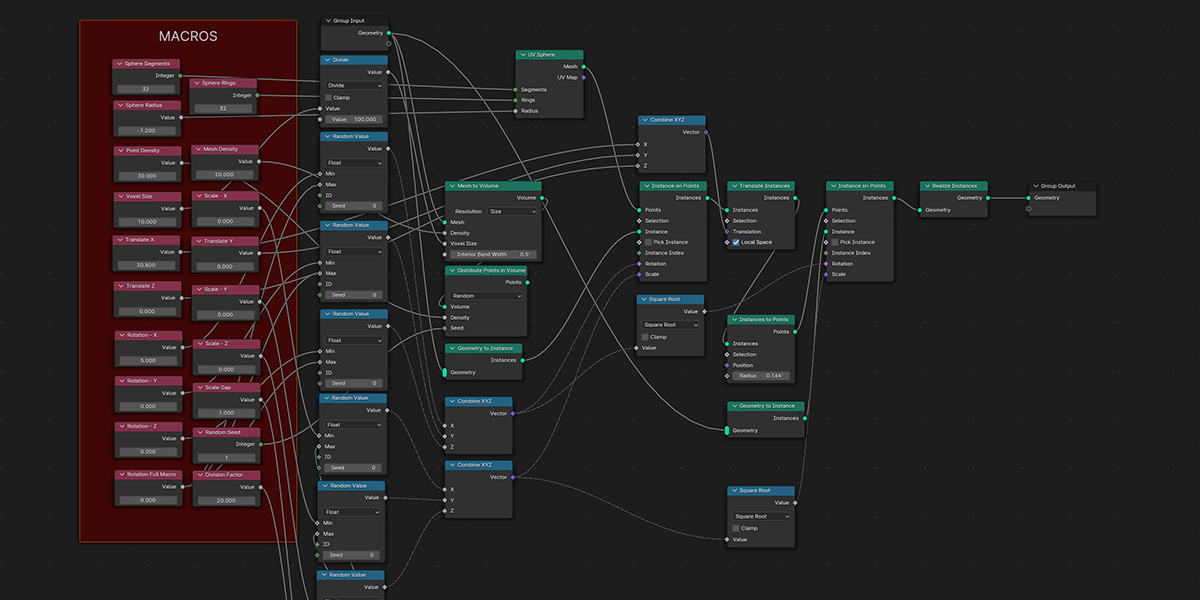
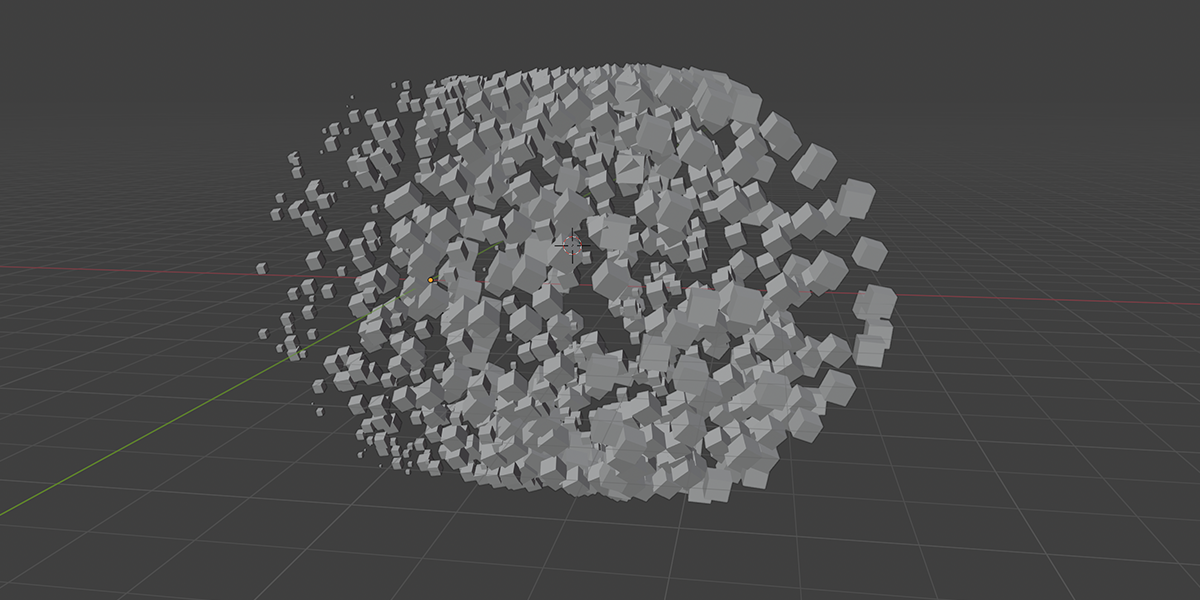
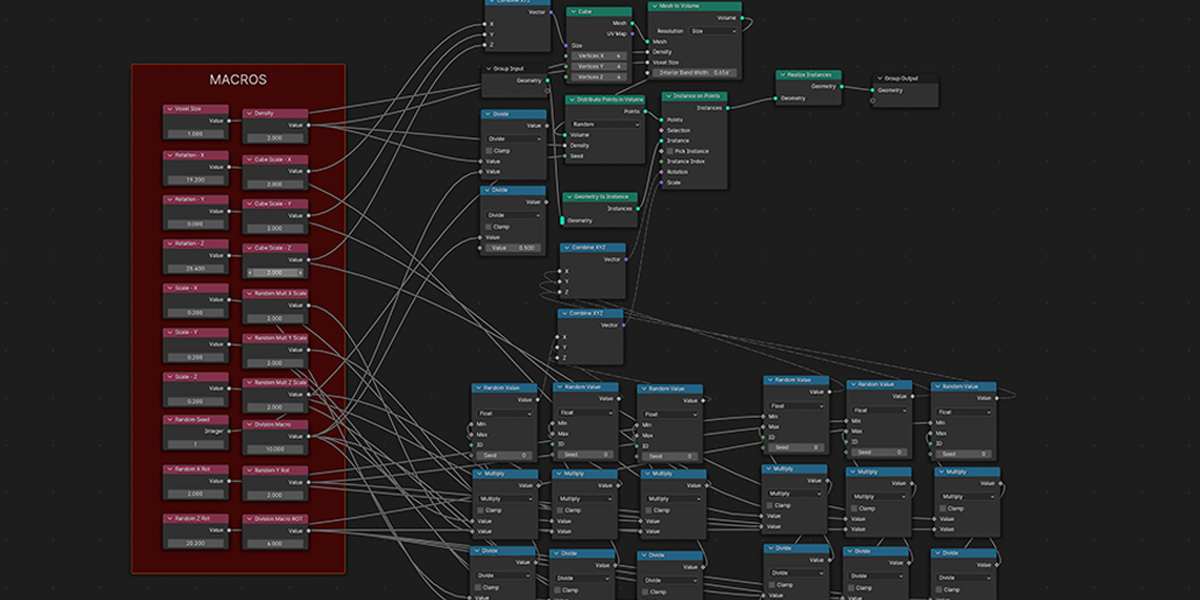
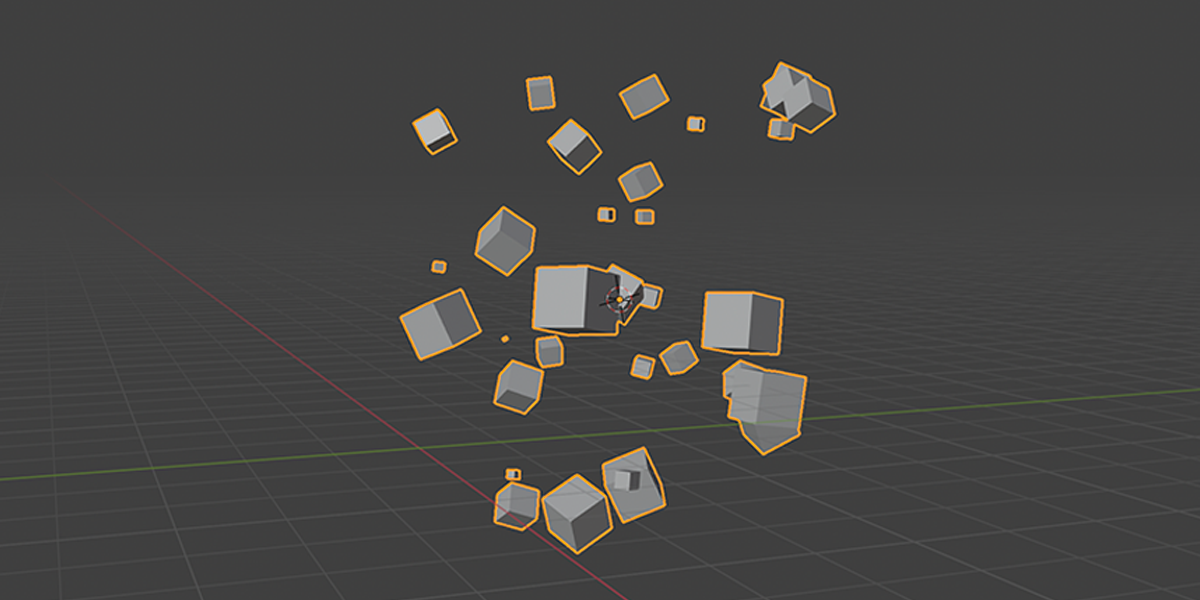
3) Distribute in Volume
Another common instancing method, similar to distribute on faces, but instead will instance within the volume of a selected mesh. Offers control over distribution type, density, randomization controls.
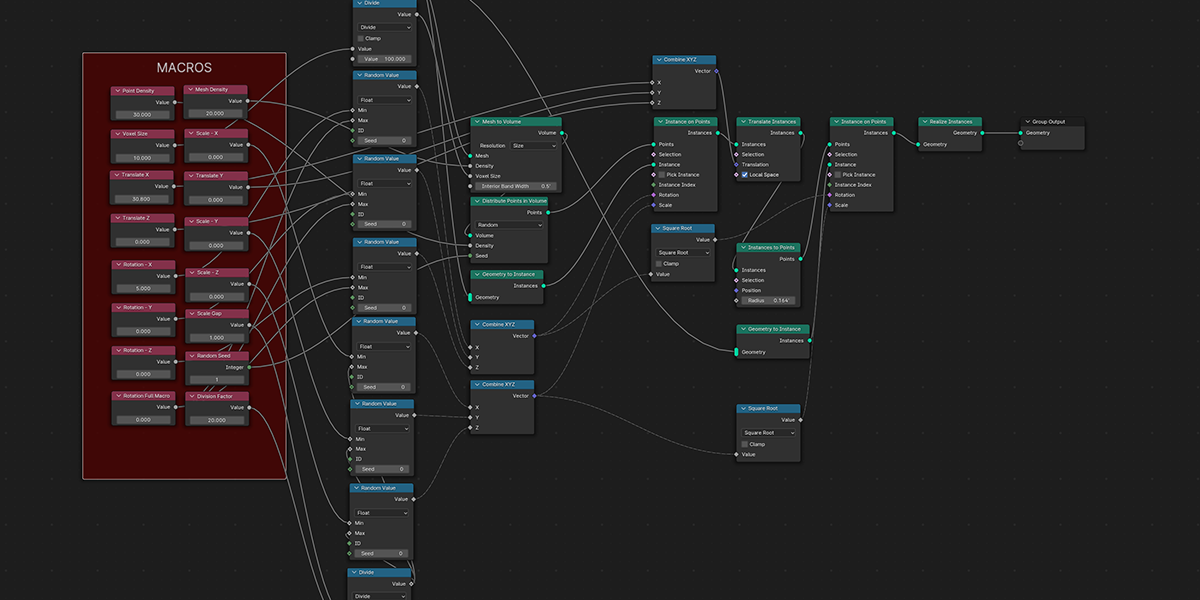
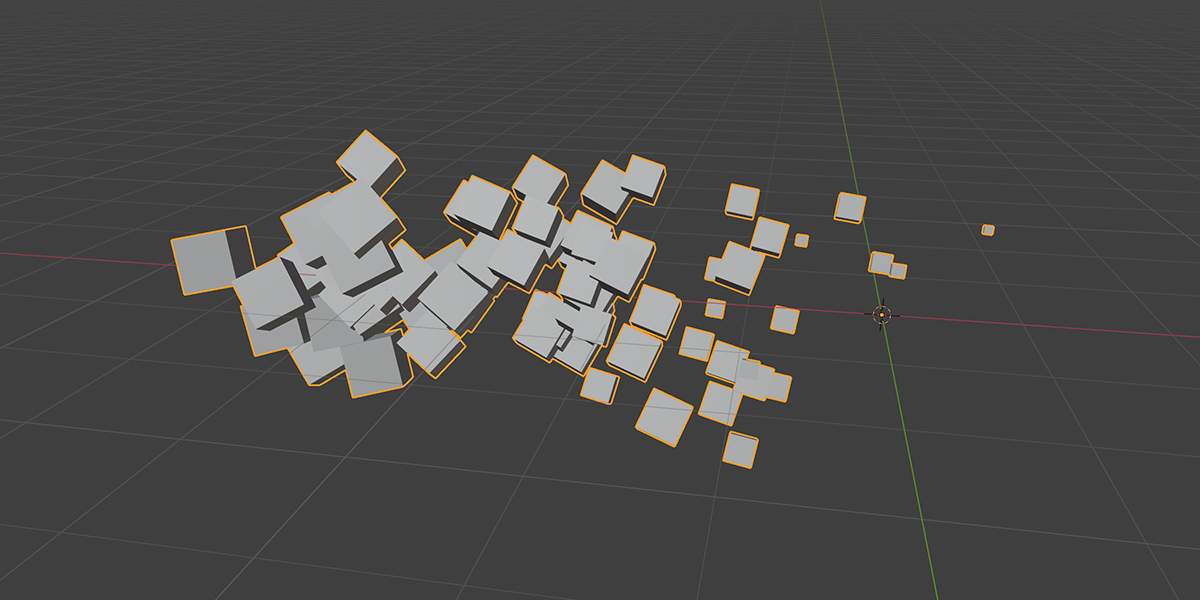
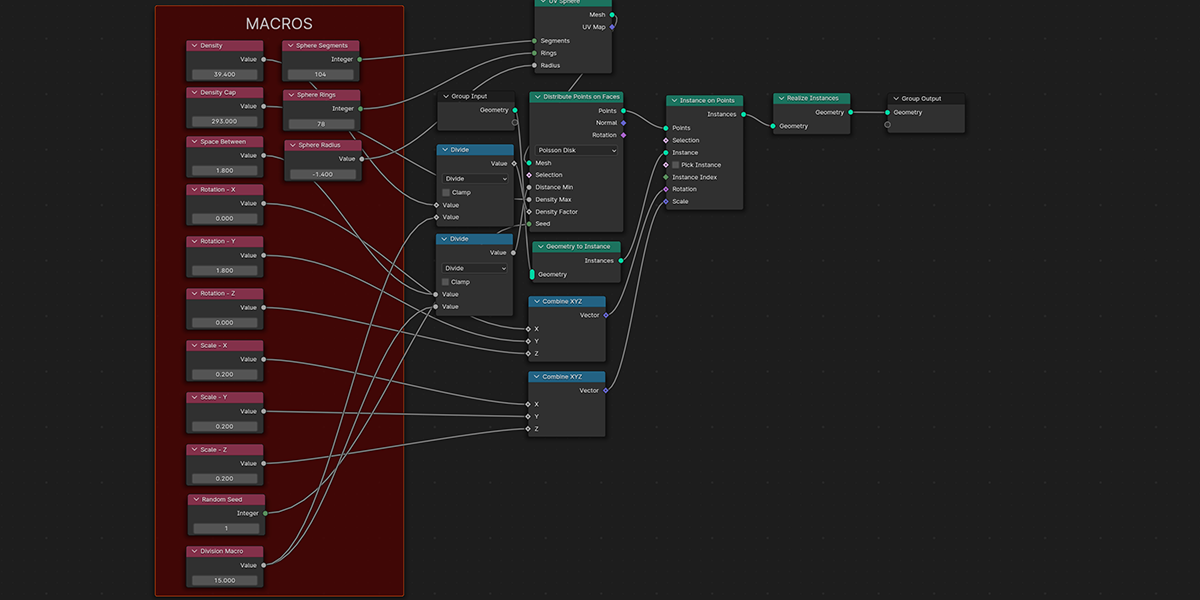
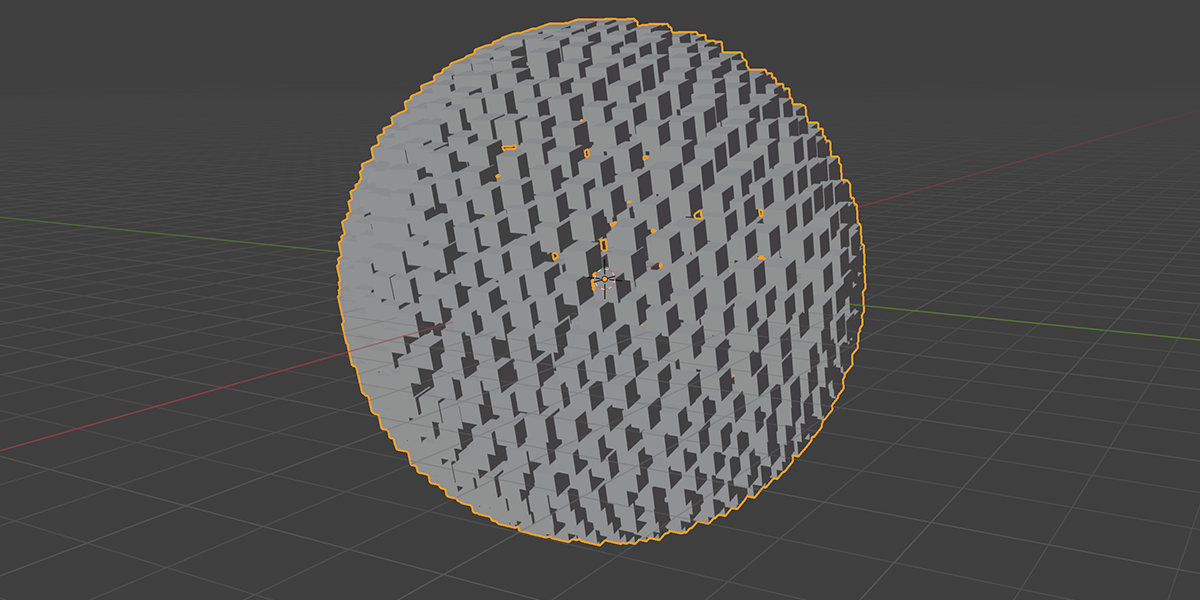
4) To Sphere
Uses a primitive sphere shape to distribute an object into a sphere with a variety of controls.
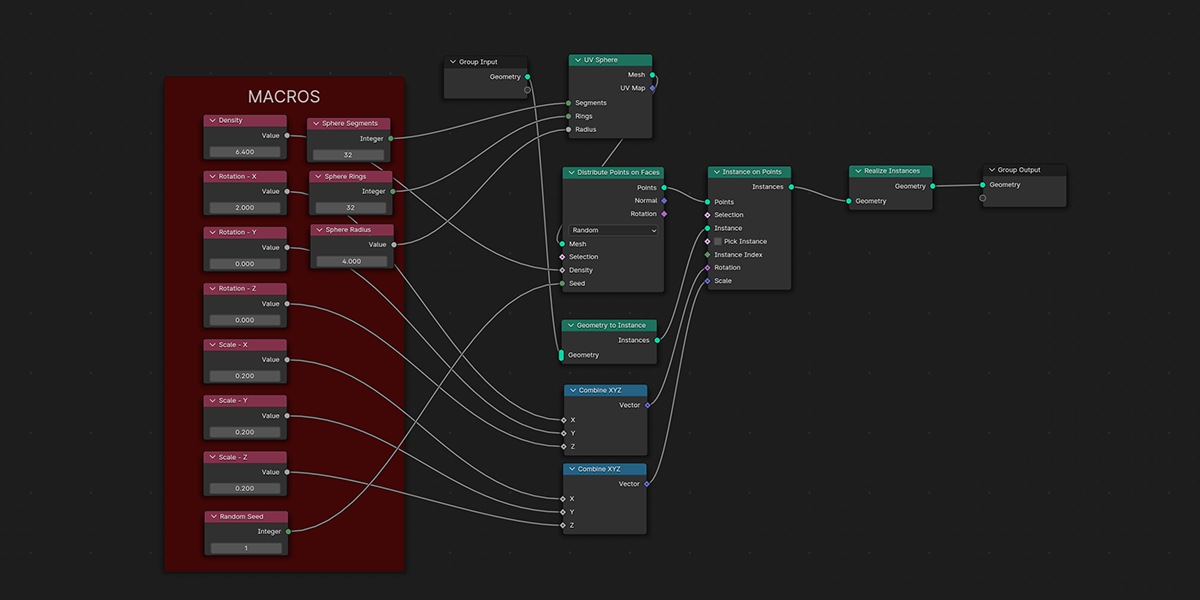
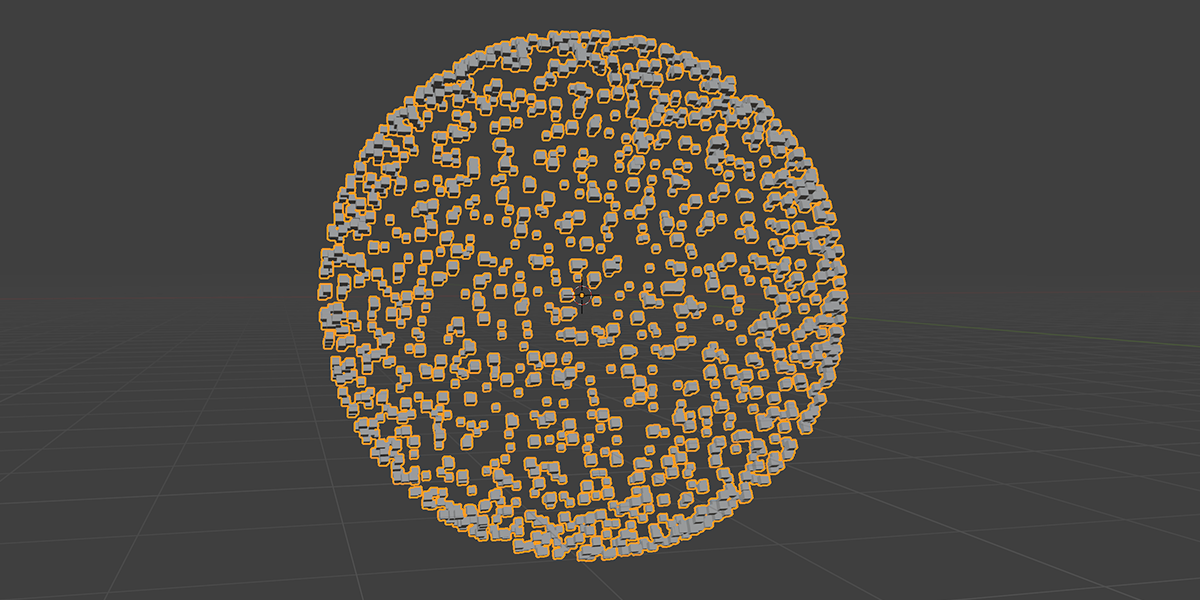
5) To Cube
Uses a primitive Cube shape to distribute an object into a sphere with a variety of controls.
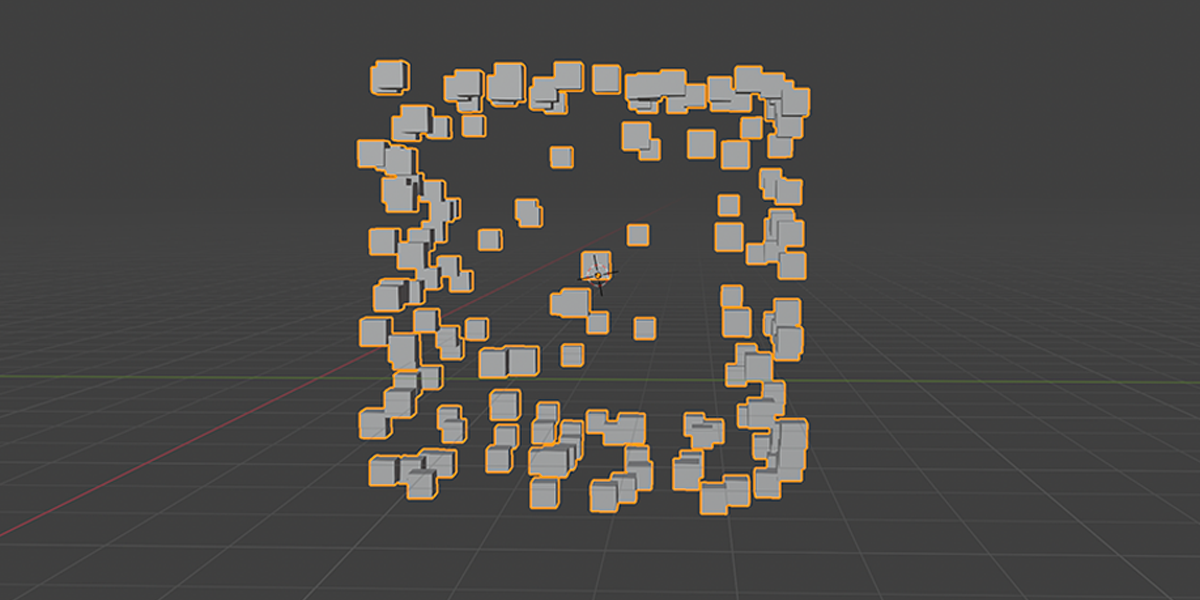
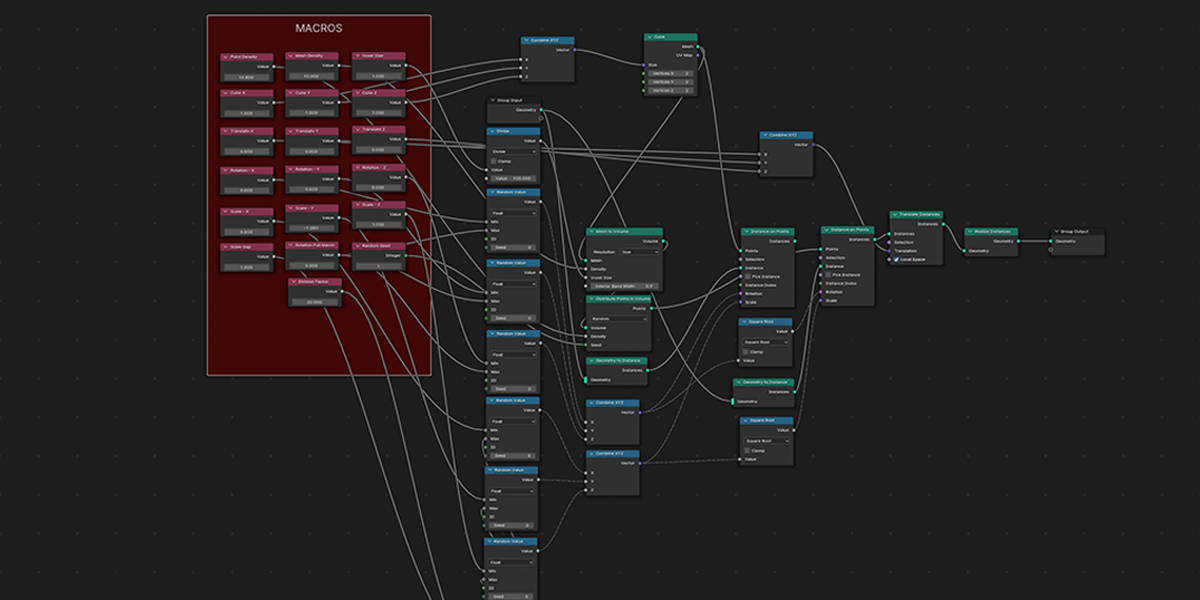
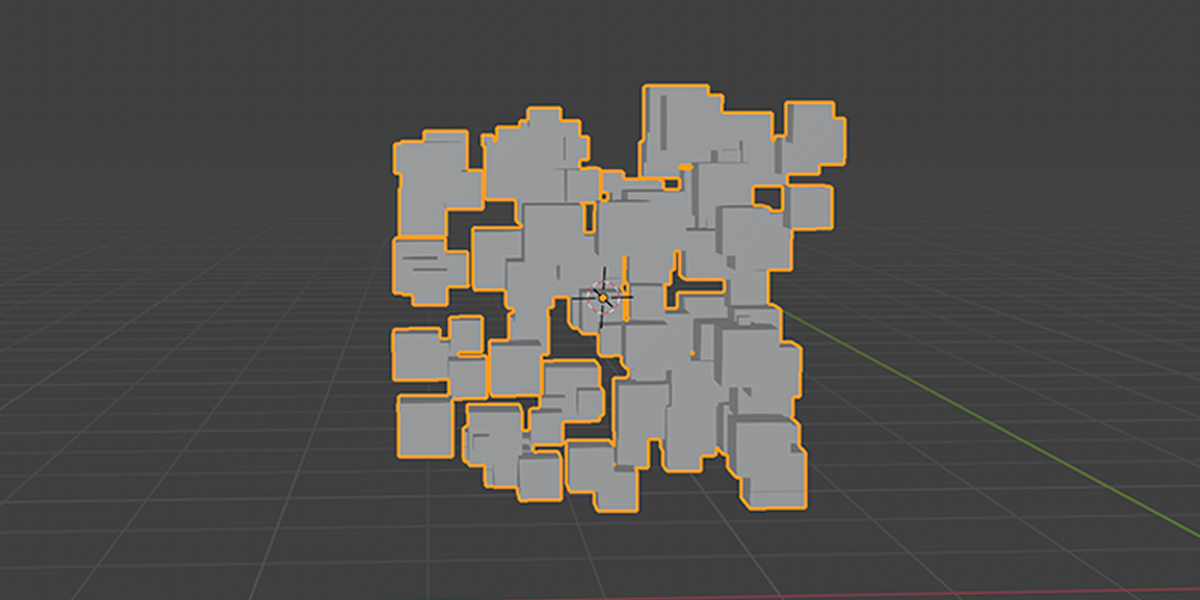
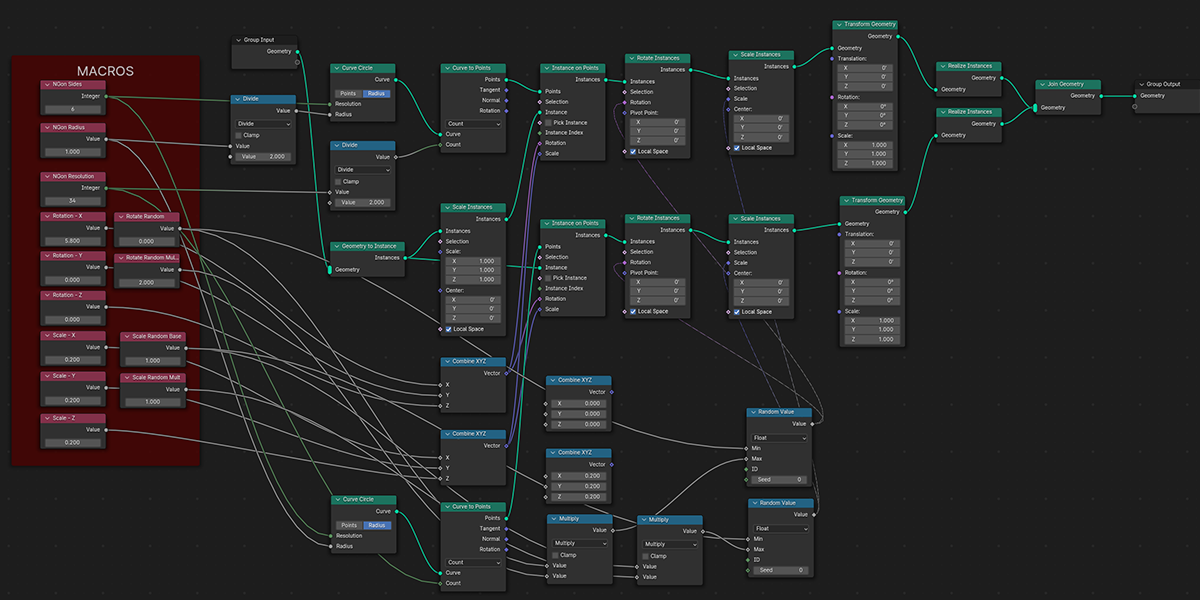
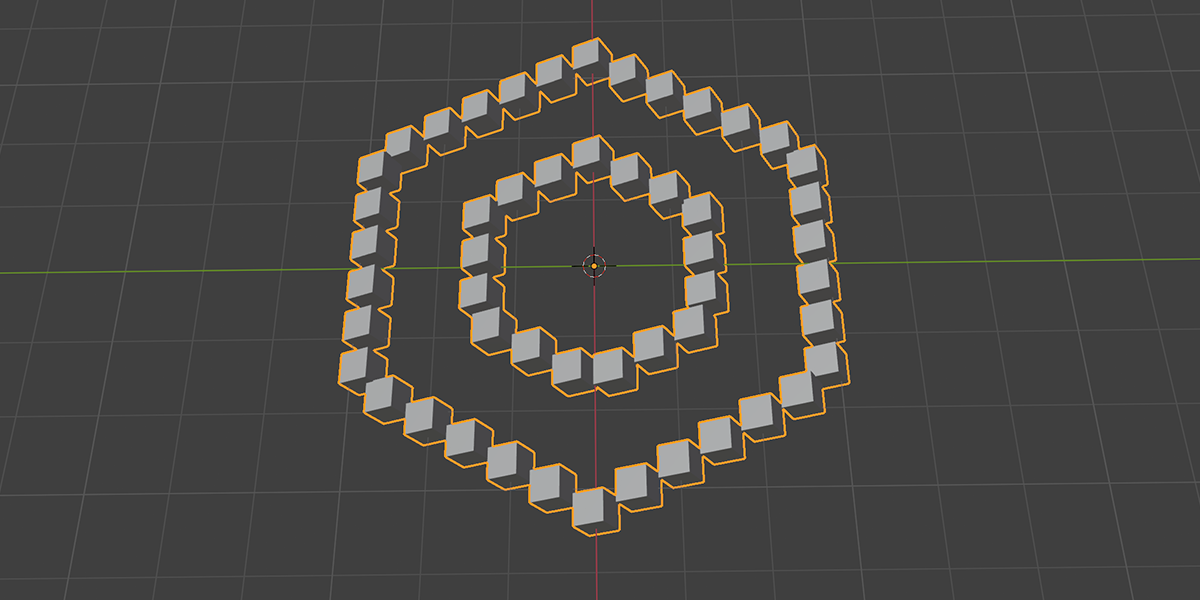
6) To N-Gon
Uses a primitive circle shape with side count control to distribute an object into an N-Gon with a verity of controls. Manipulate the number of sides to change the shape of distribution.
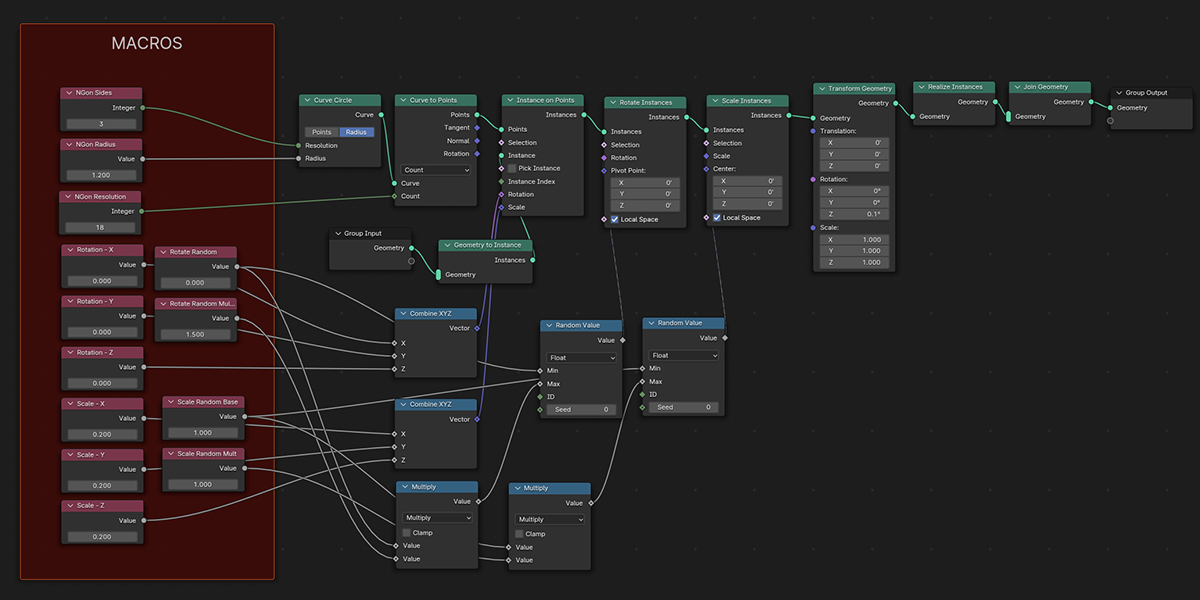
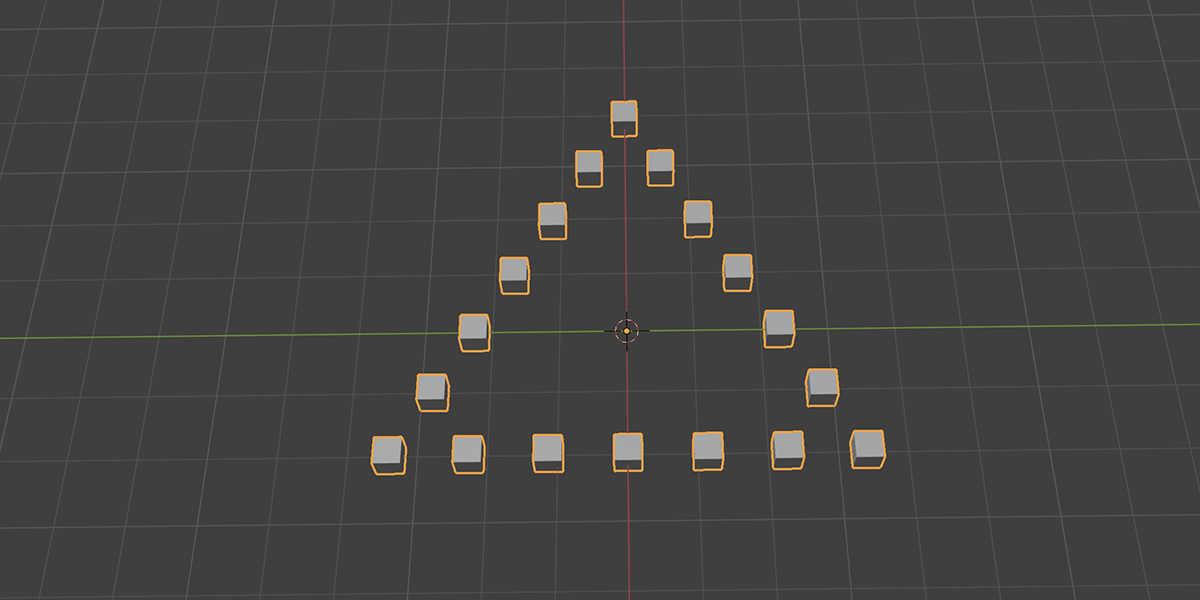
7) To Cone
Uses a primitive Cone shape to distribute an object into a sphere with a variety of controls.
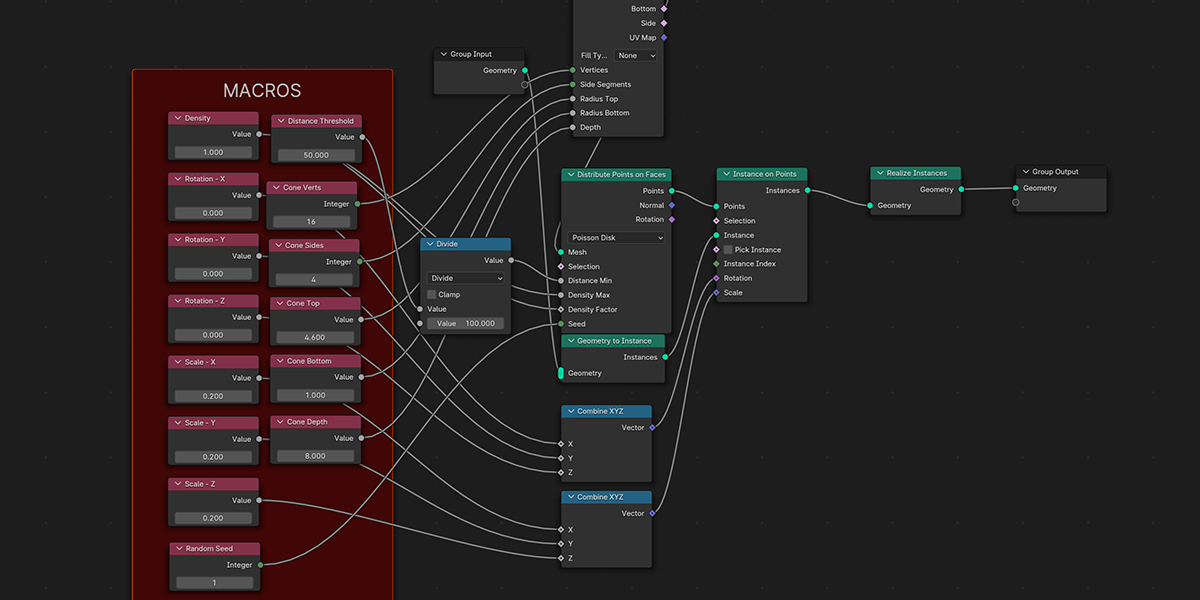
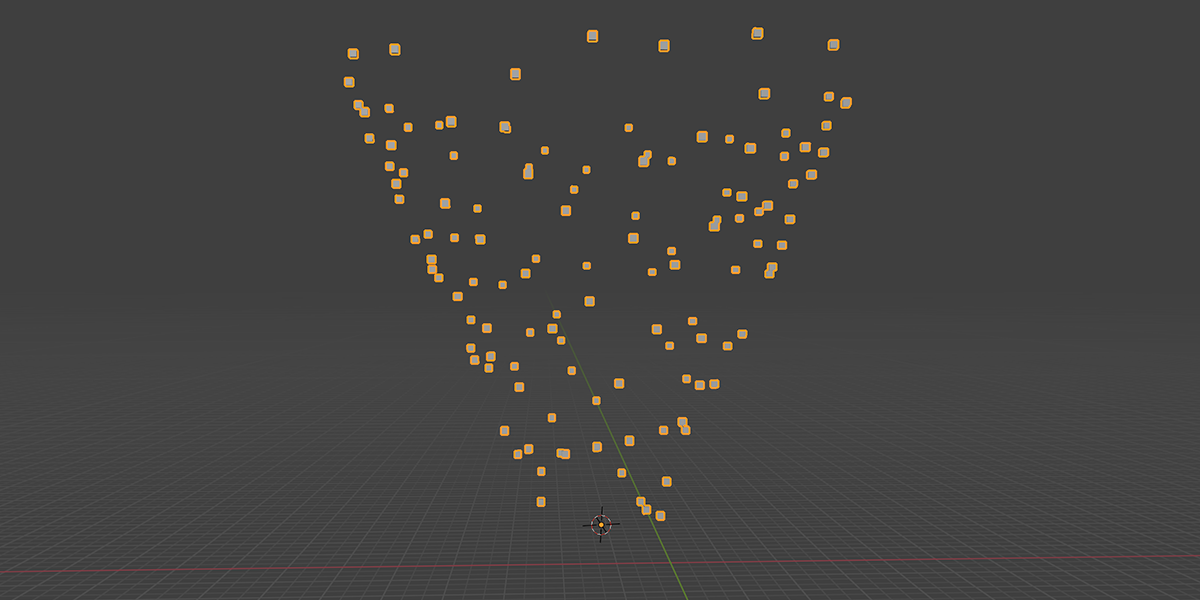
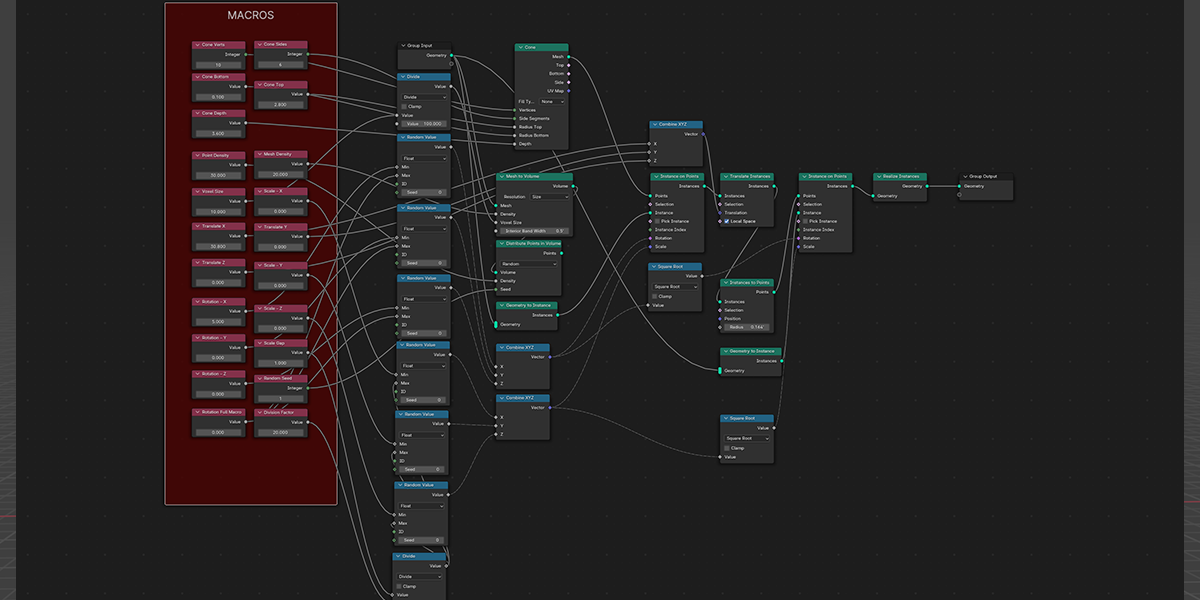
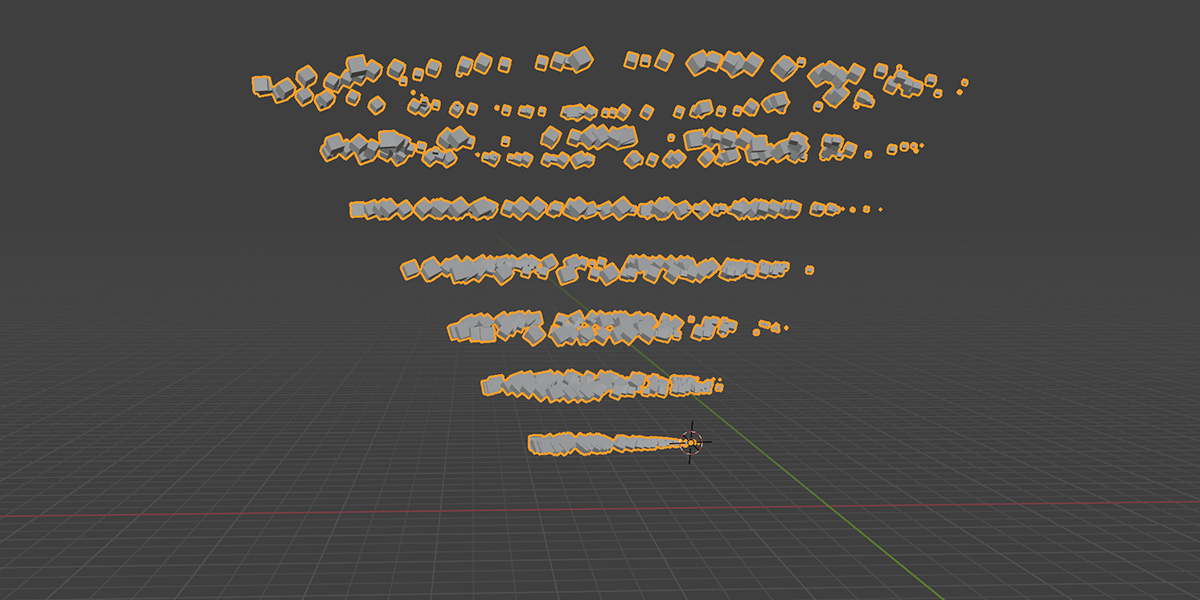
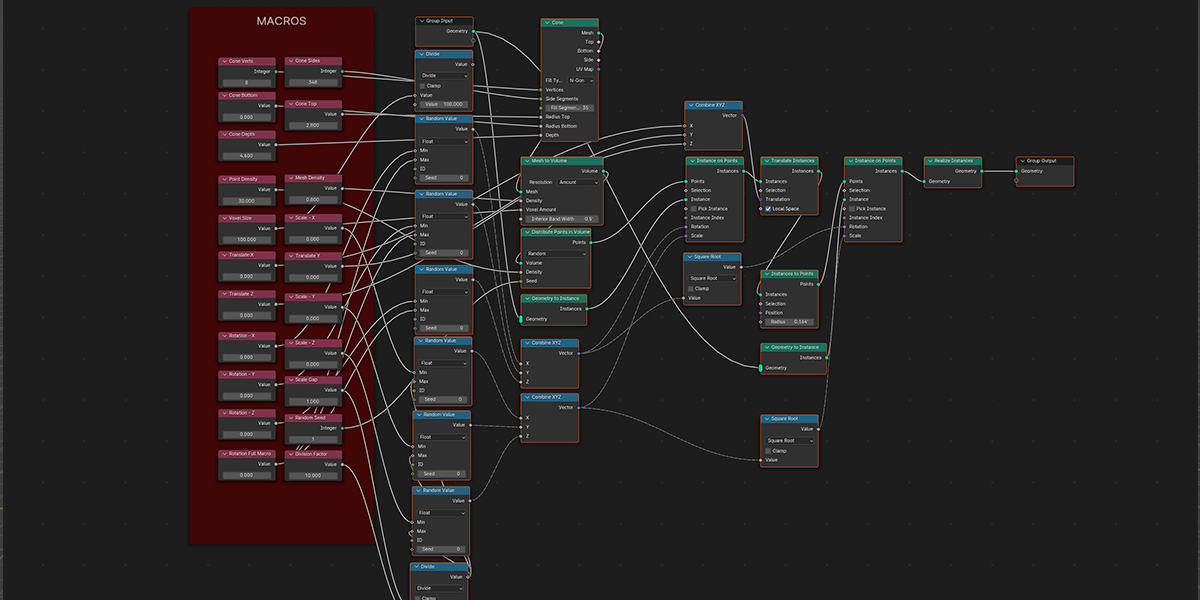
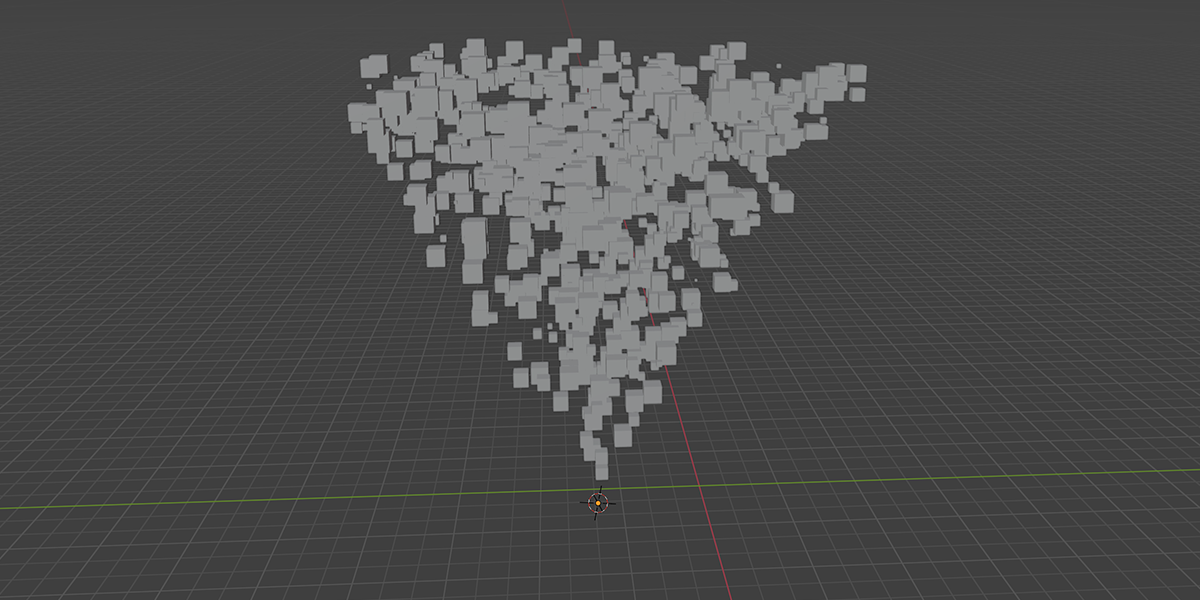
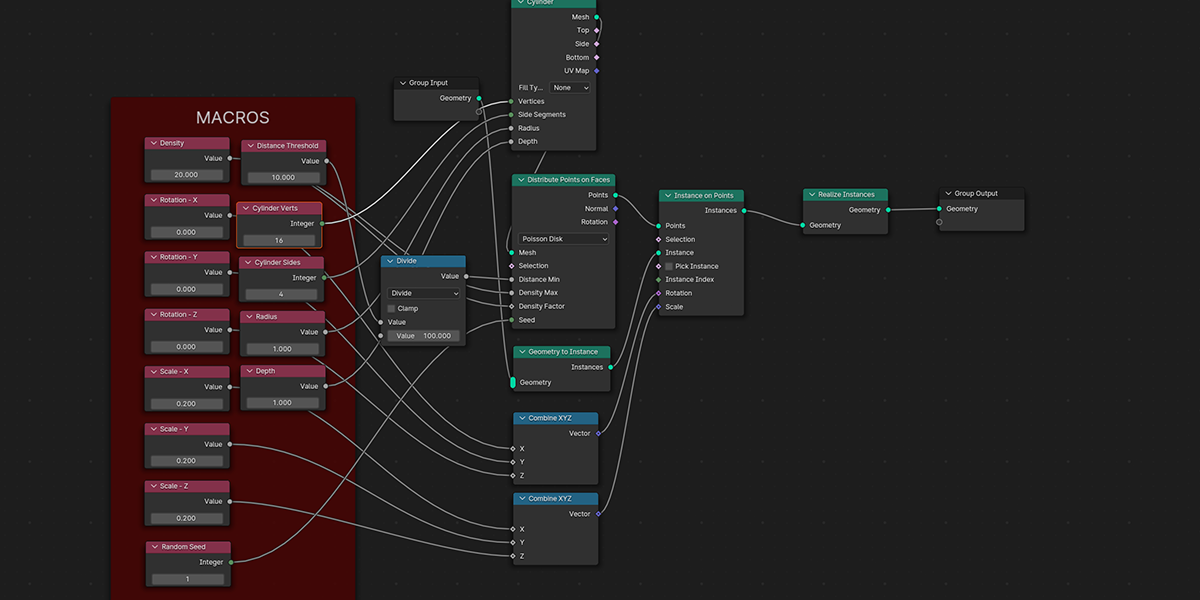
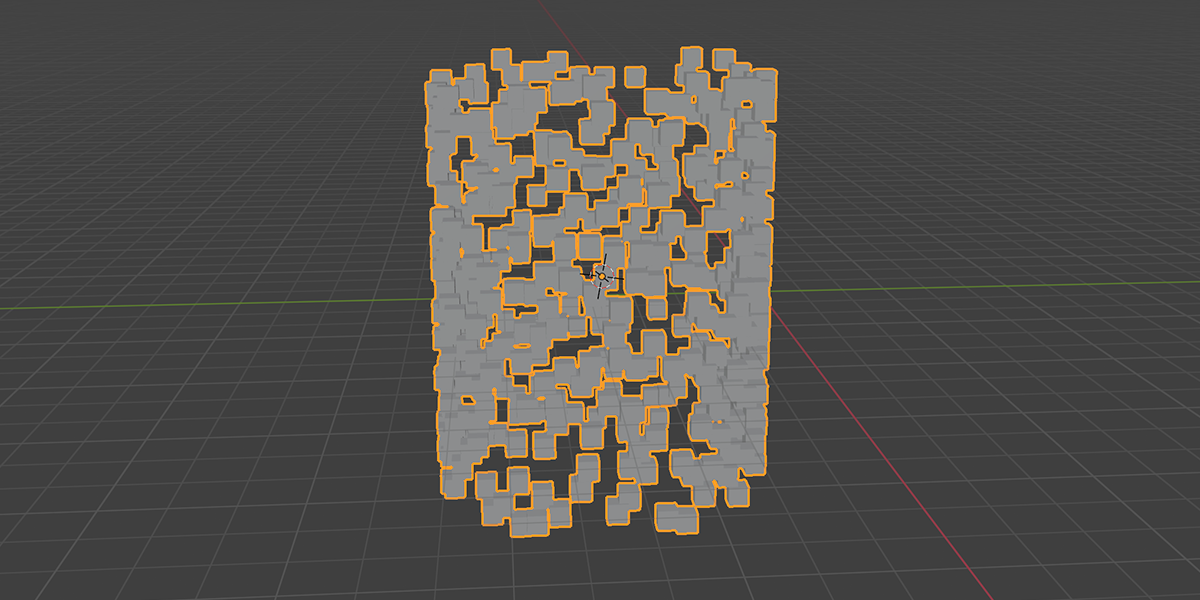
8) To Cylinder
Uses a primitive Cylinder shape to distribute an object into a sphere with a variety of controls.
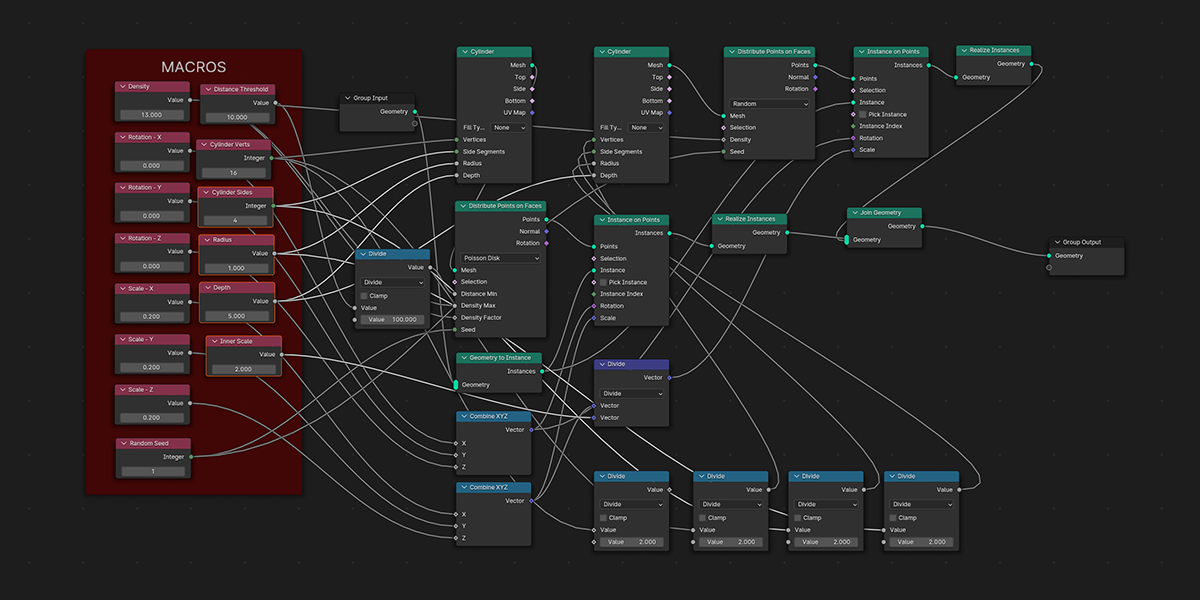
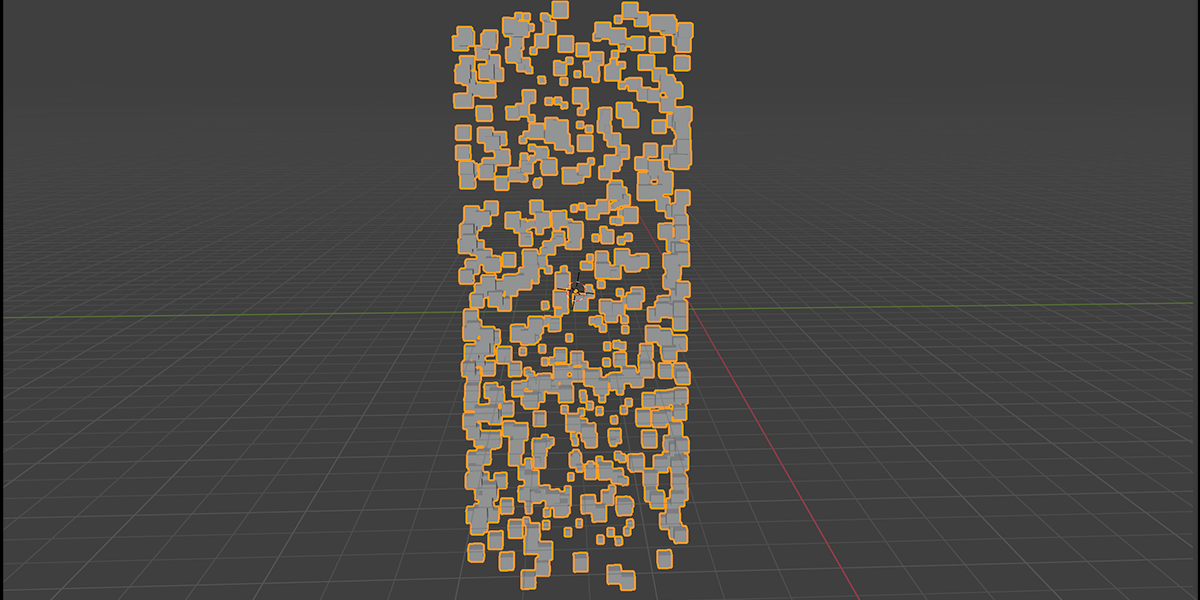
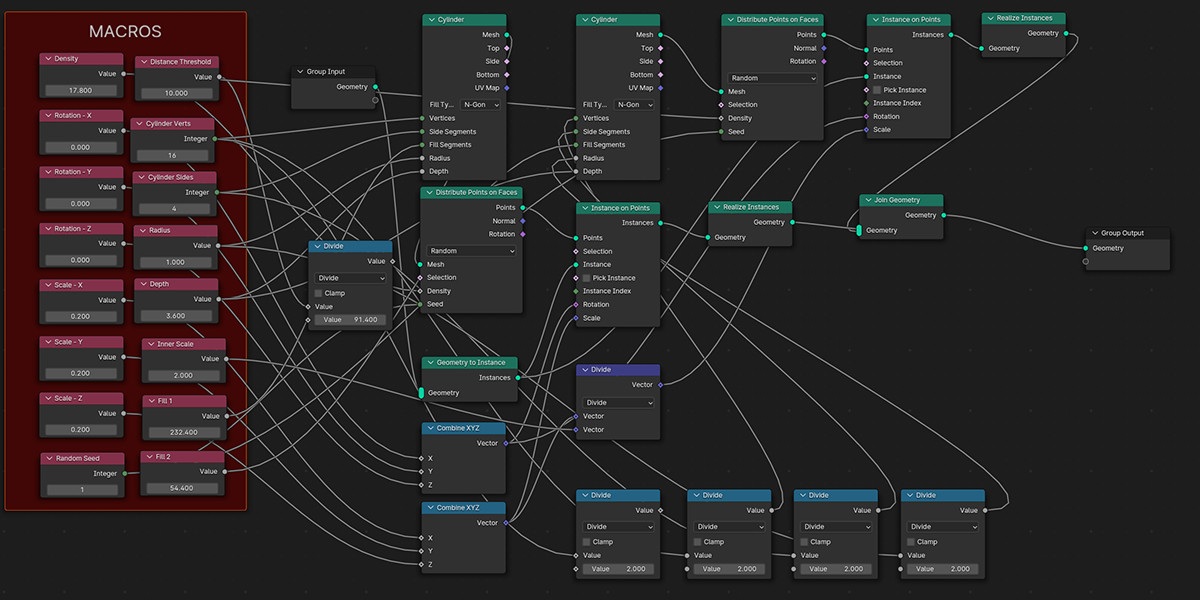
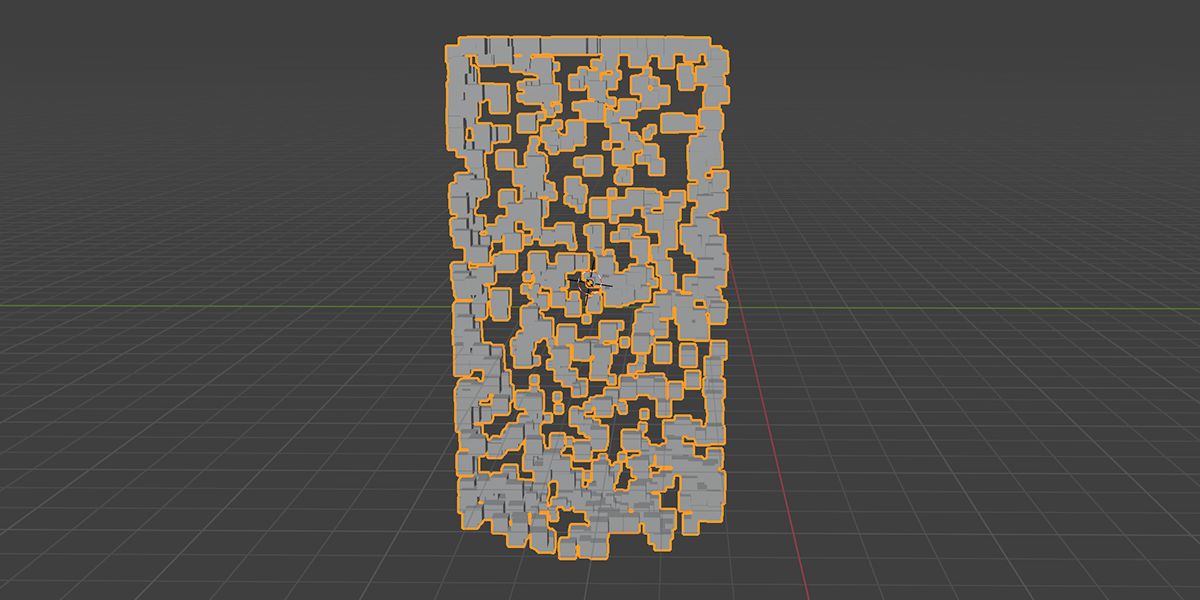
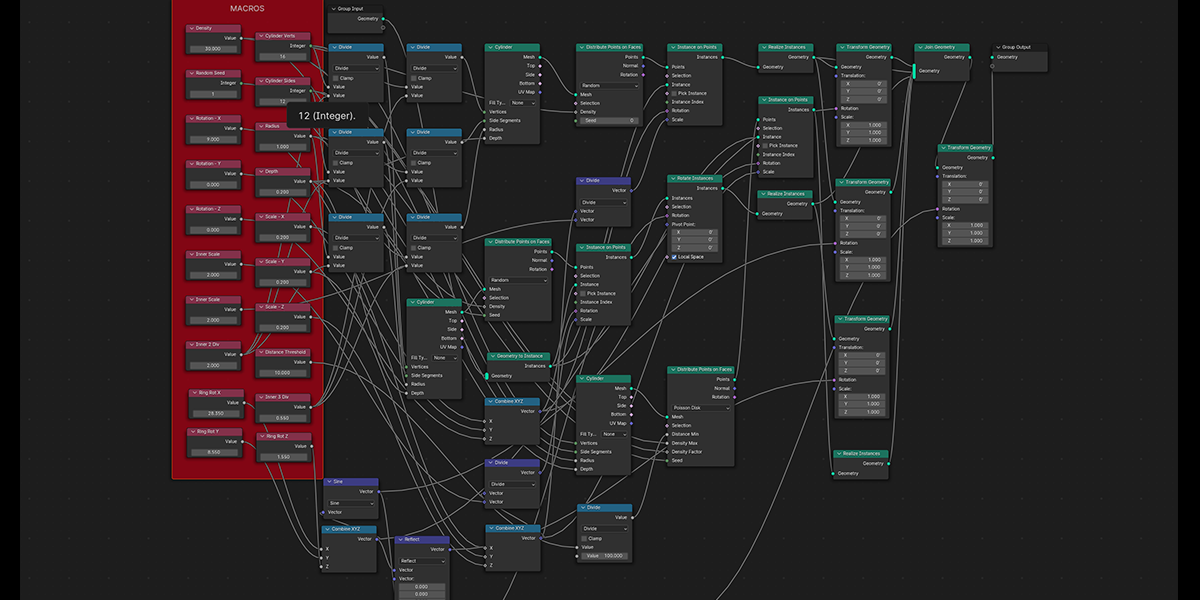
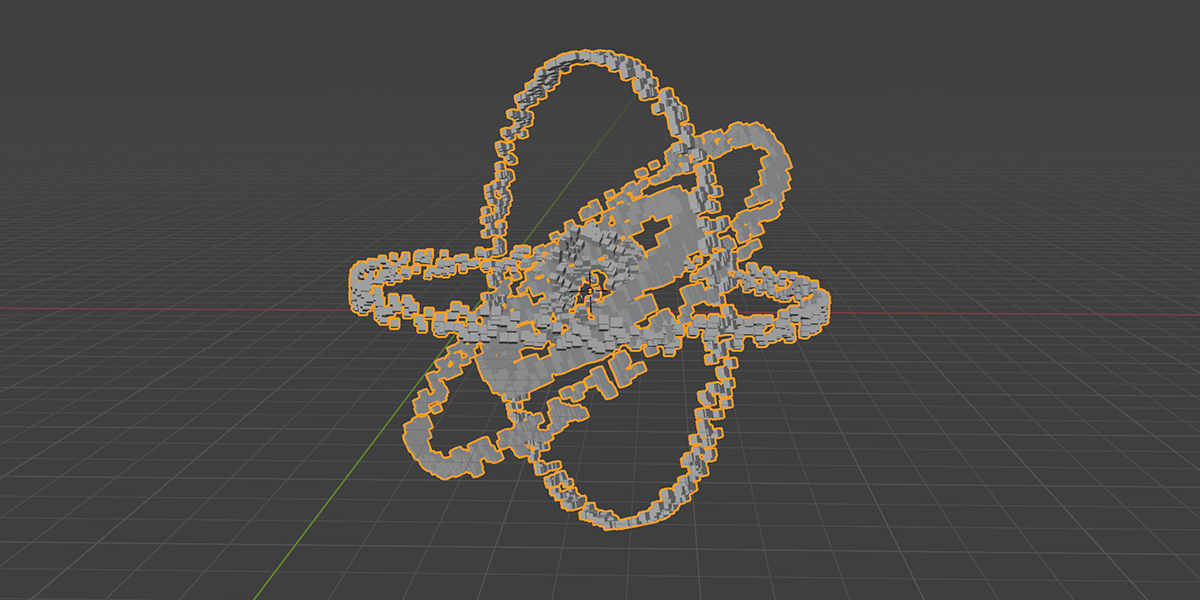
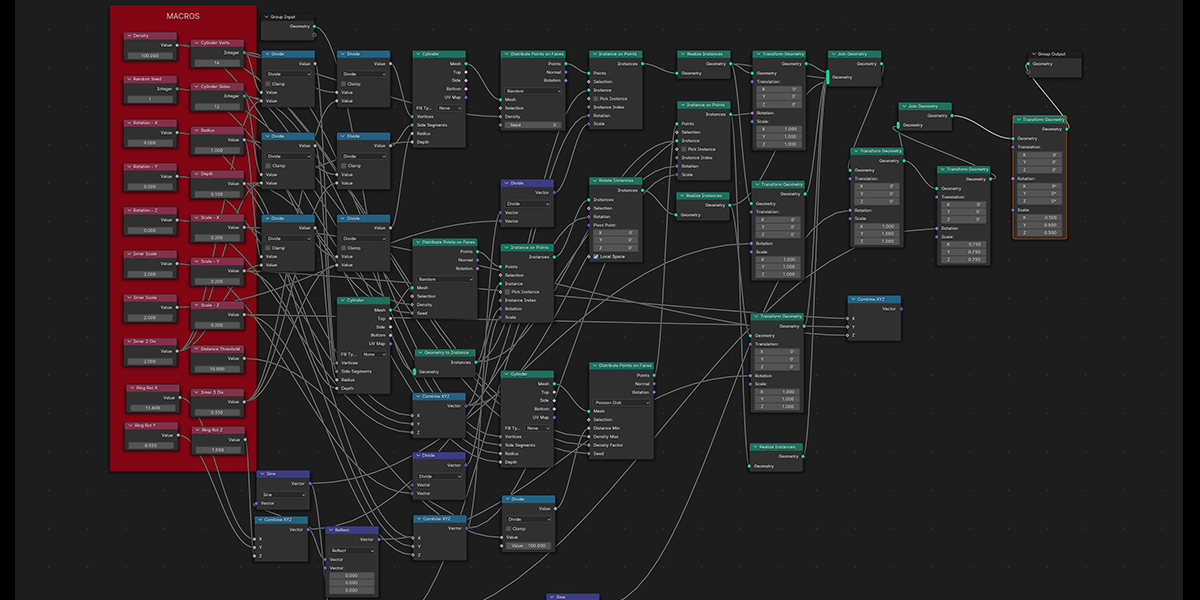
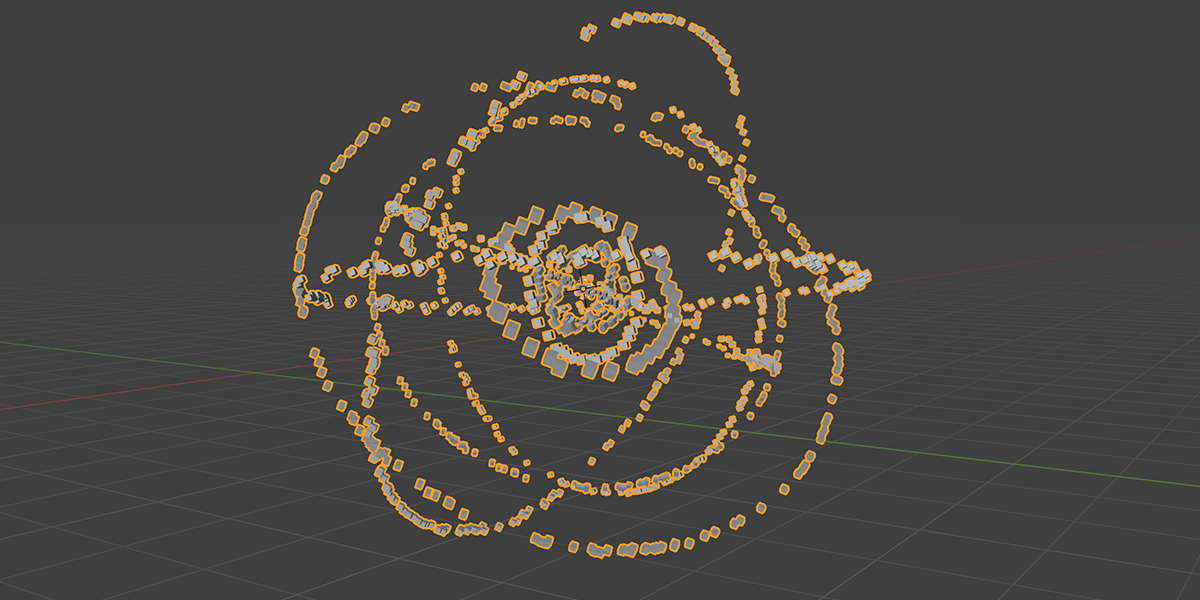
9) Atomic
Uses a combination of circles and transforms to distribute an object into an atomic like structure.
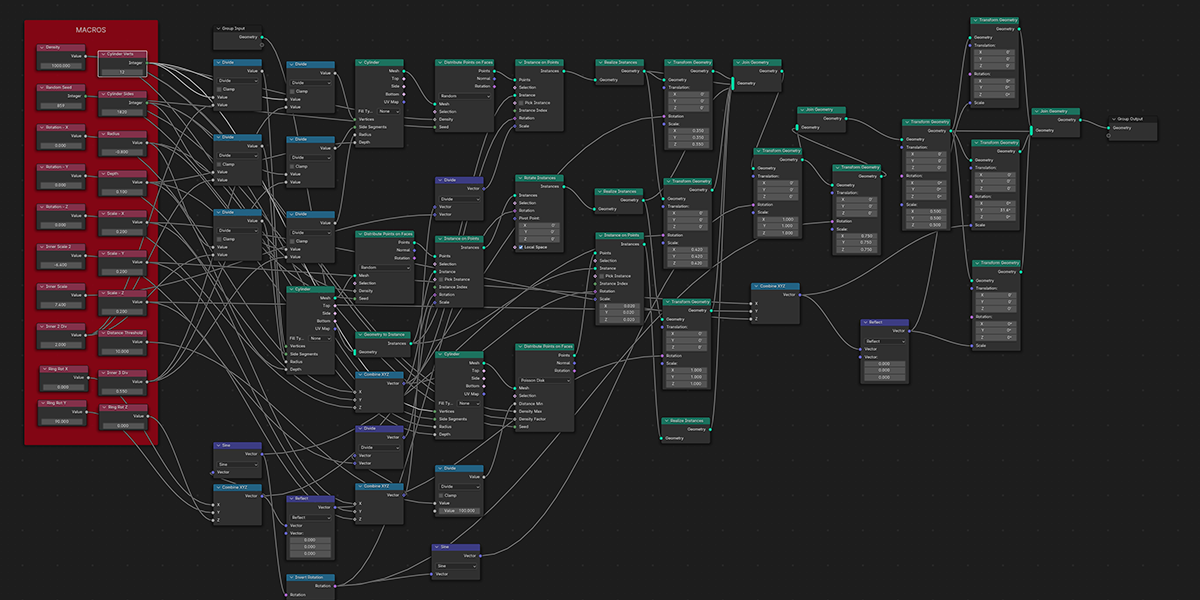
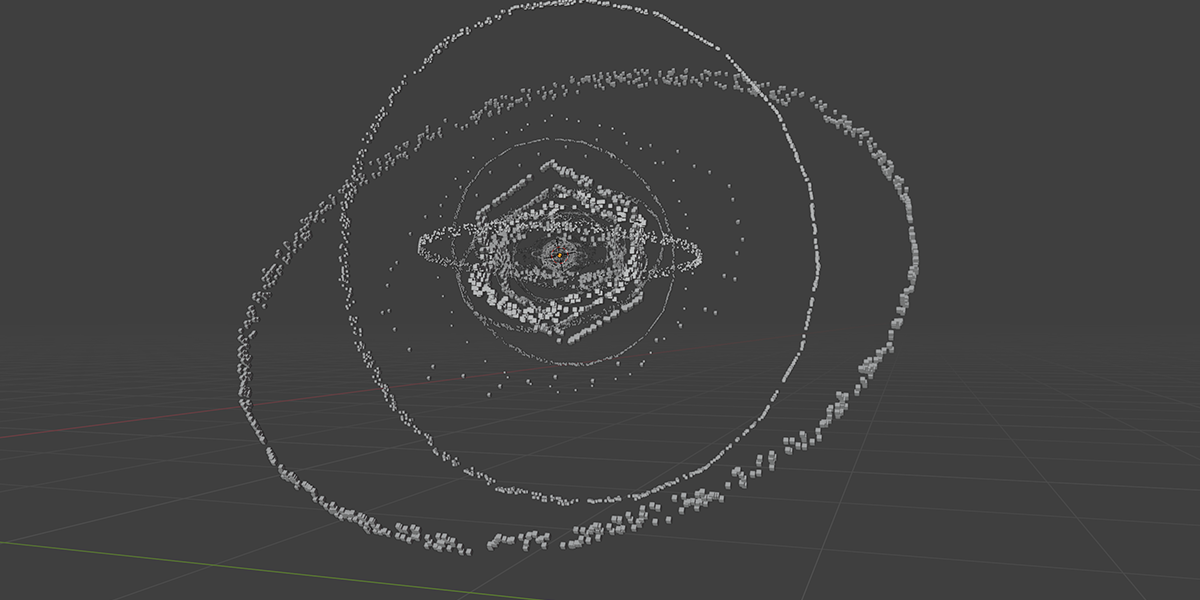
10) Seed of Life
Uses 7 Circles with calculated ratios to distribute an object into the seed of life formation with a number of controls for animating and manipulating.
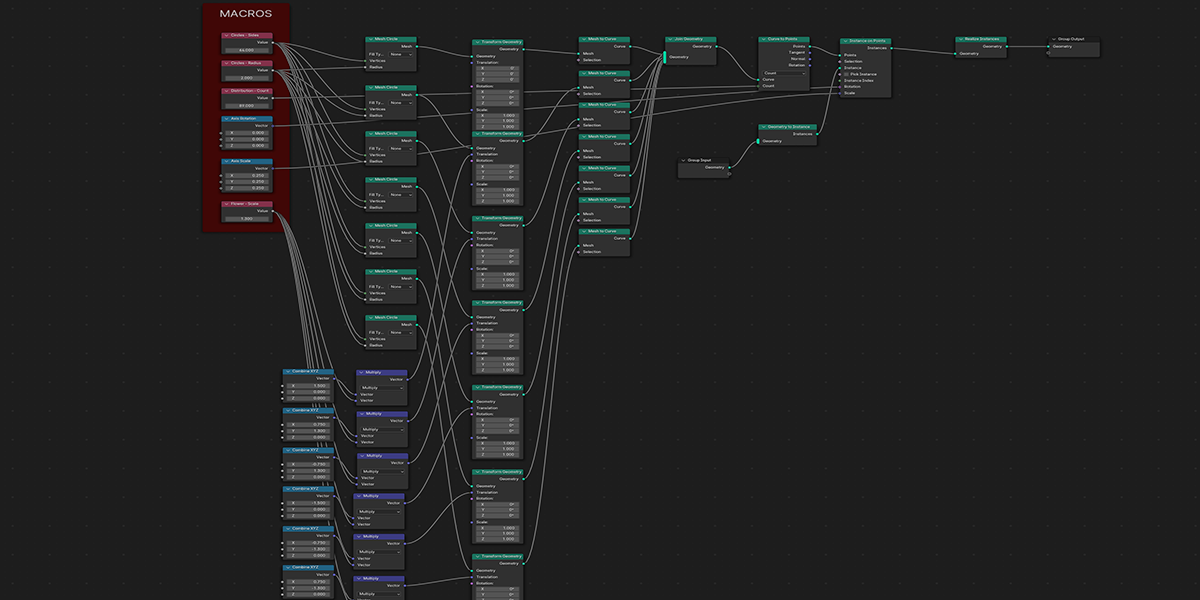
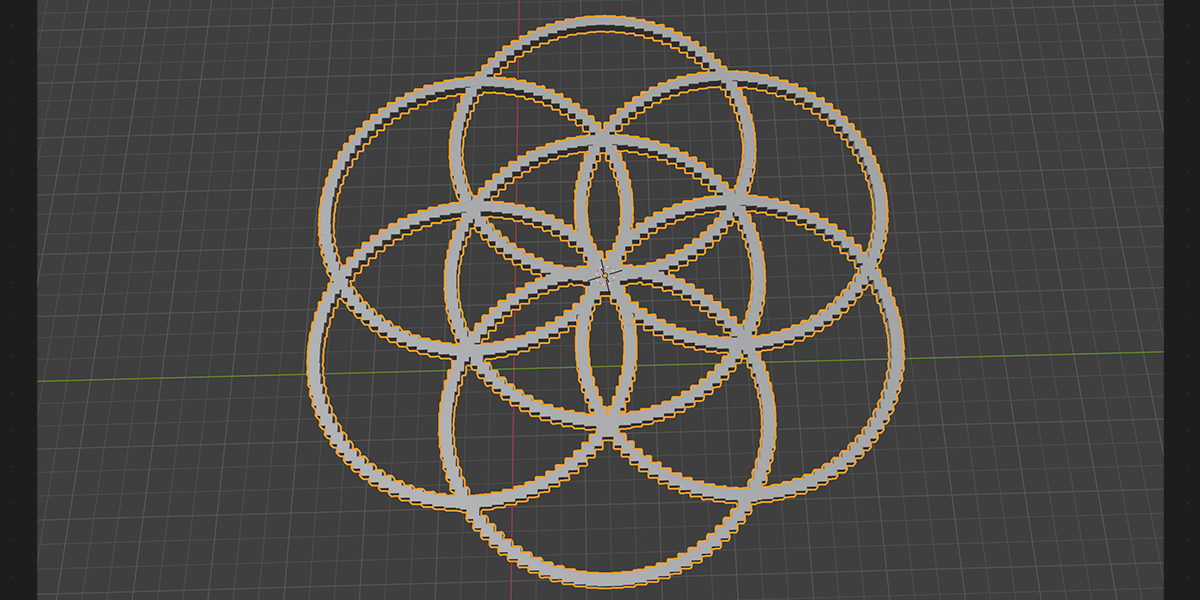
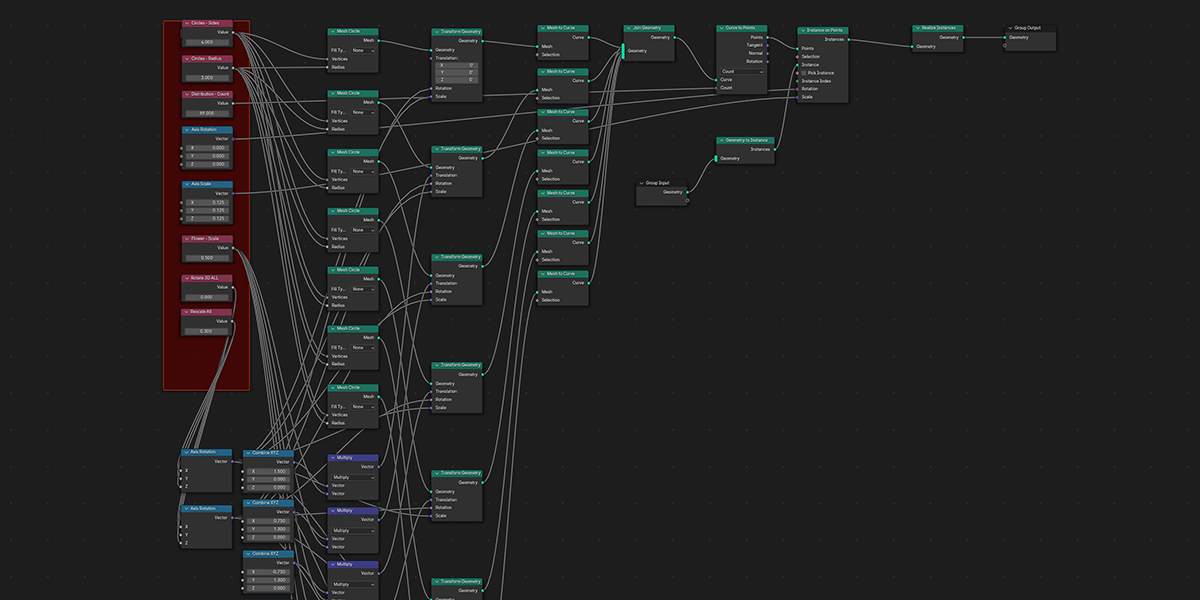
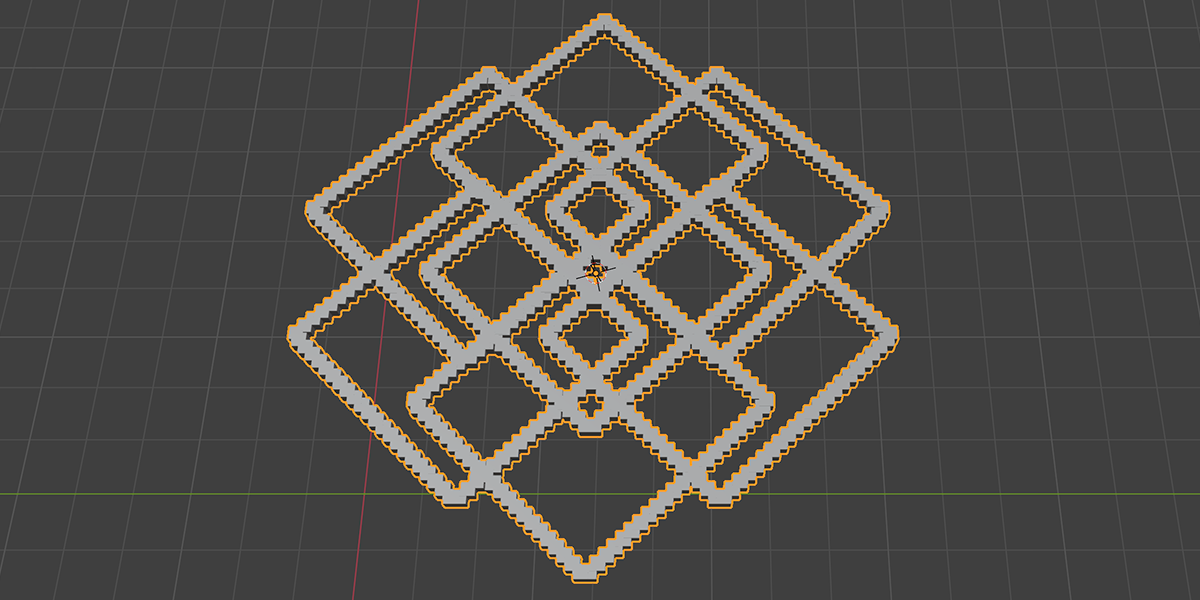
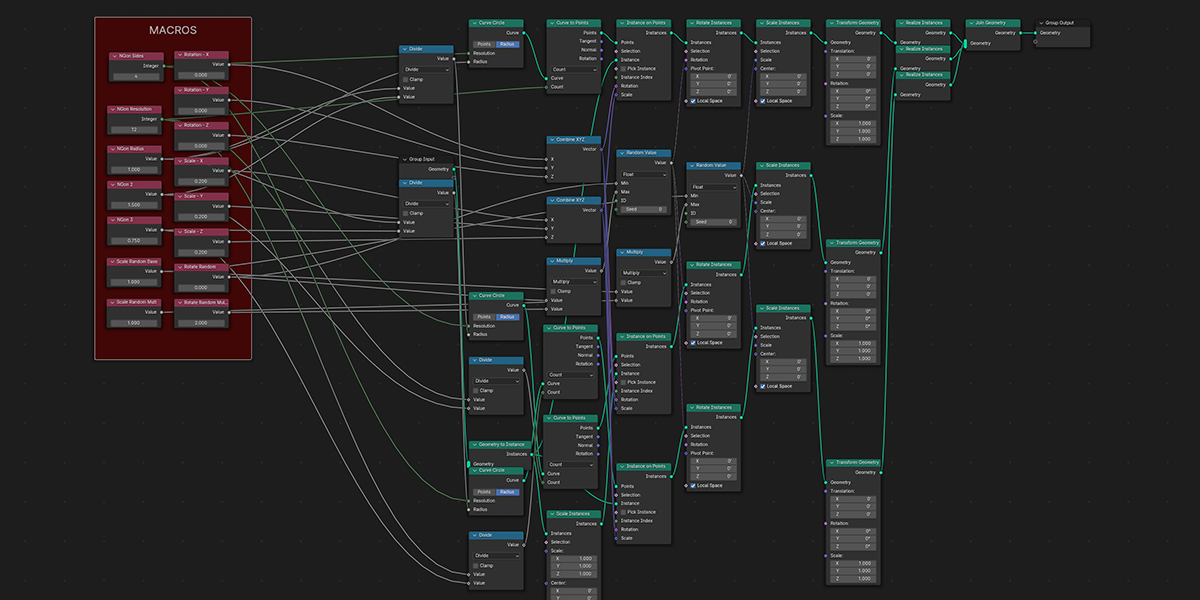
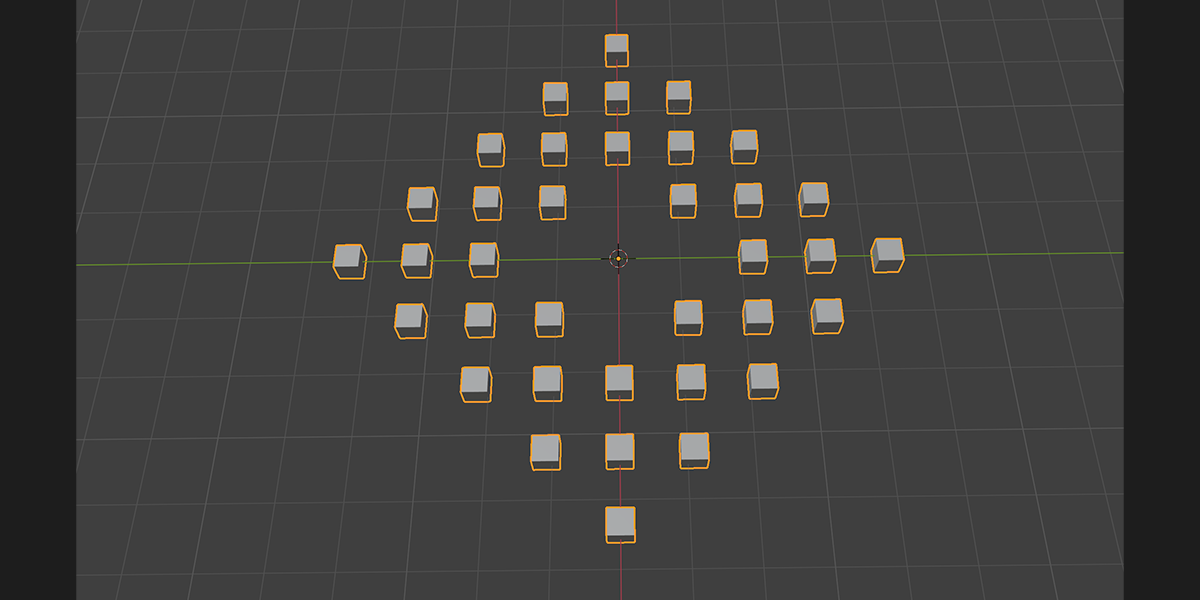
11) To Grid
Distribute any object into a grid with controls over count, rows, columns, density, and randomization.
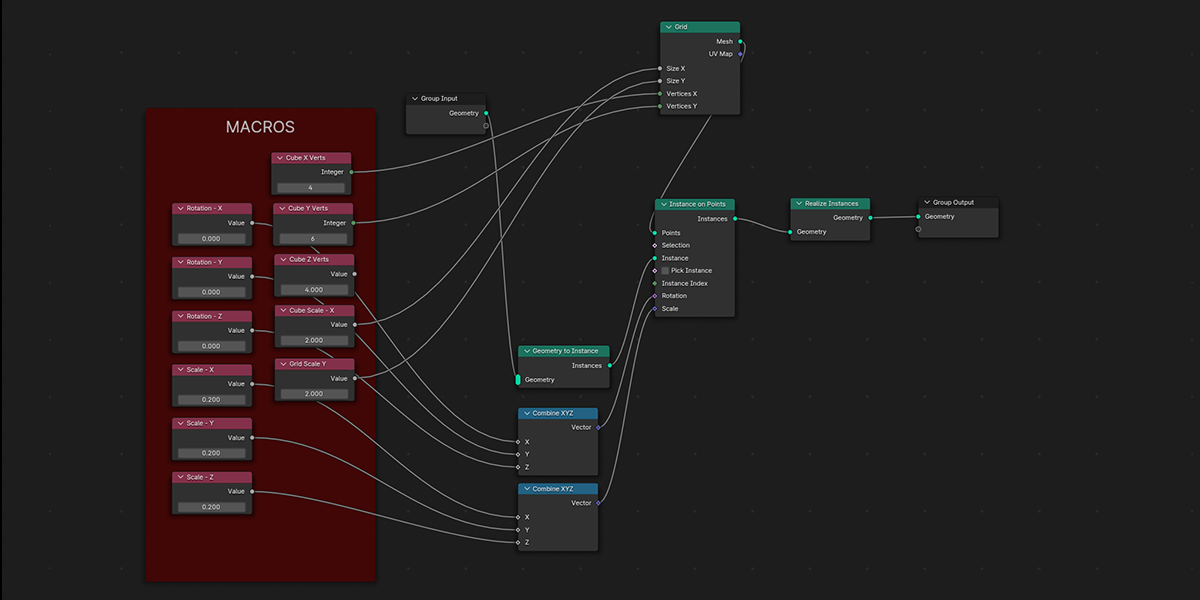
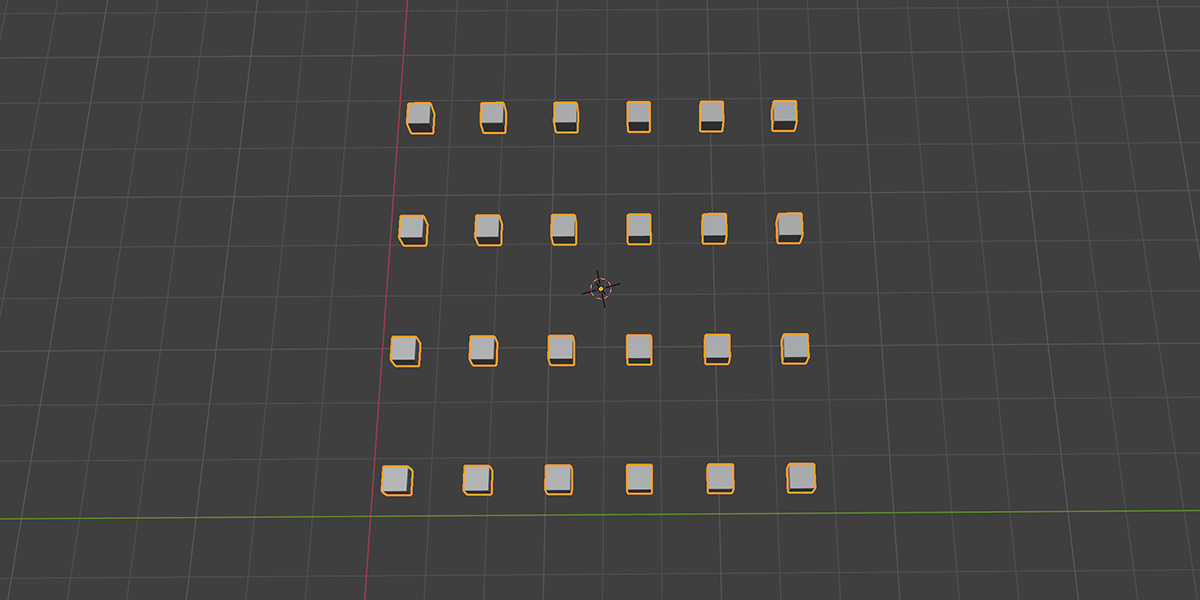
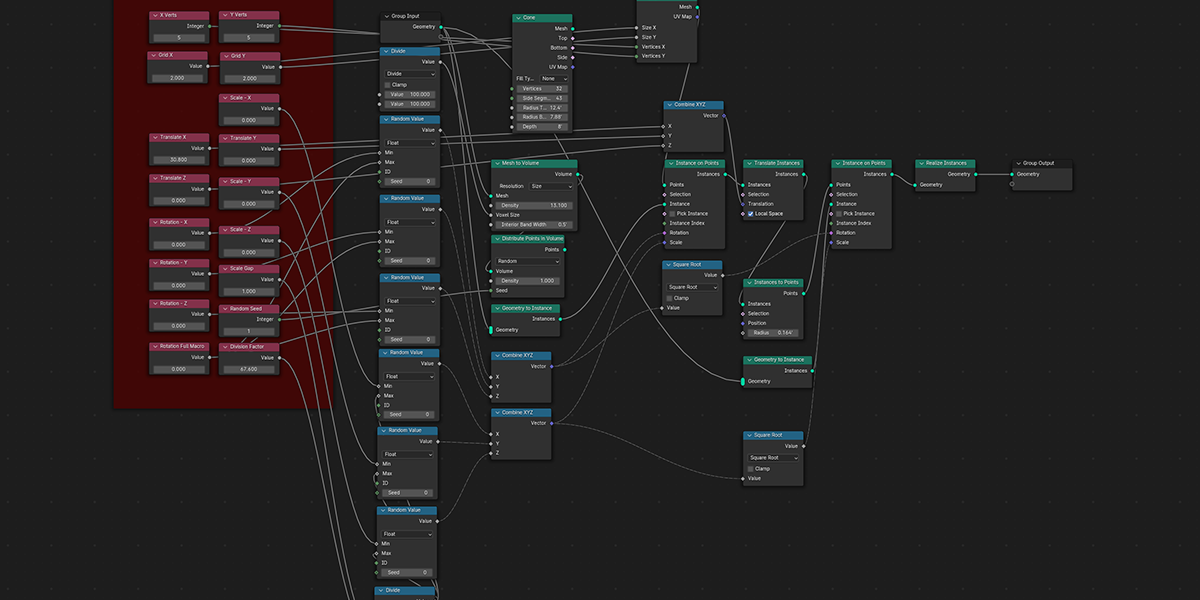
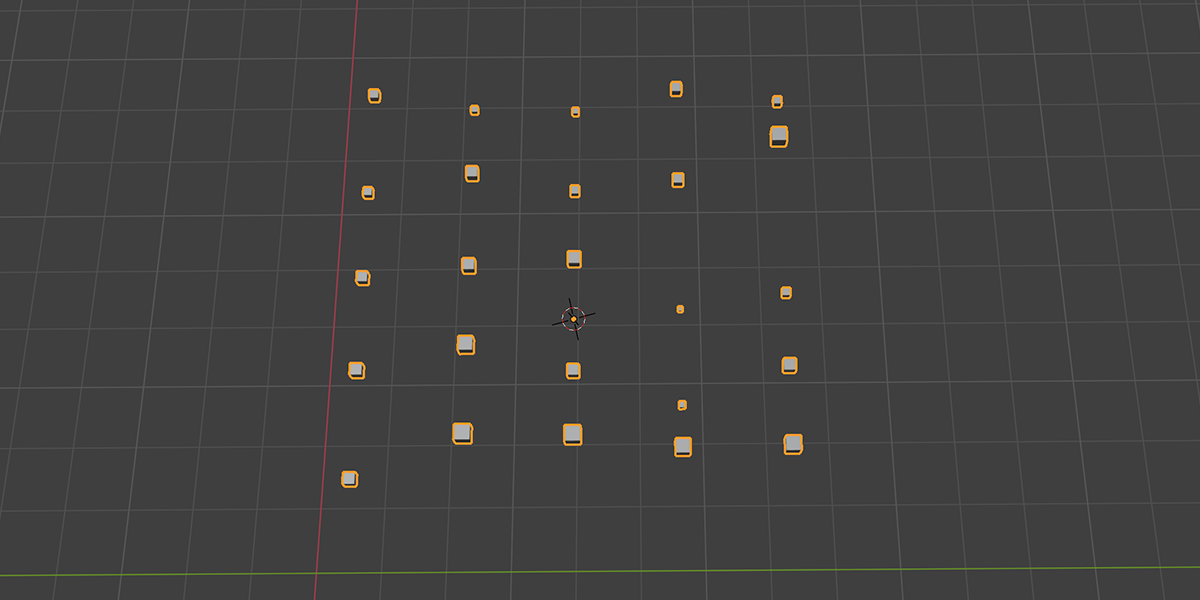
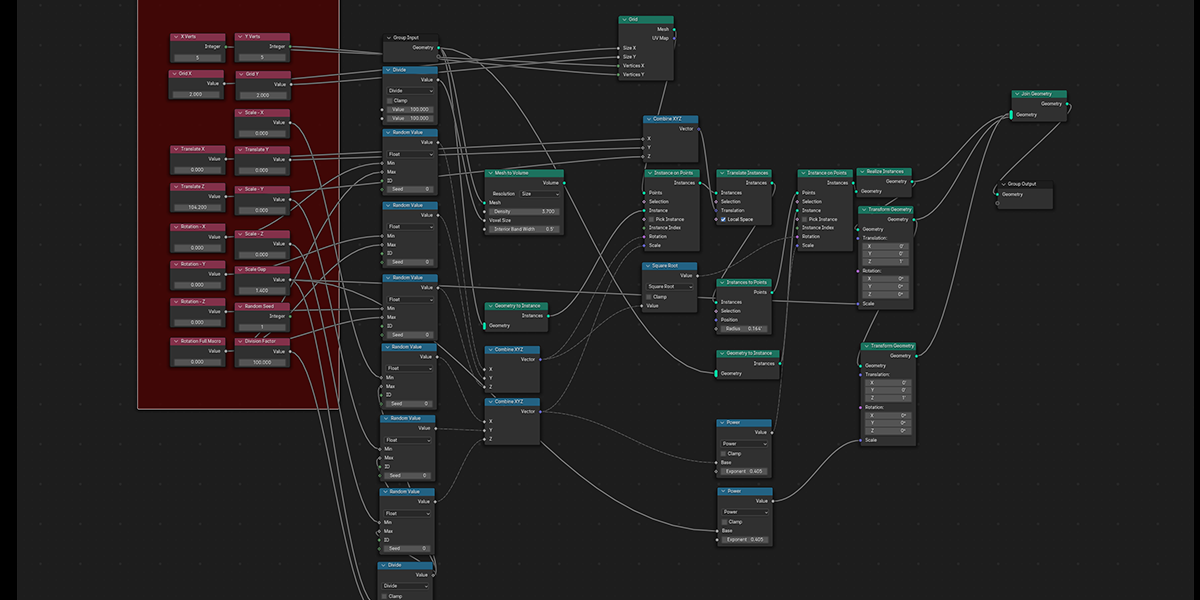
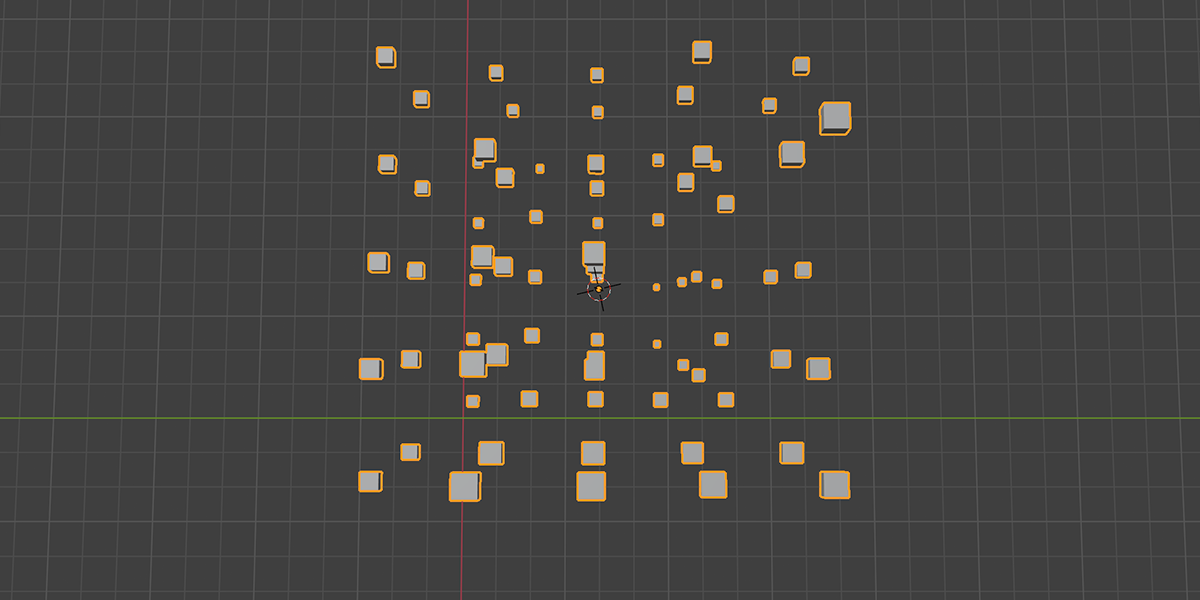
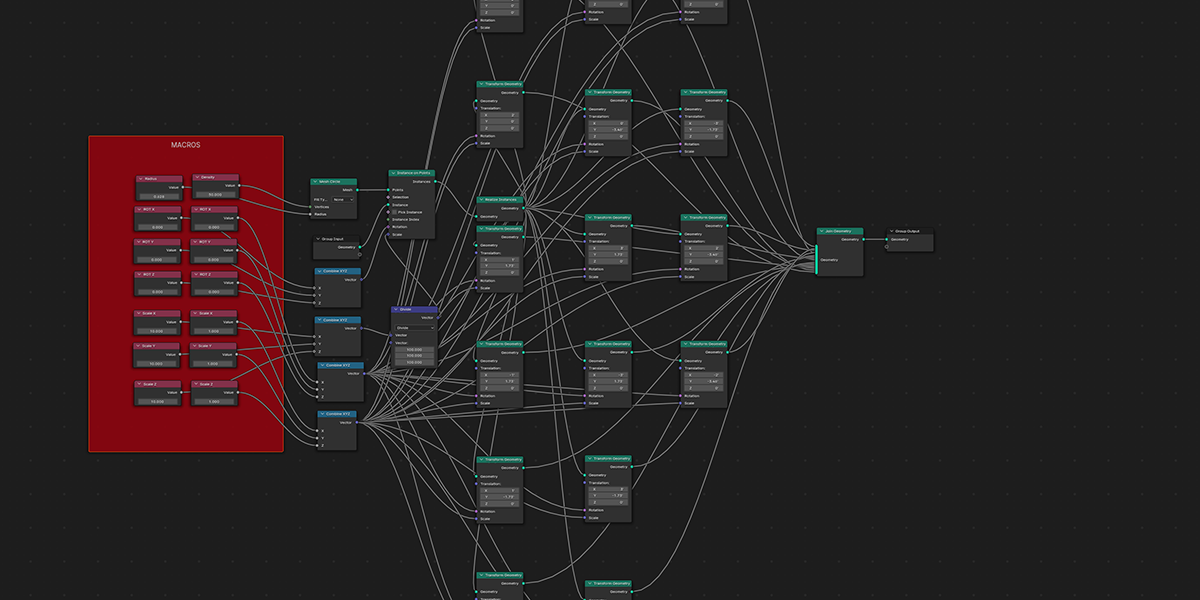
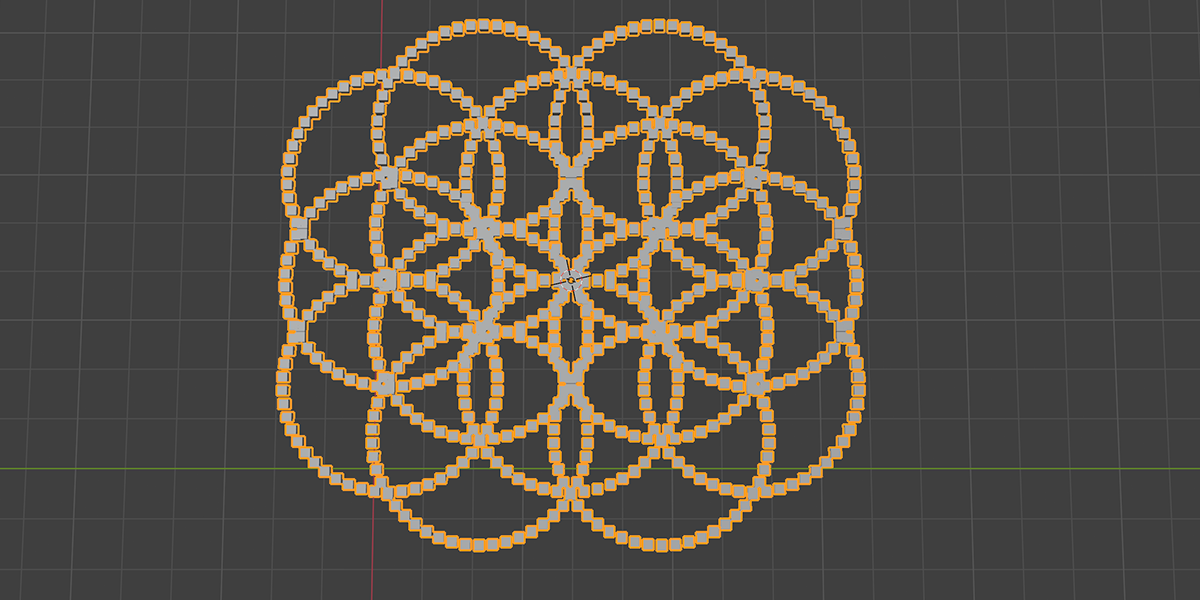
12) Flower of Life
Uses 16 Circles with calculated ratios to distribute an object into the flower of life formation with a number of controls for animating and manipulating.
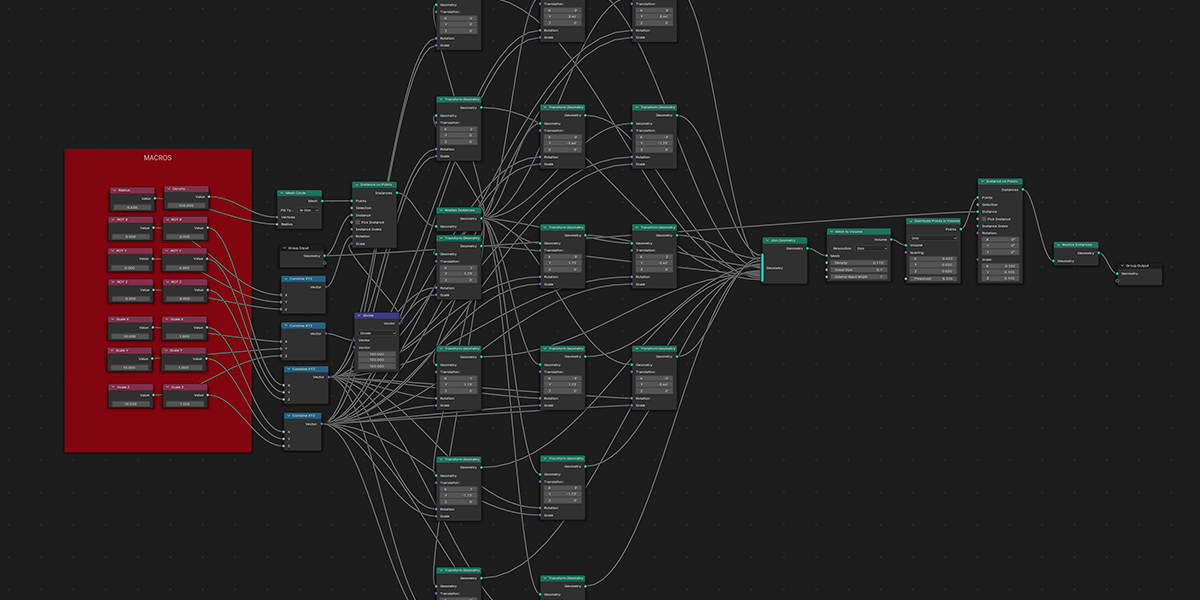

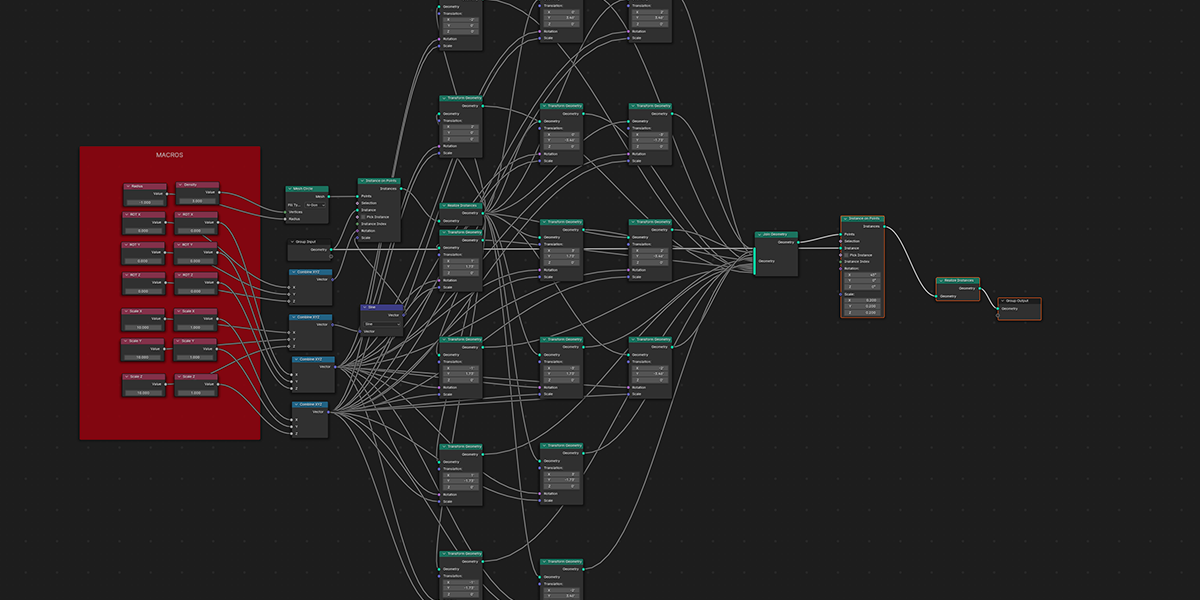
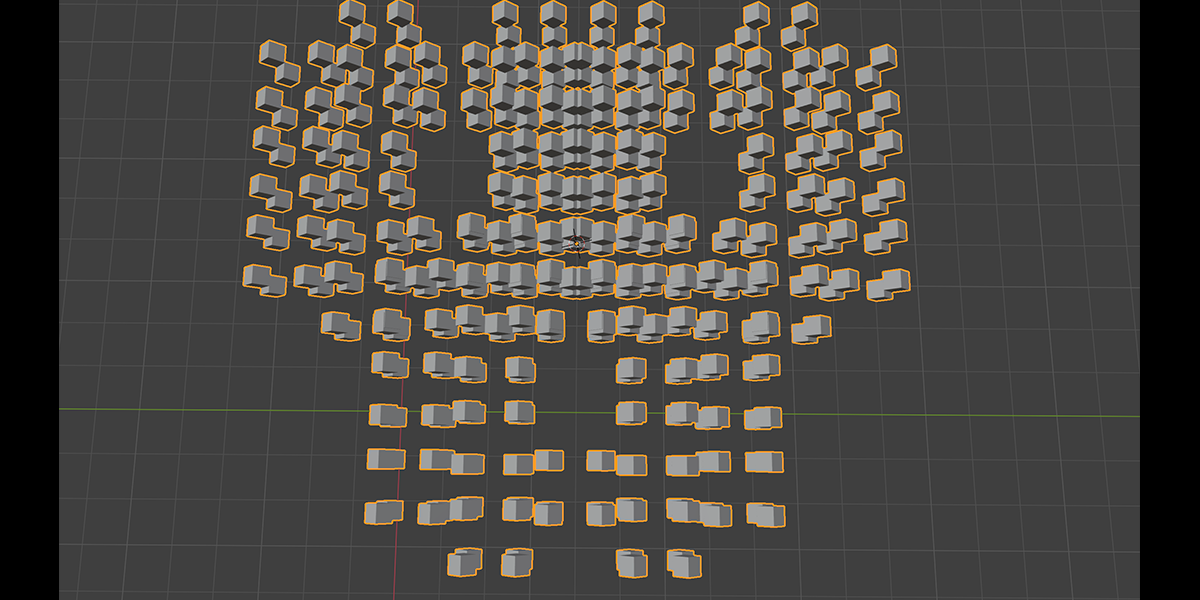
13) Hologram
Uses a combination of delete geometry, instancing, and transforming, to create a hologram effect from any selected object.
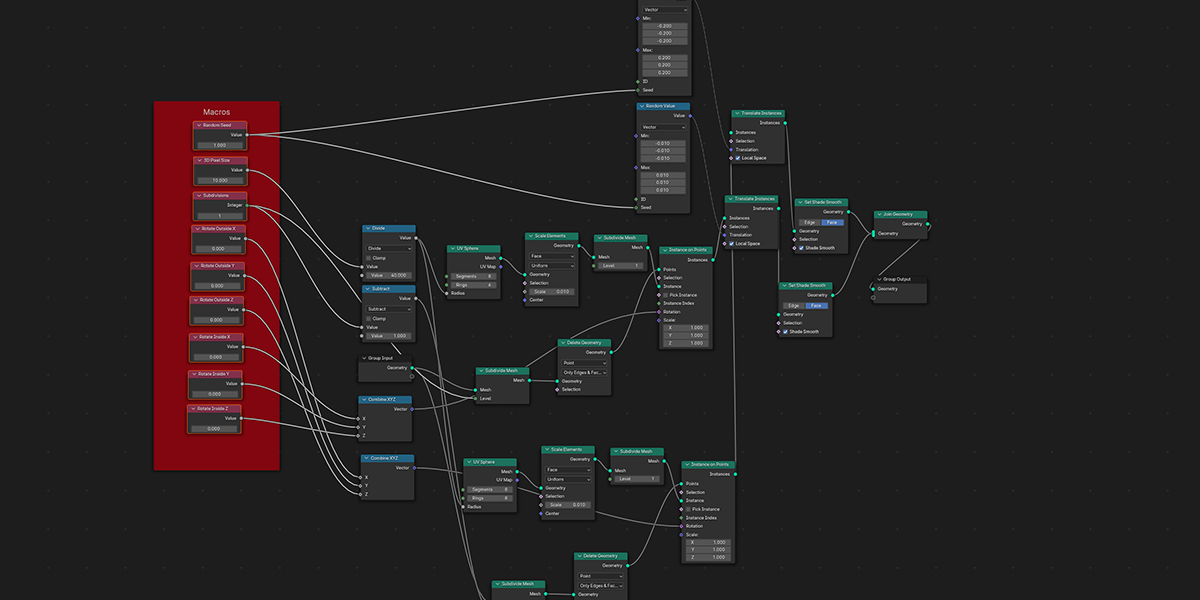
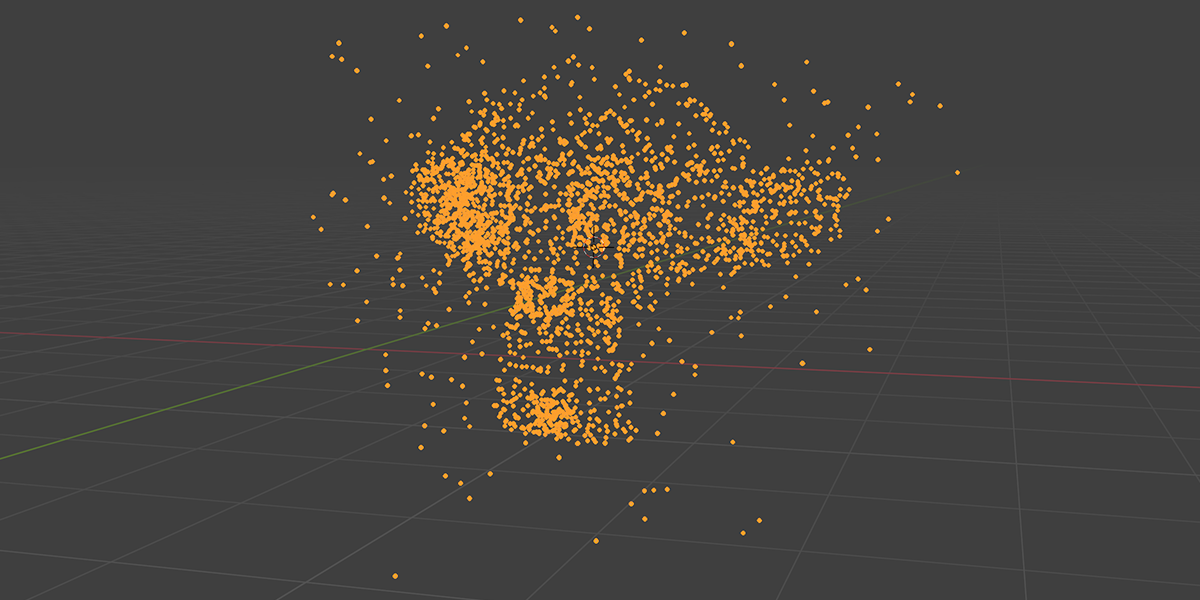
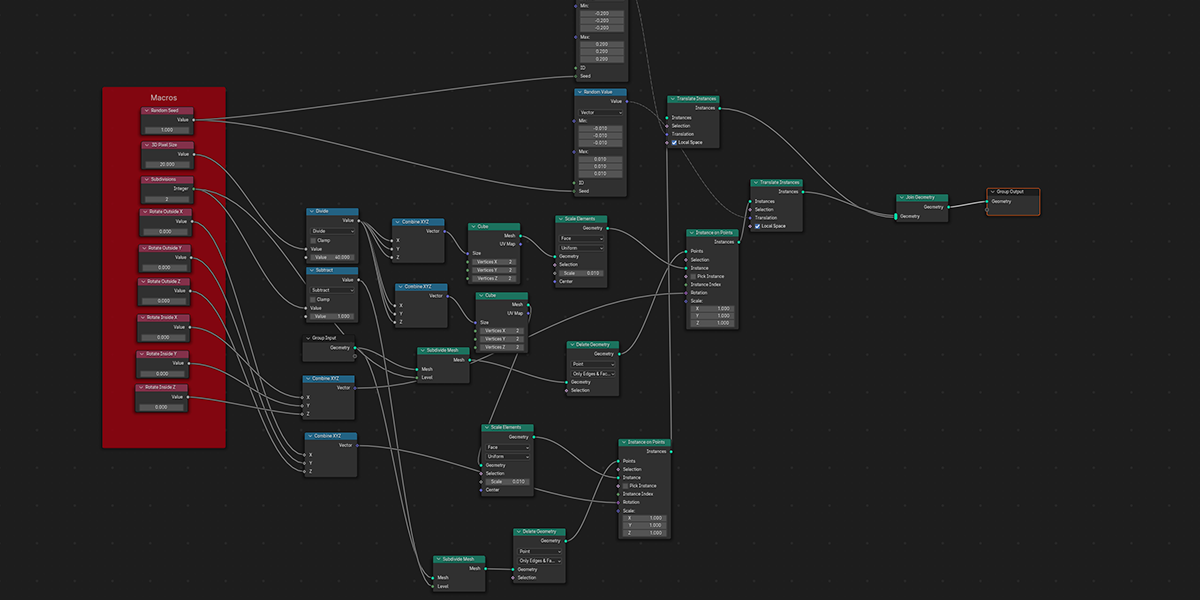
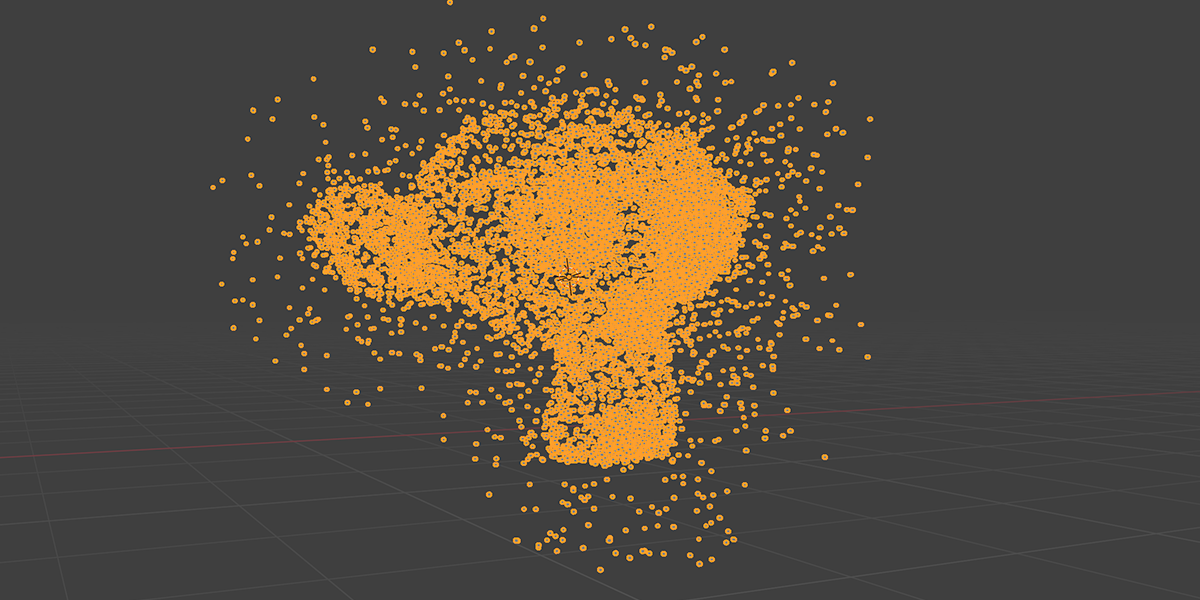
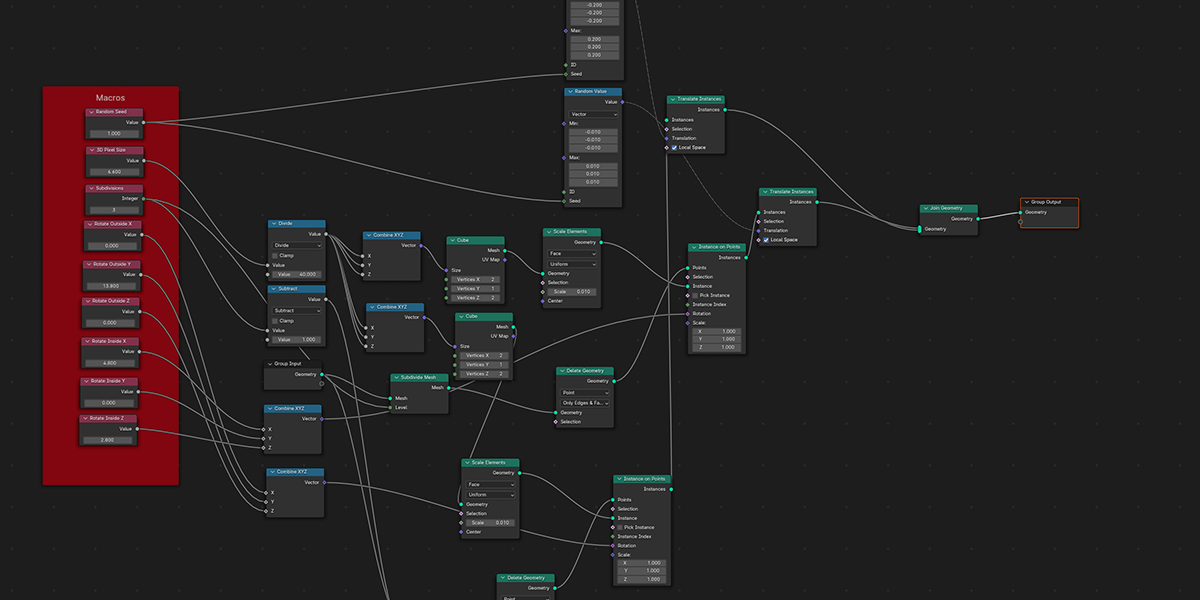
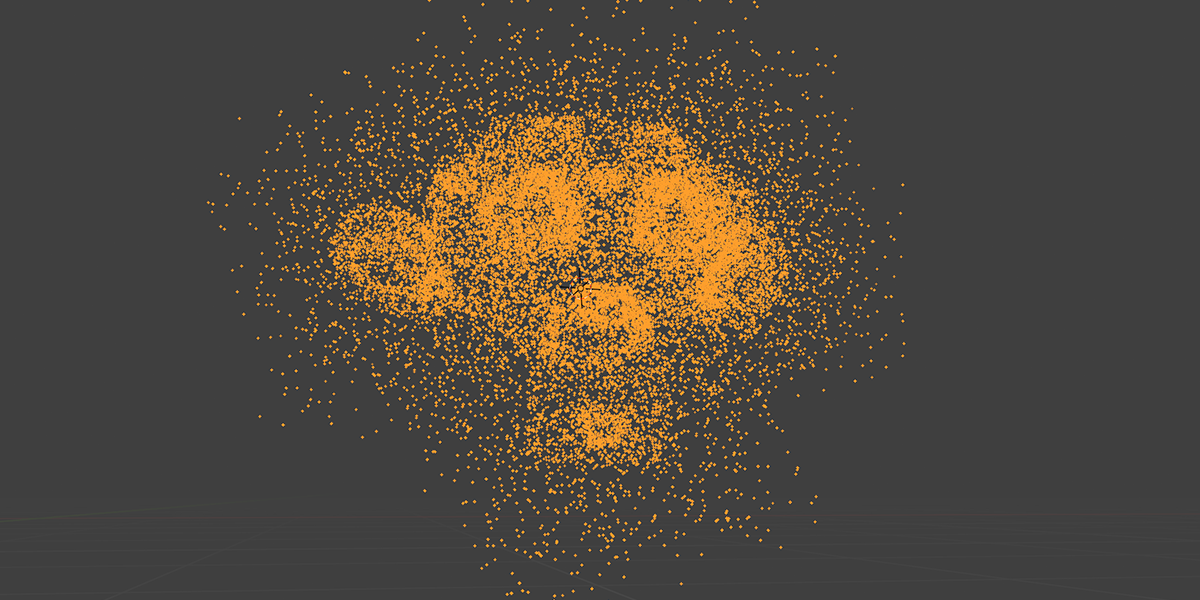
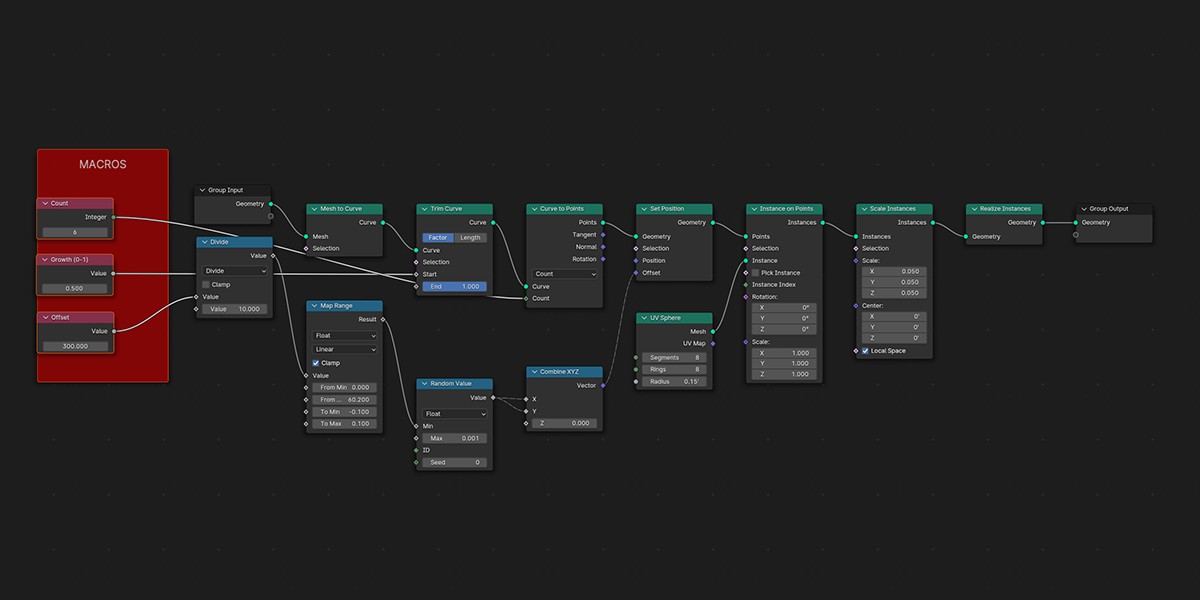
14) Edge Machine
Uses Map Range, Set Position, and trim curve to trace edges and distribute along the manipulated trace values to create an effect of tracing the edges of an object with another object.
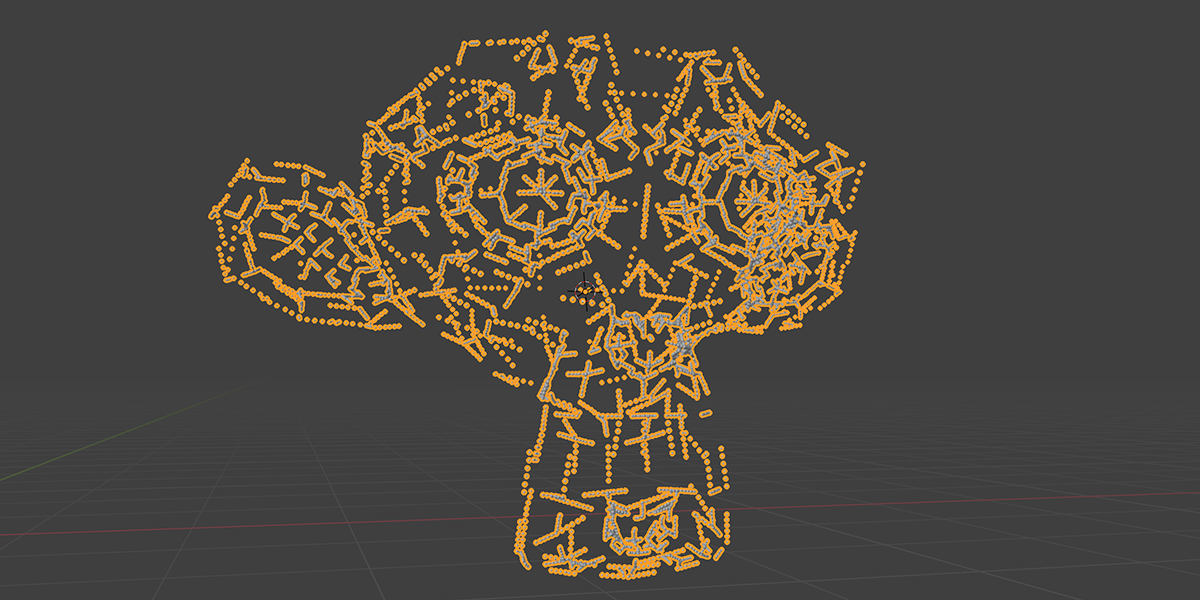
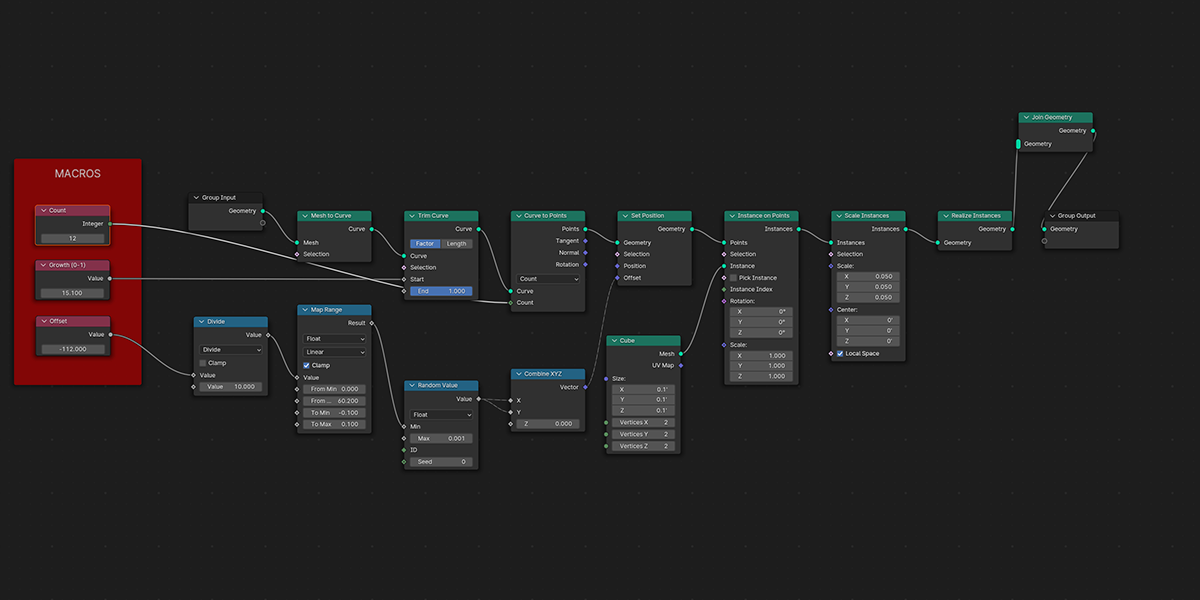
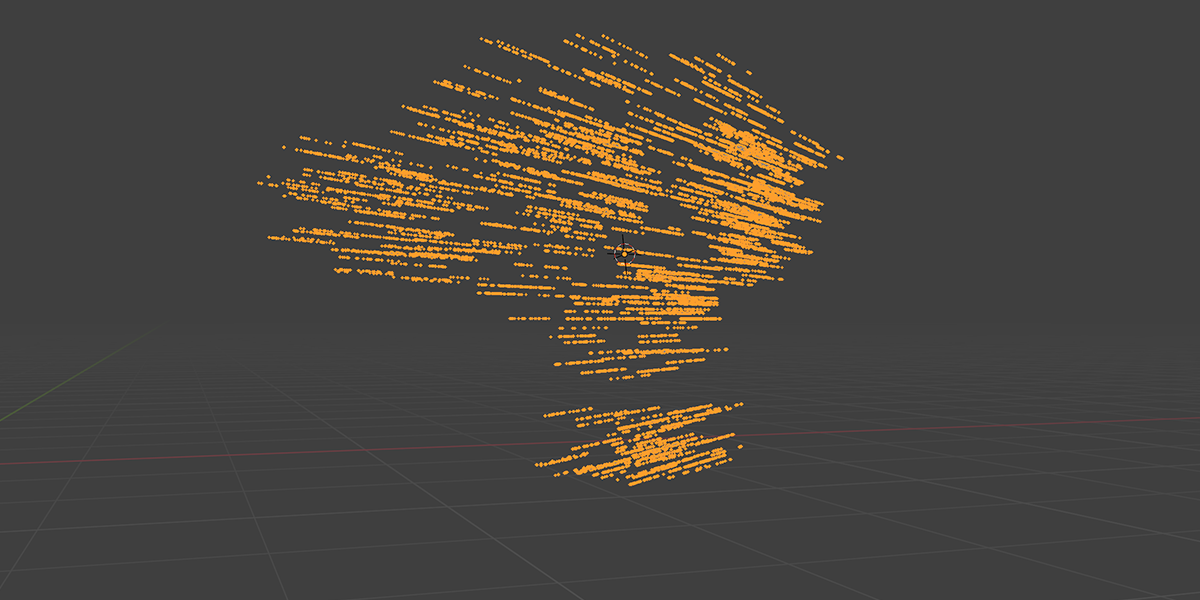
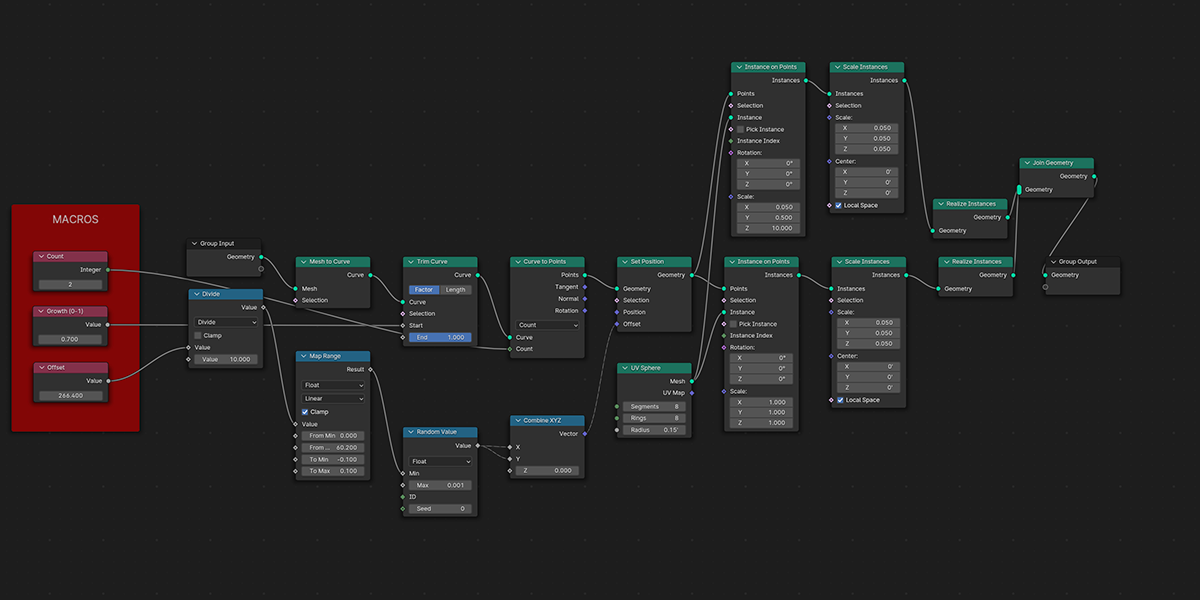
15) Starboy
Uses curves to create a combination of star-like distributions.
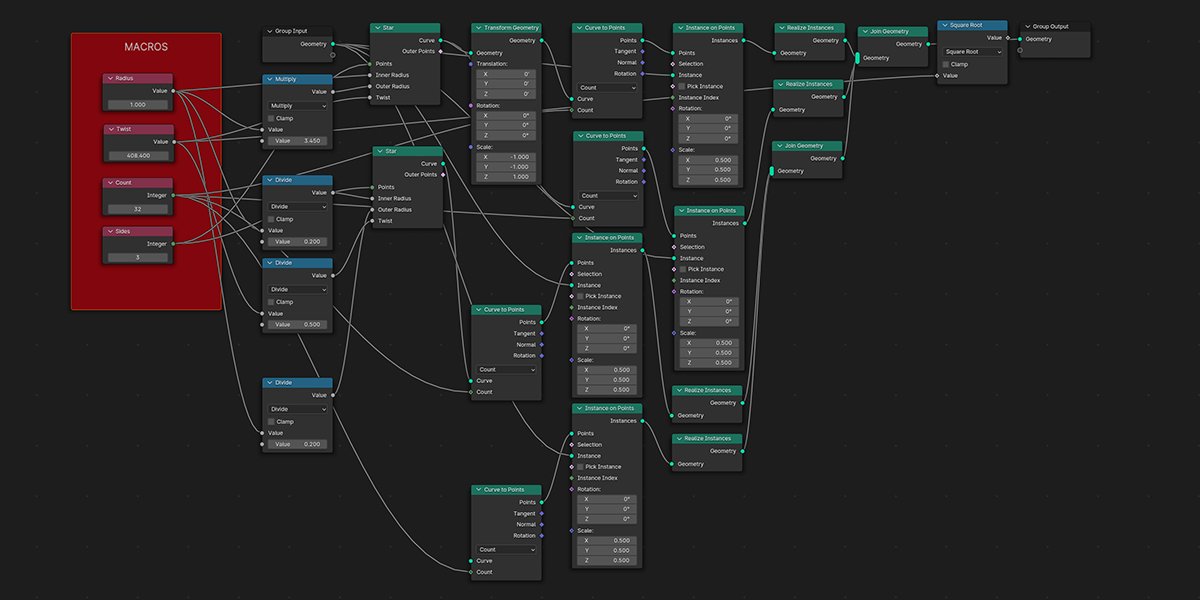
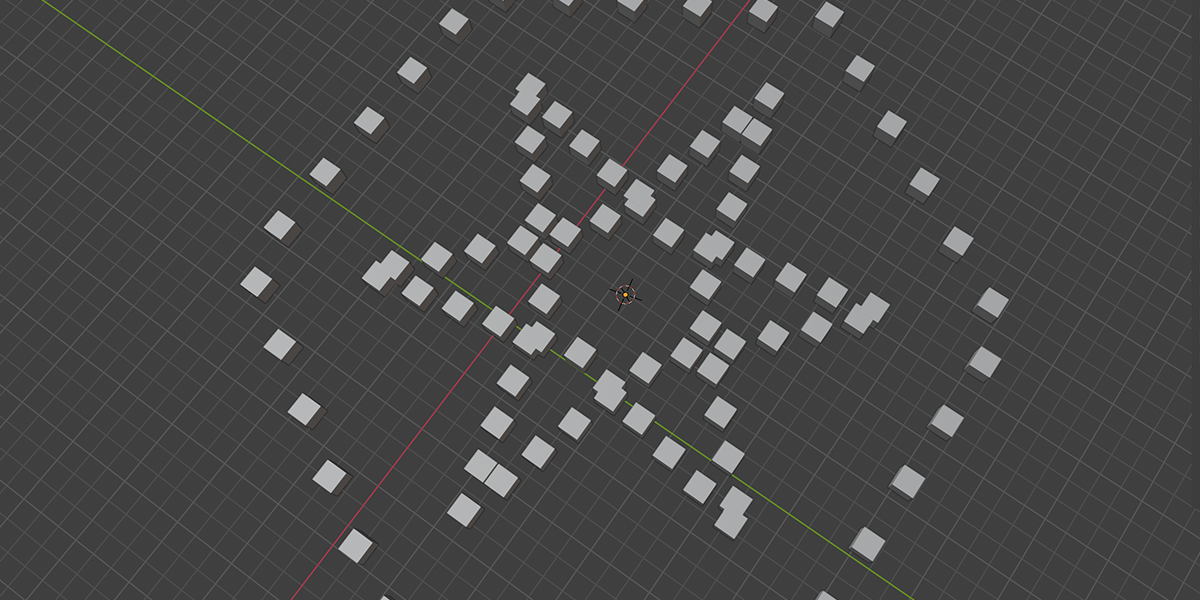
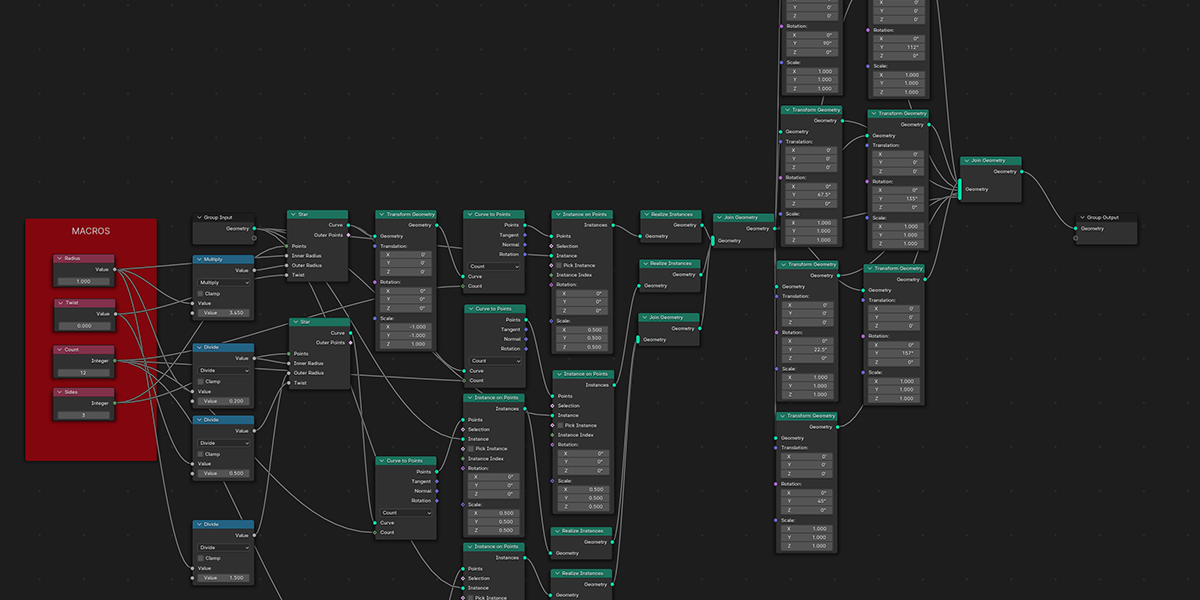
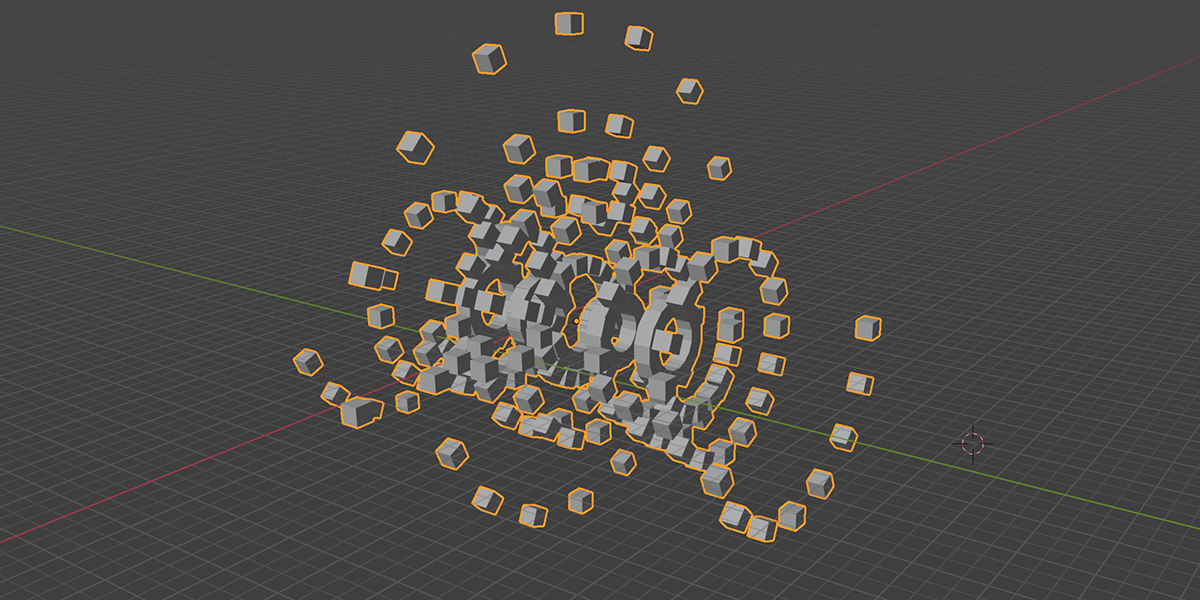
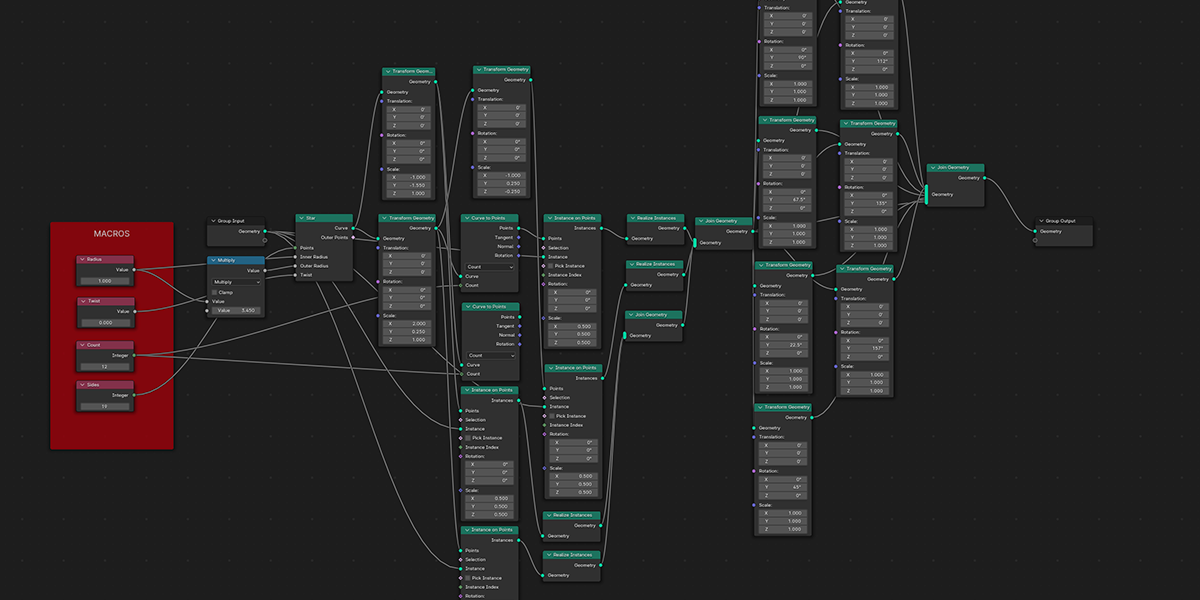
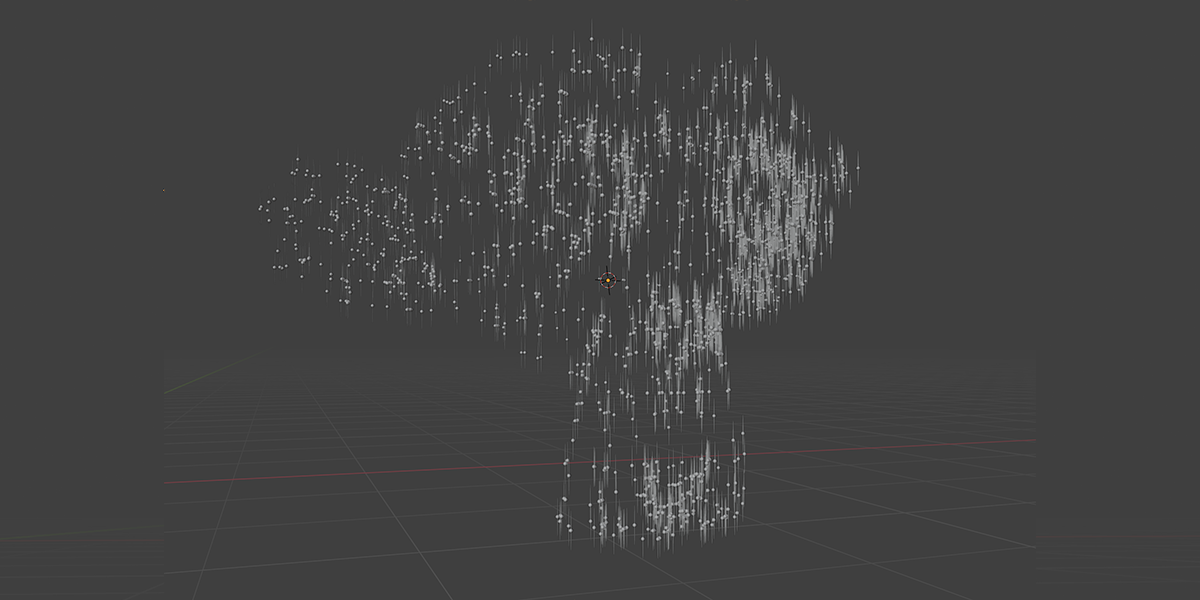
16) Curveball
Uses curves to create a combination of ball-like distributions.
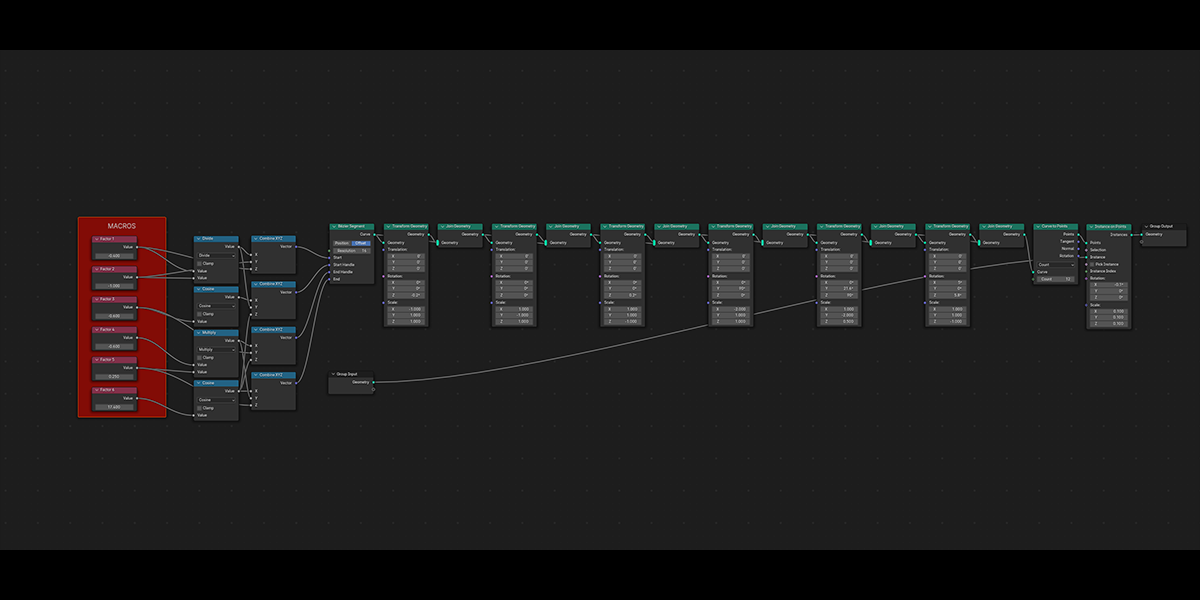
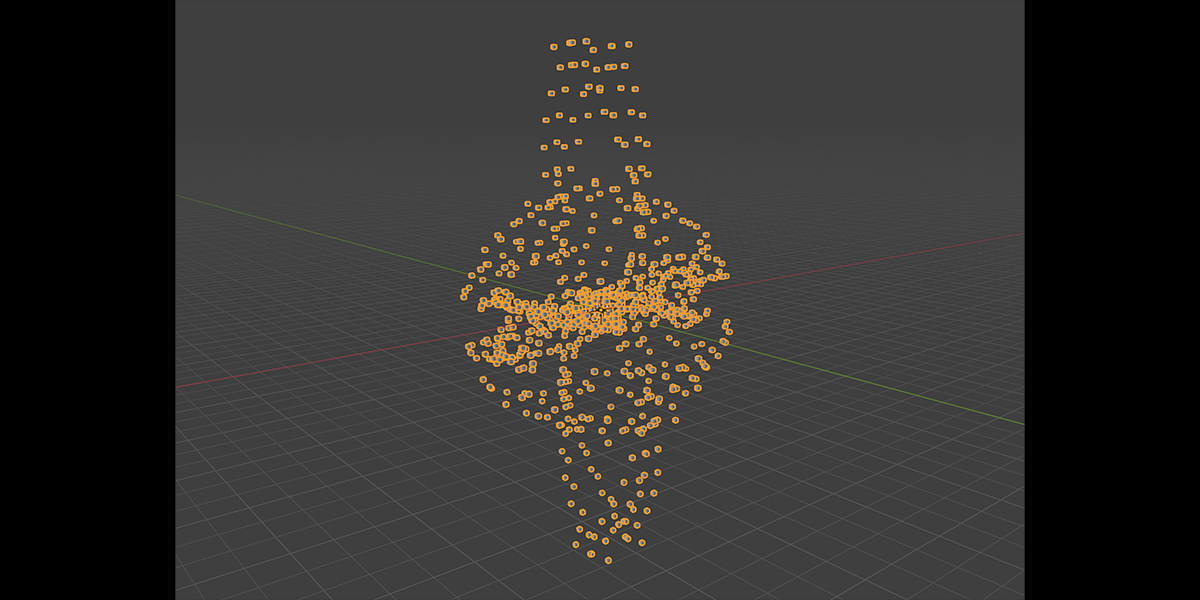
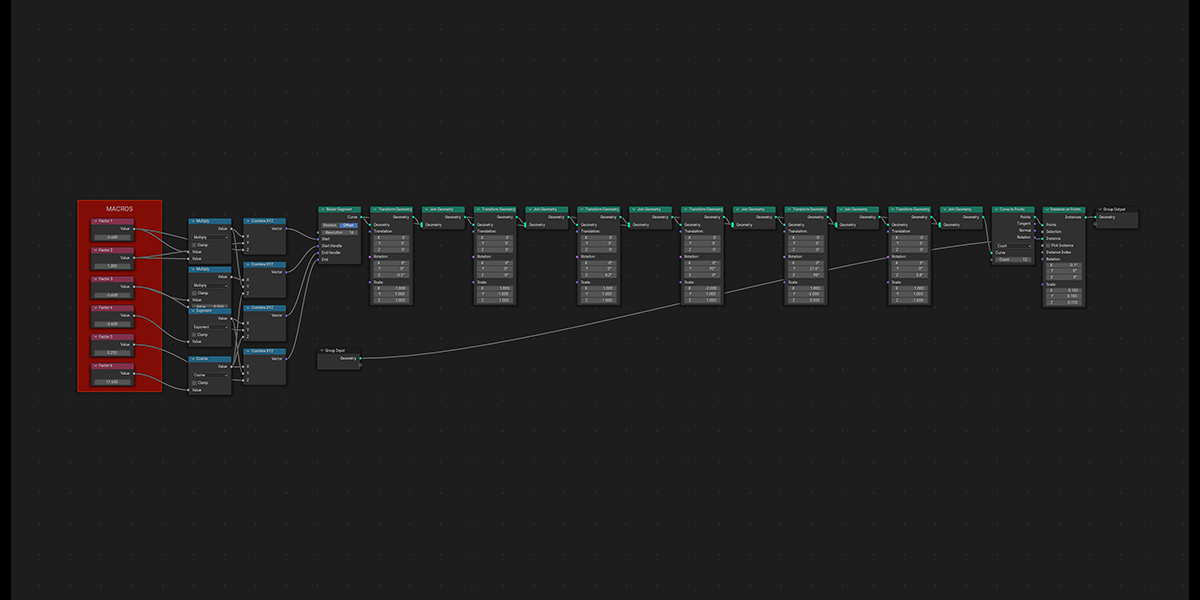
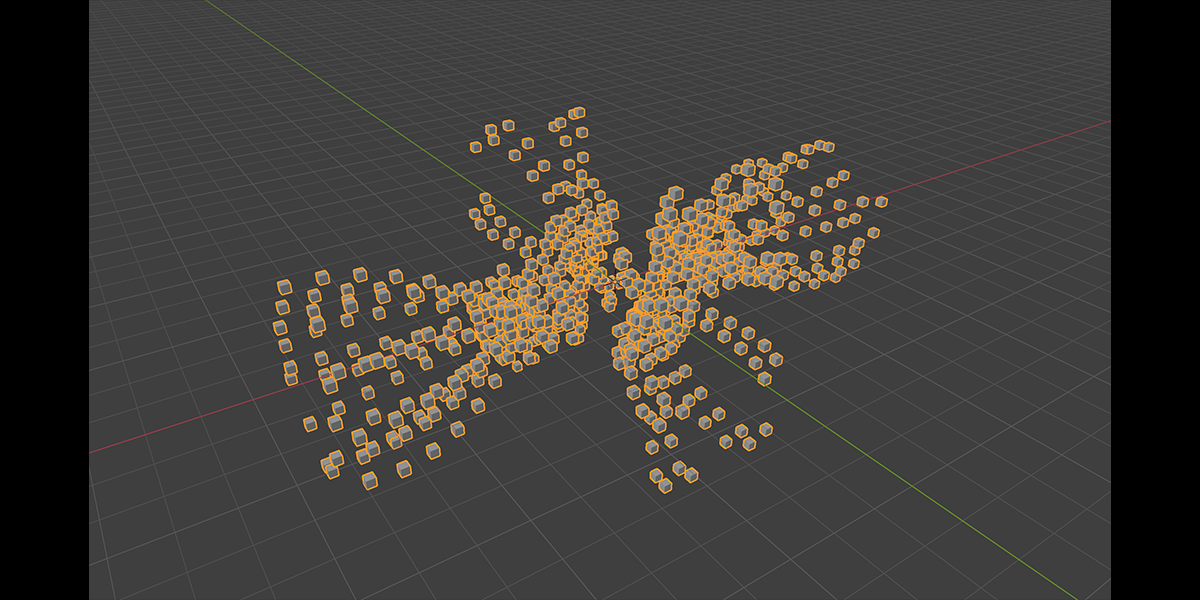
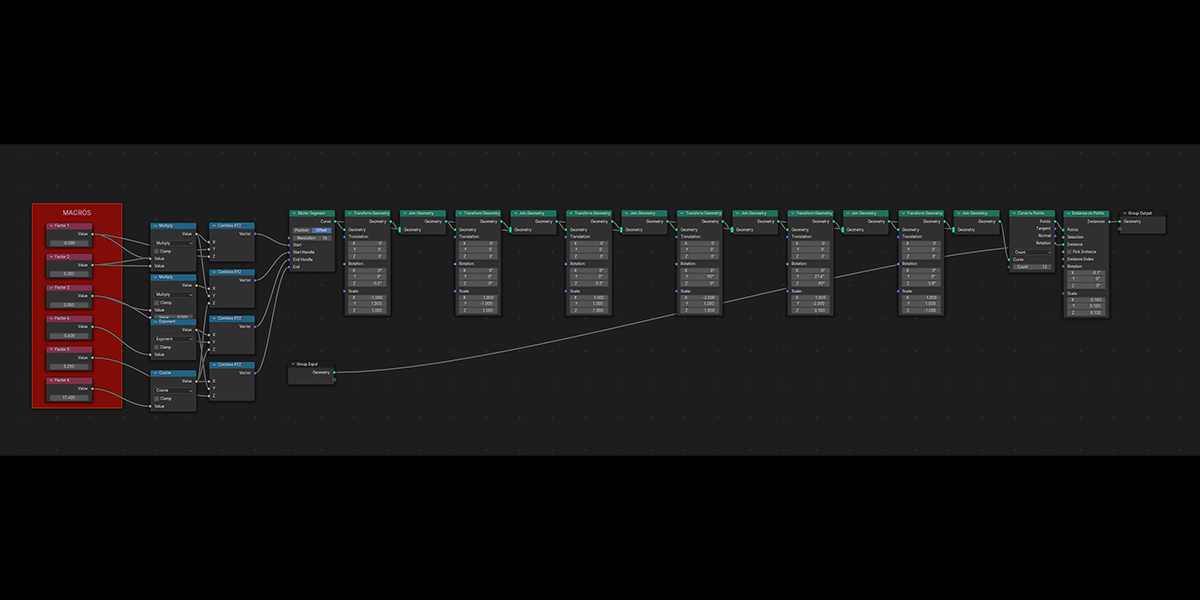
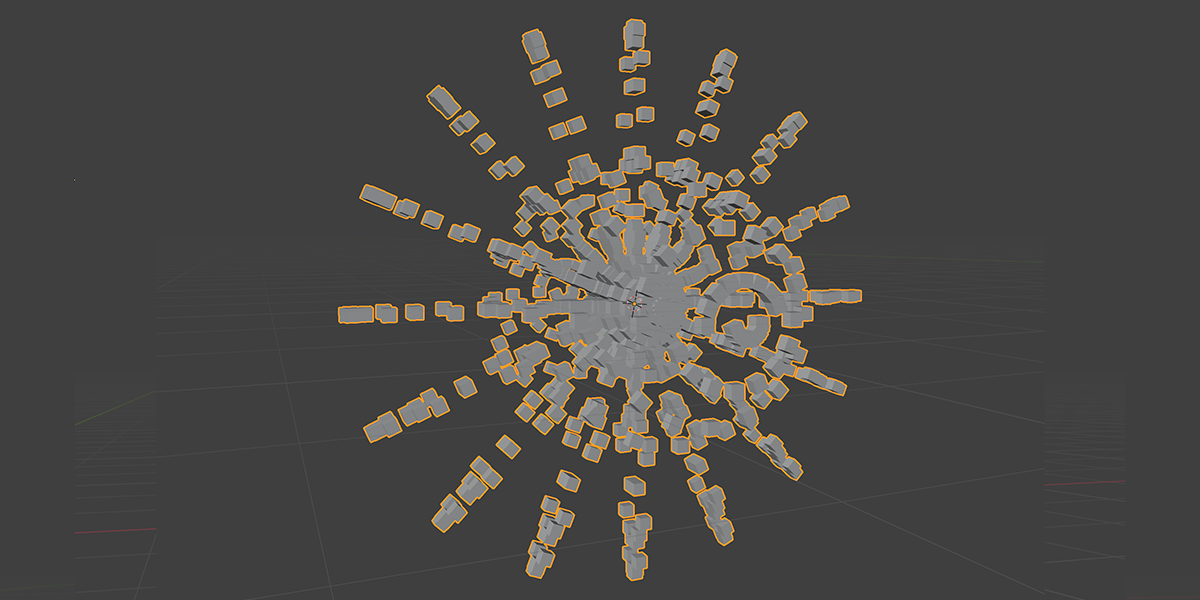
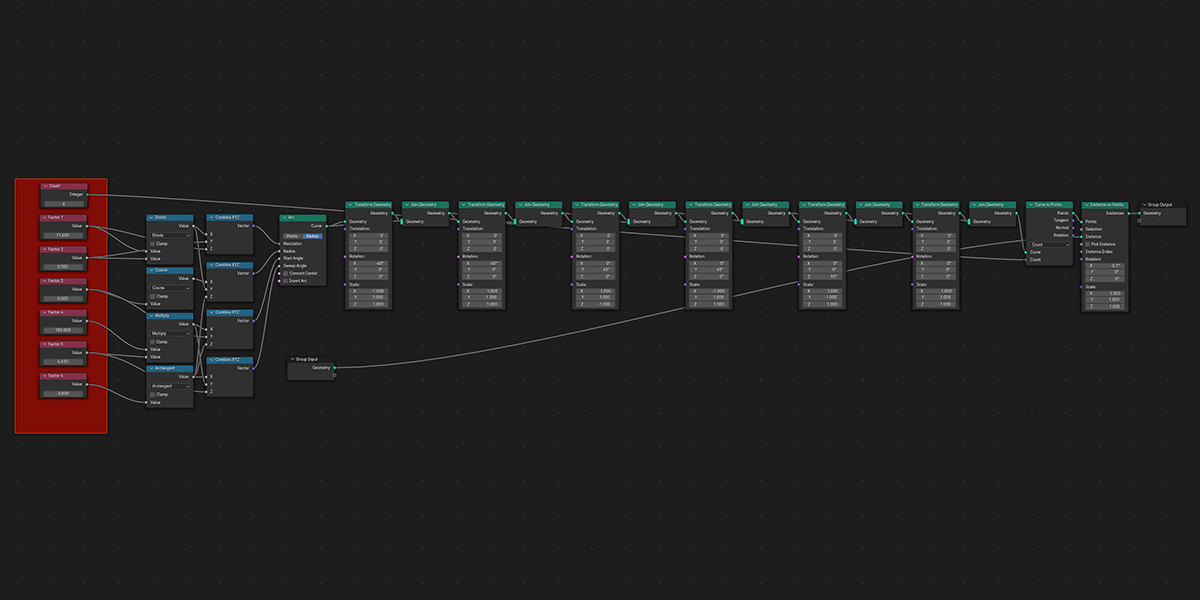
17) Arcsphere
Uses arcs to create a combination of interesting sphere-ish distributions.

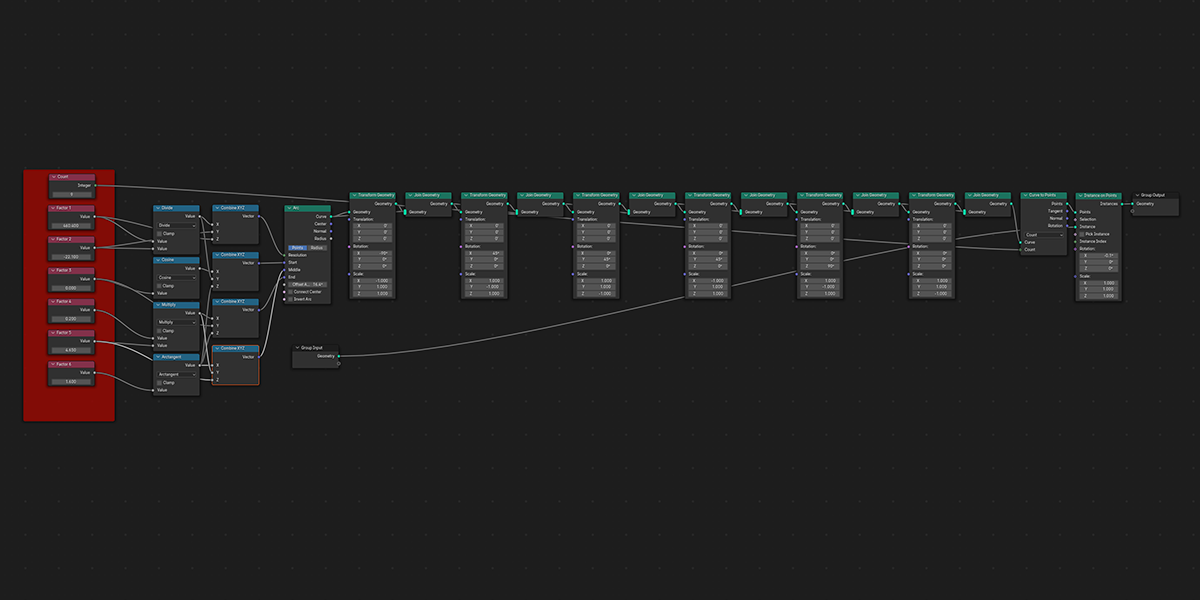


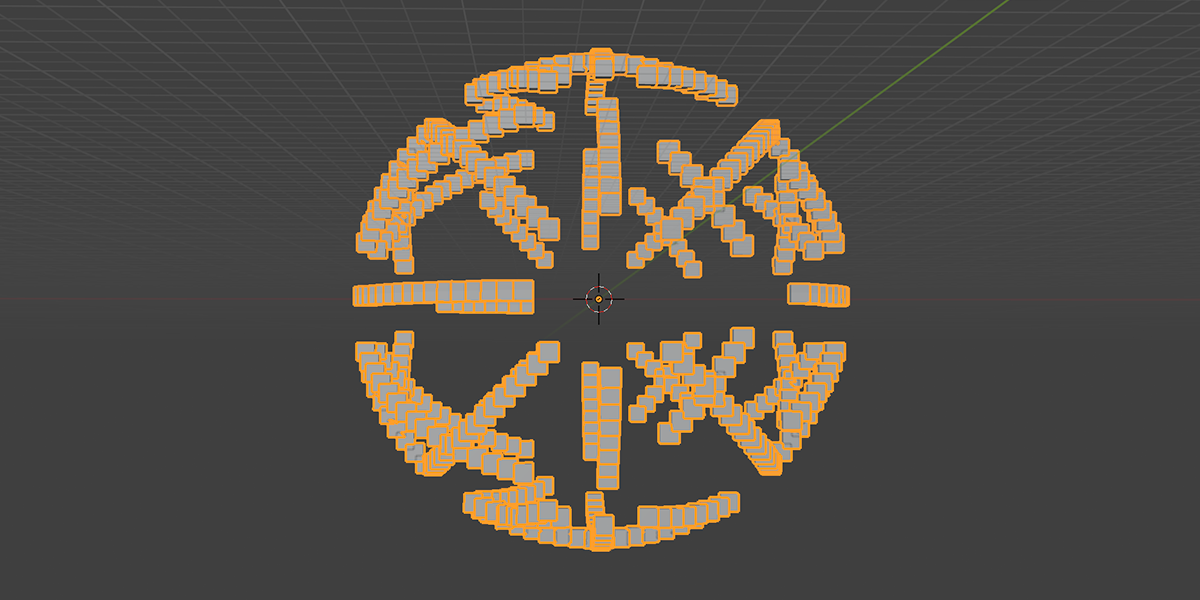
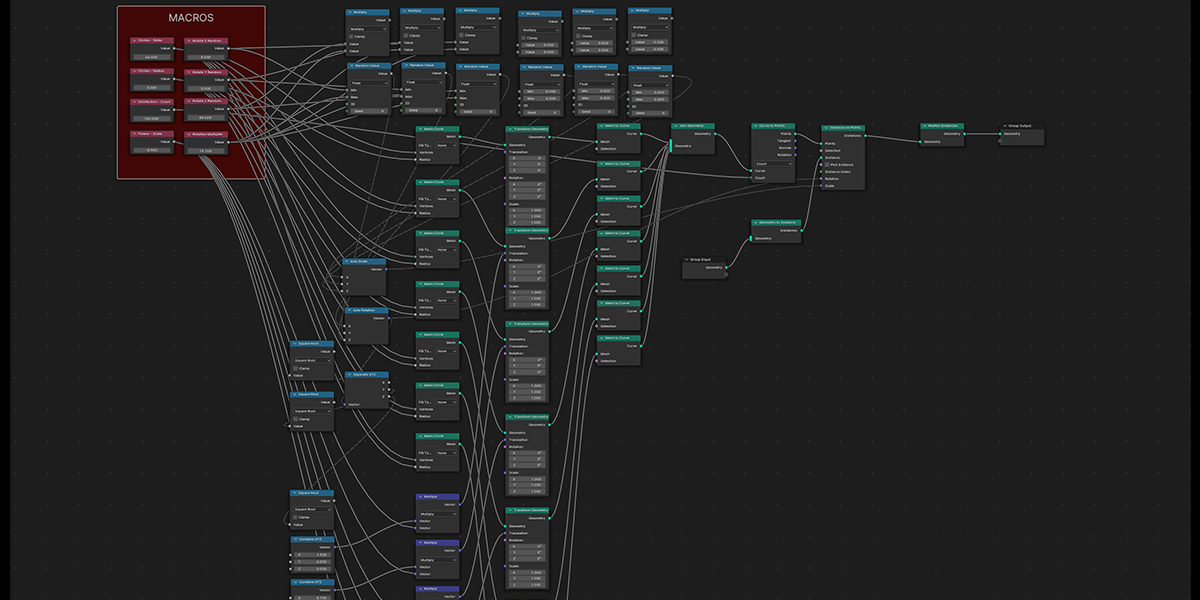
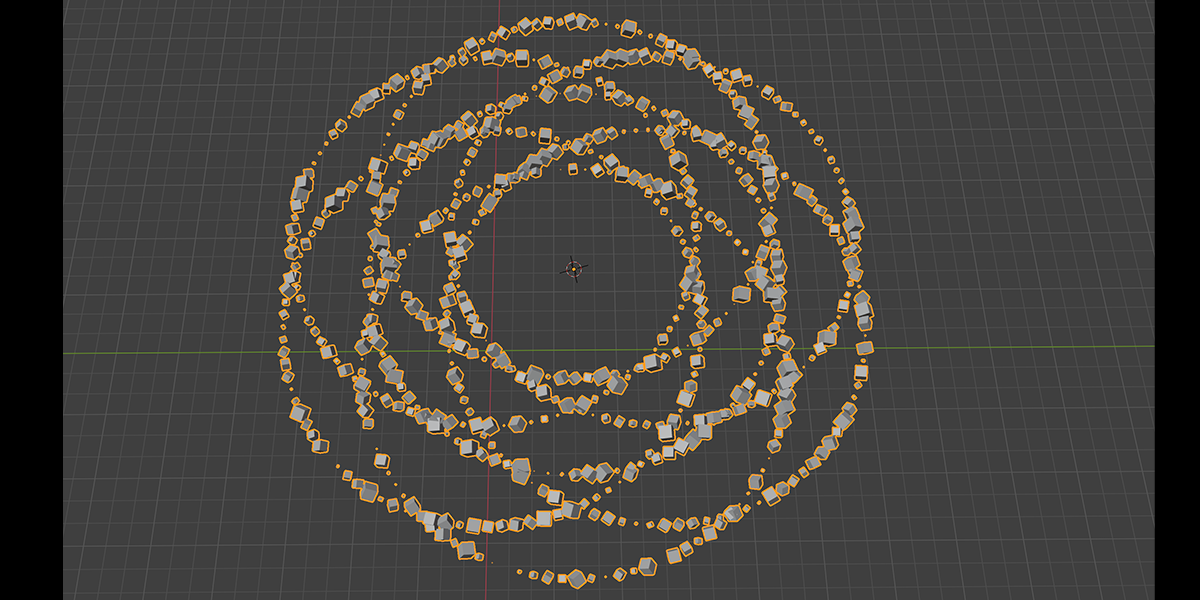
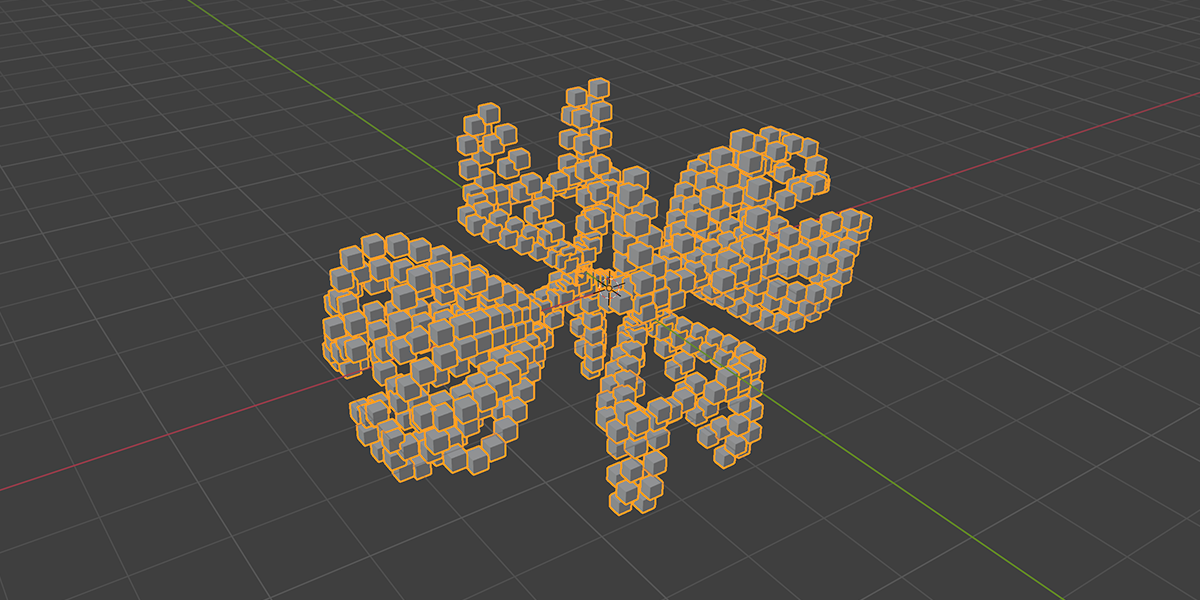
18) Fractal
Uses mathematical ratios and transform nodes to create fractal distributions.


19) Cross Product
Uses mathematical ratios and cross product nodes to create altered fractal distributions.
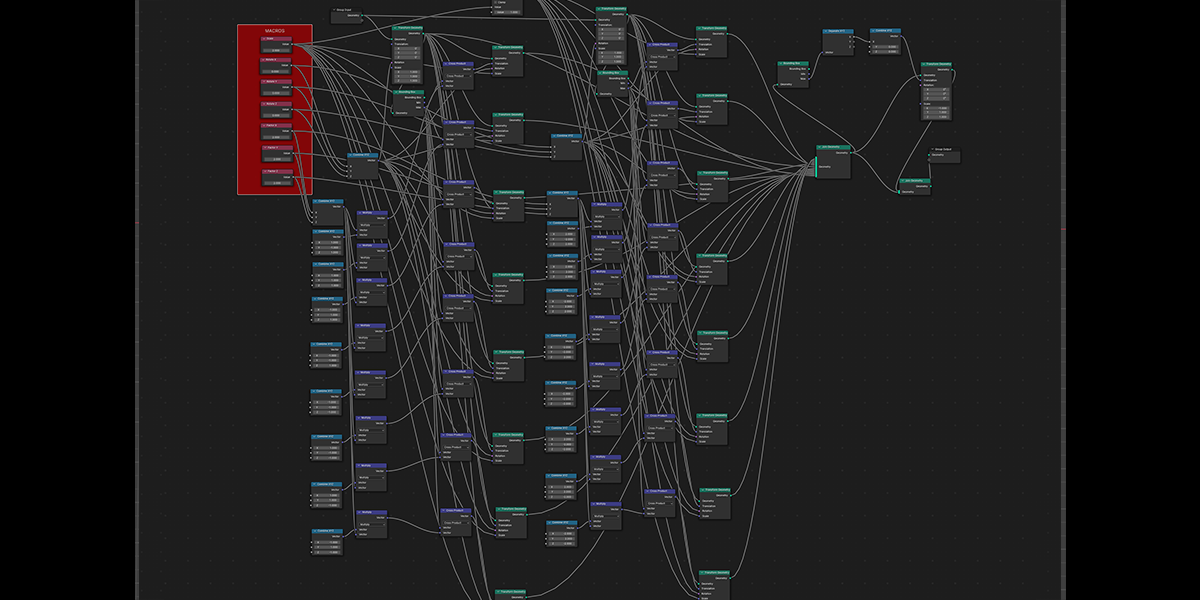
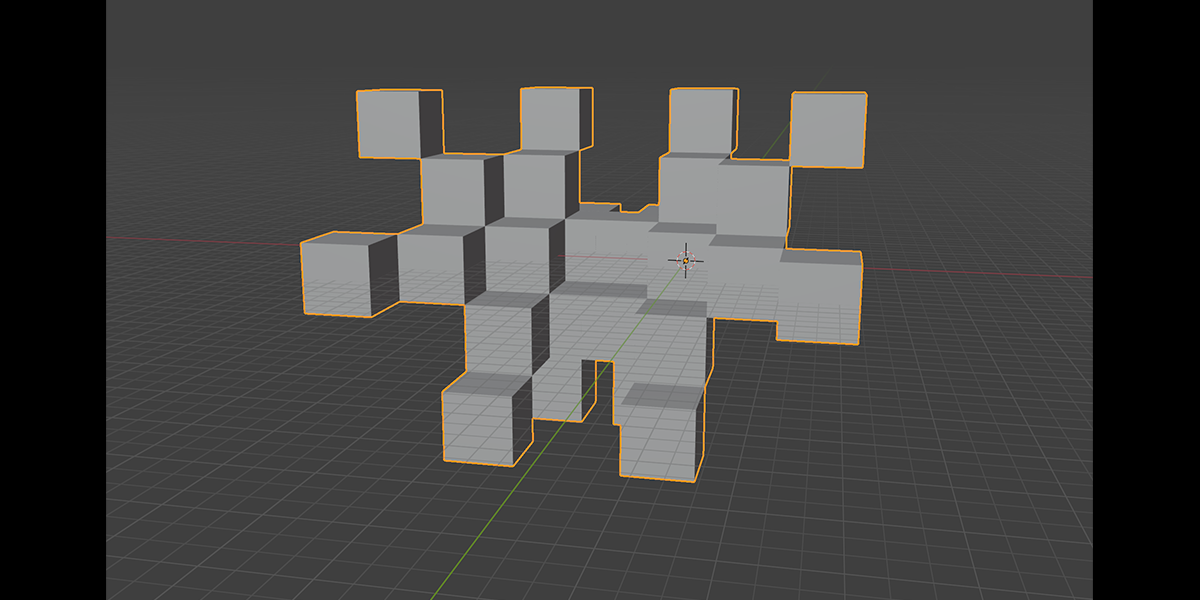
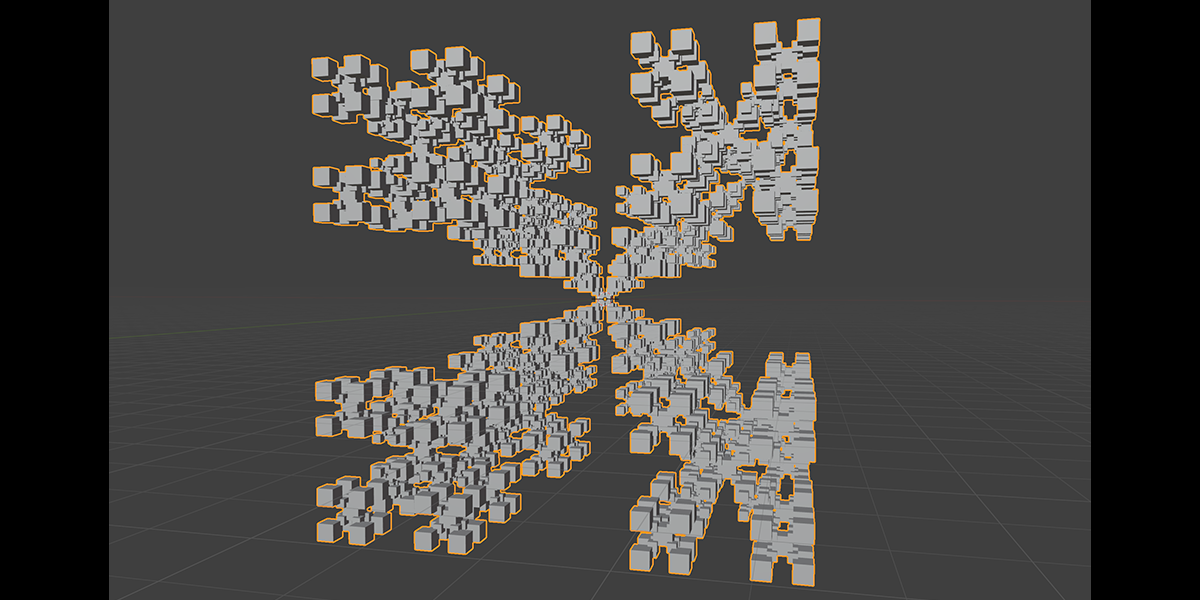
20) Fractal Bool
Uses mathematical ratios and boolean nodes to create fractal distributions that bool their own instances.
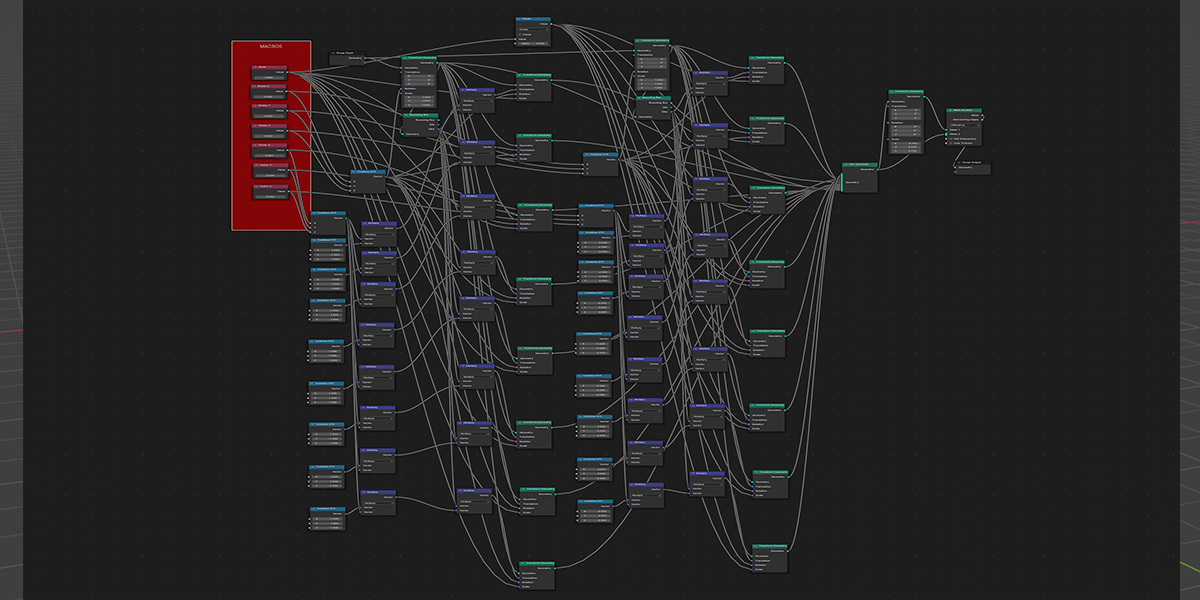
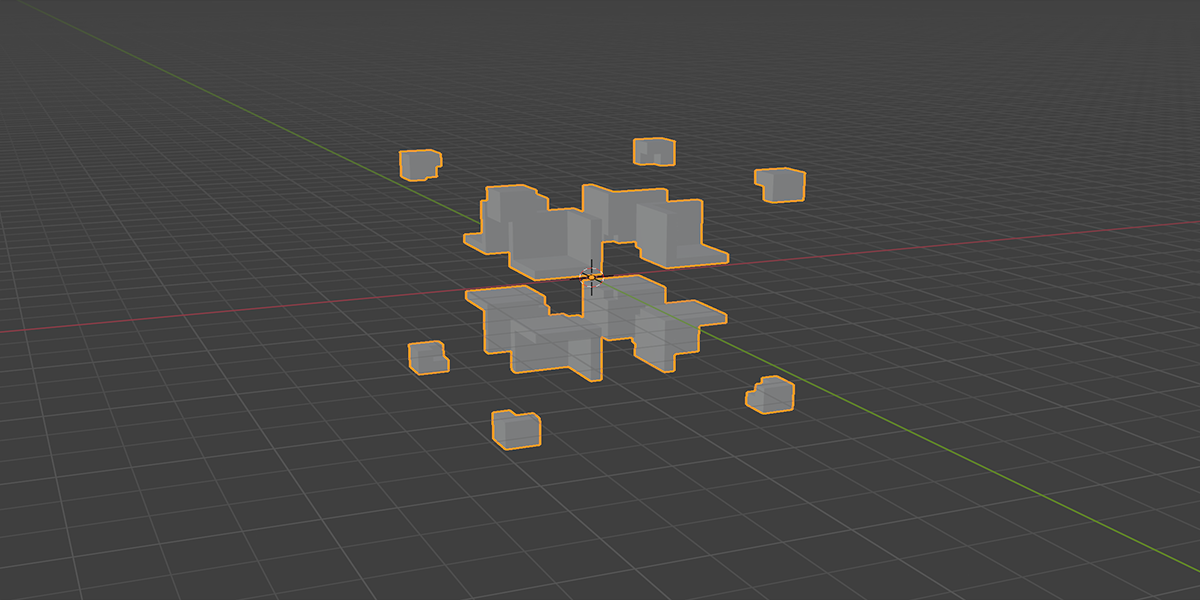
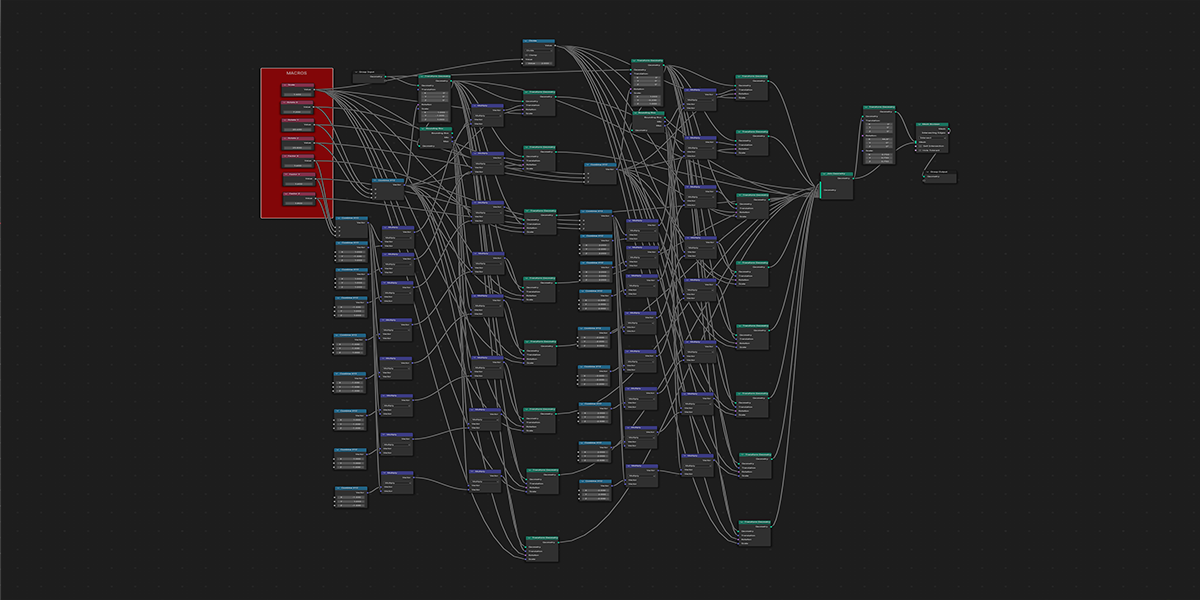
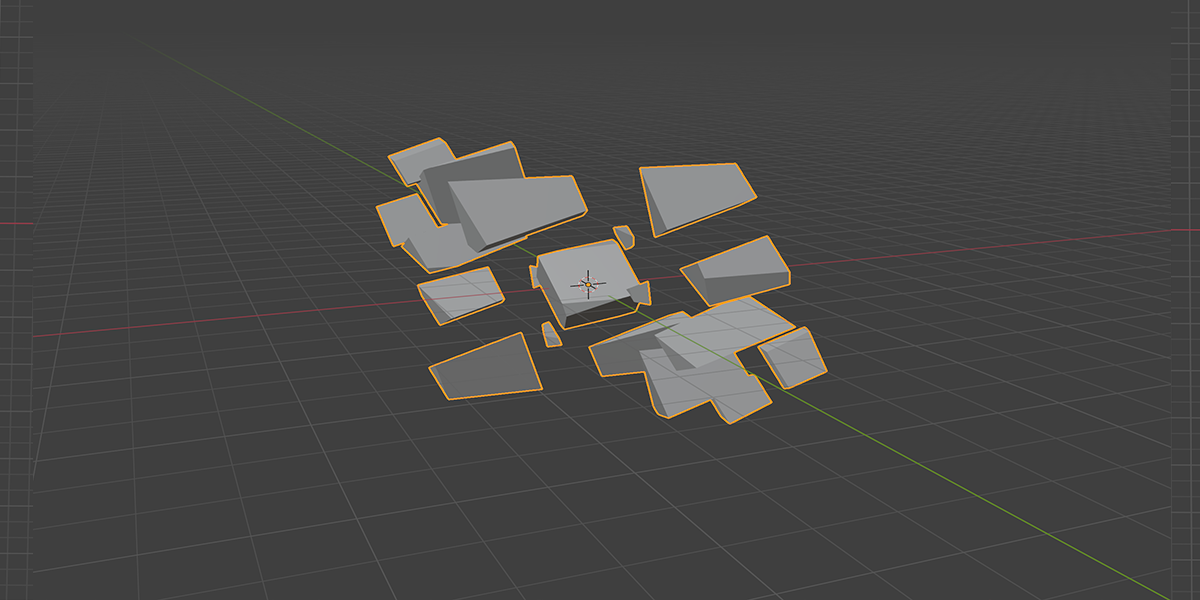
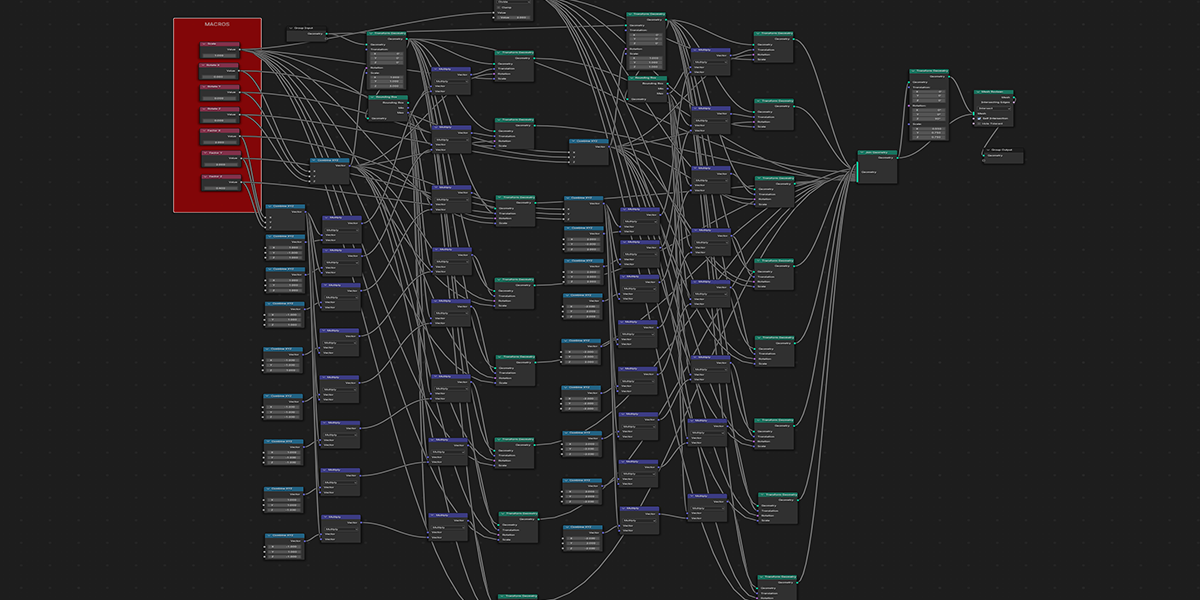
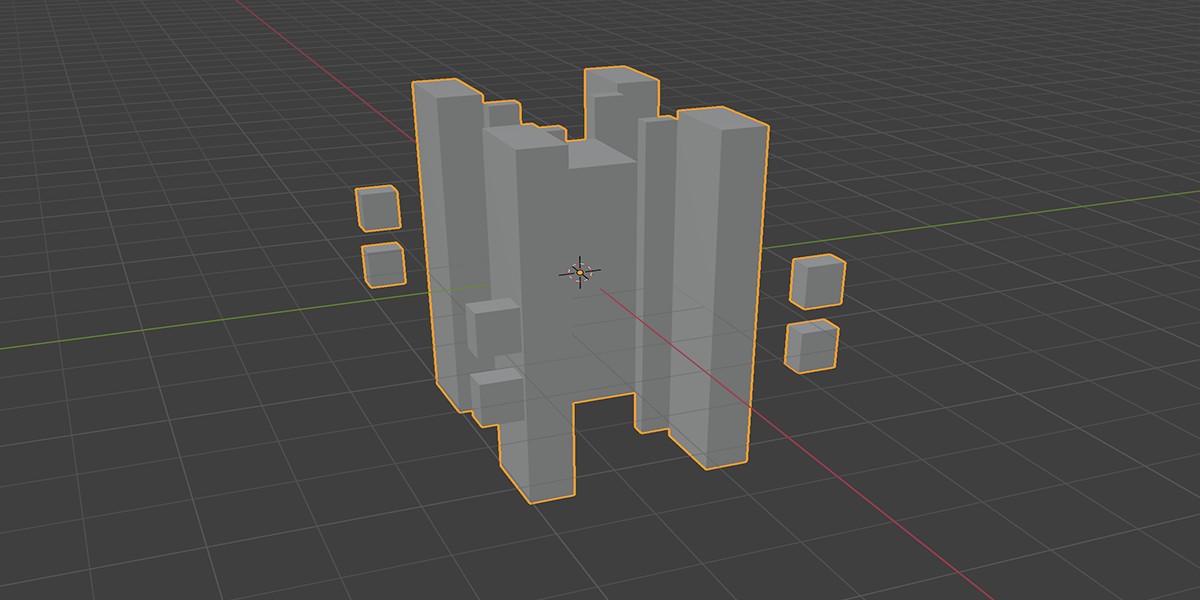
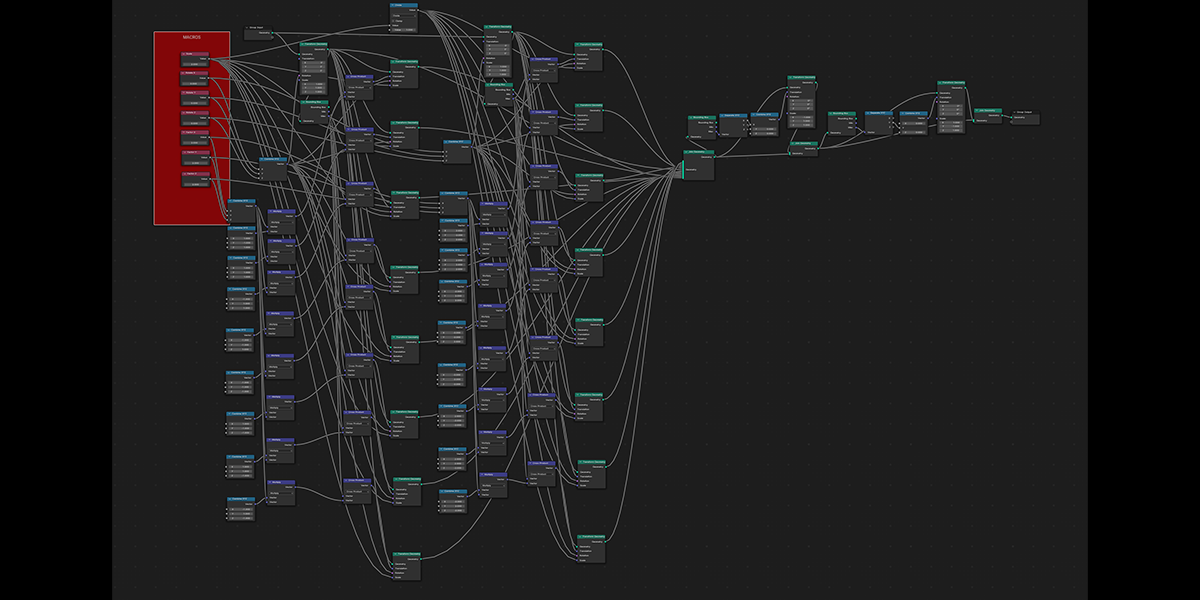
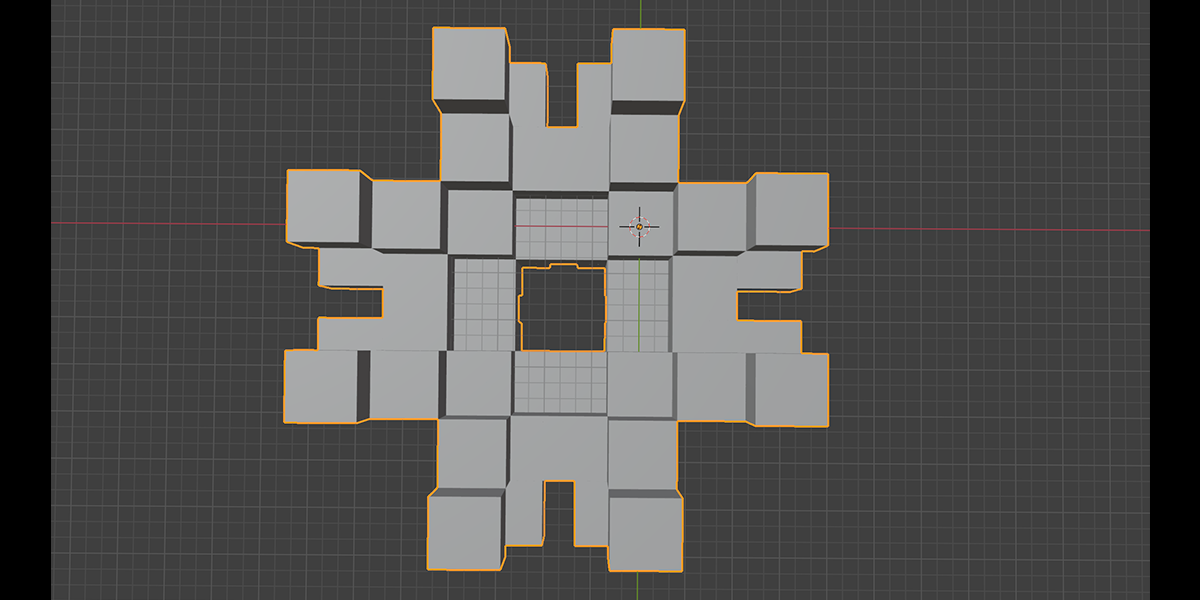
21) Cross Bool
Uses mathematical ratios and cross product nodes in combination with boolean nodes to create altered fractal cross product boolean effects.
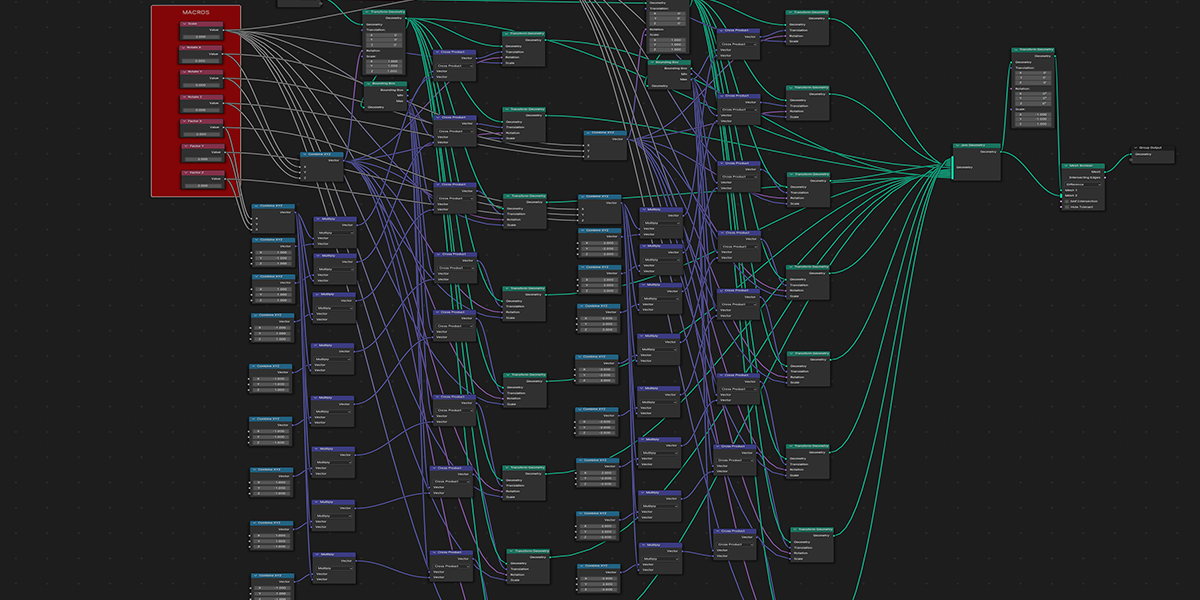
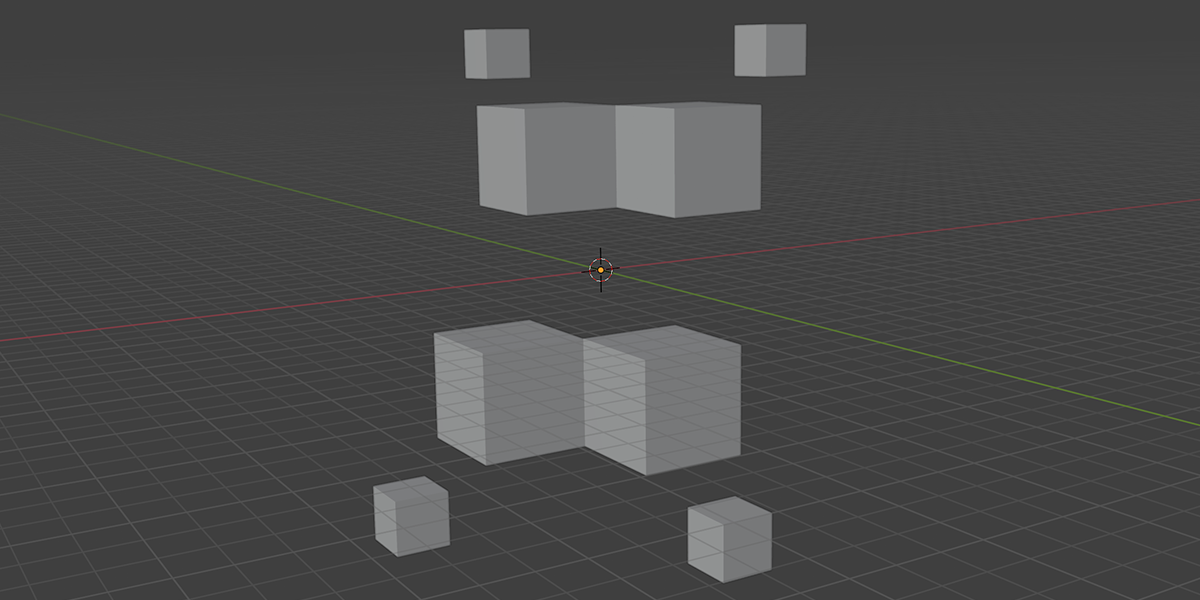
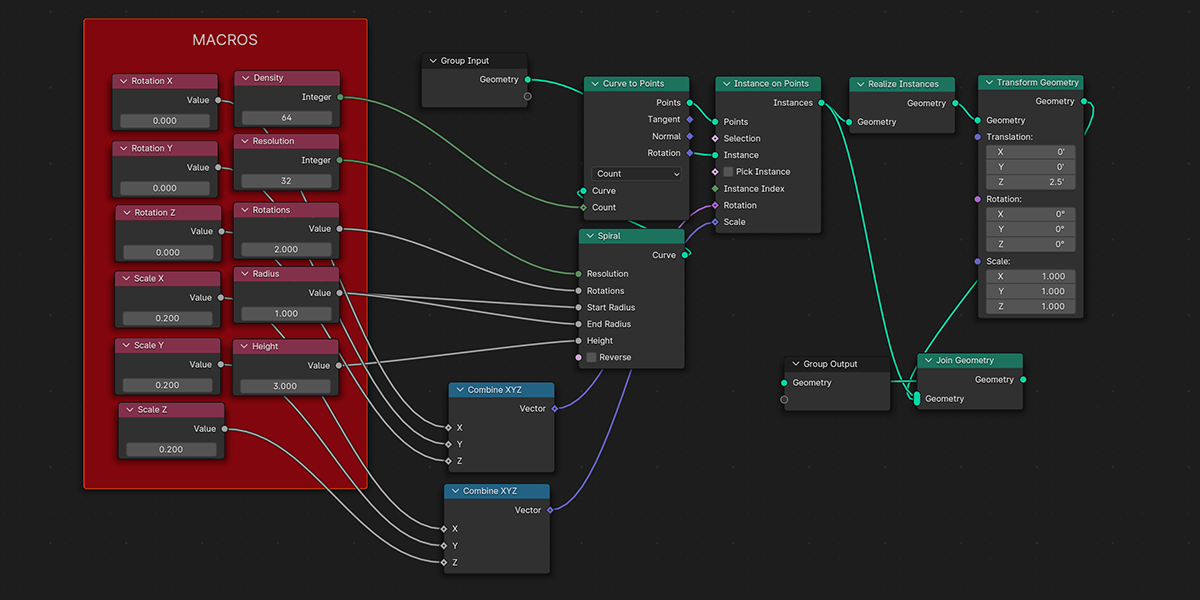
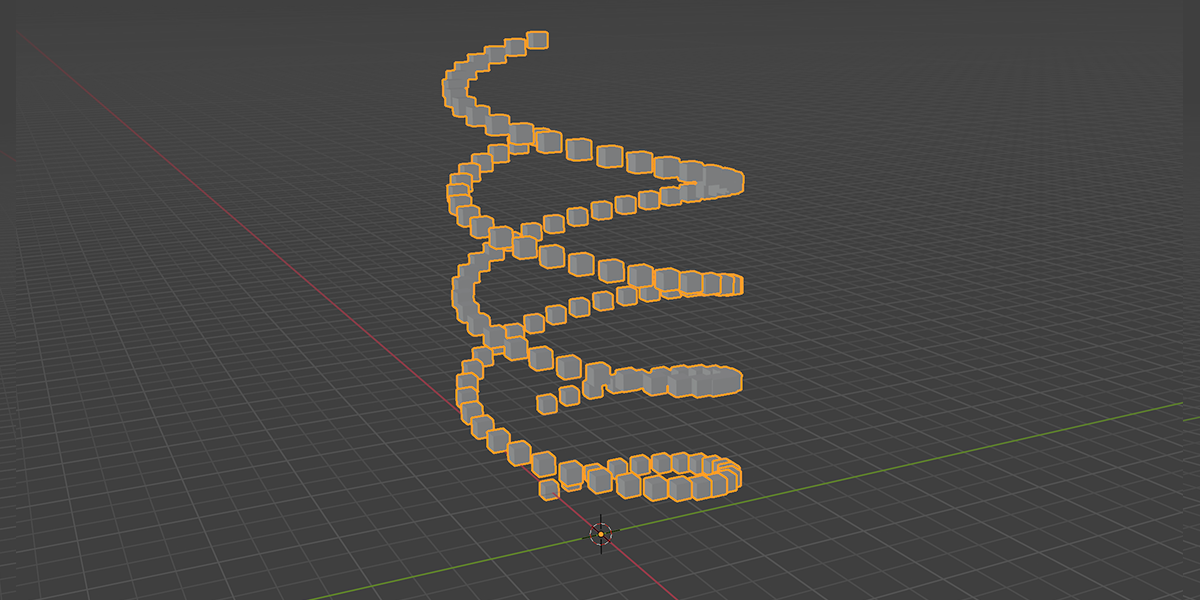
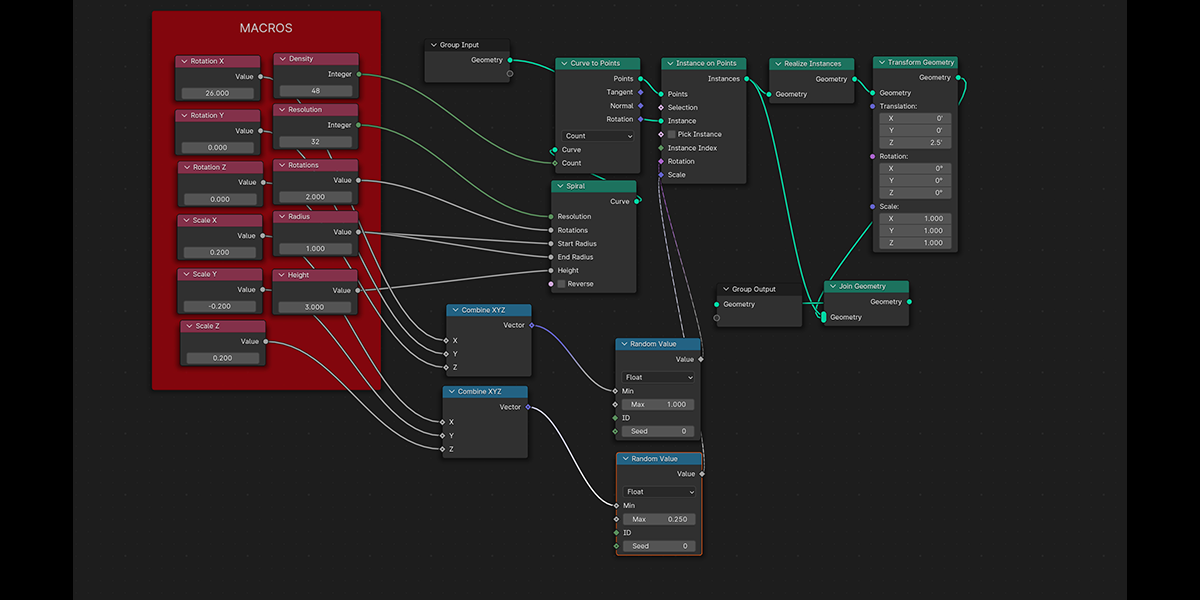
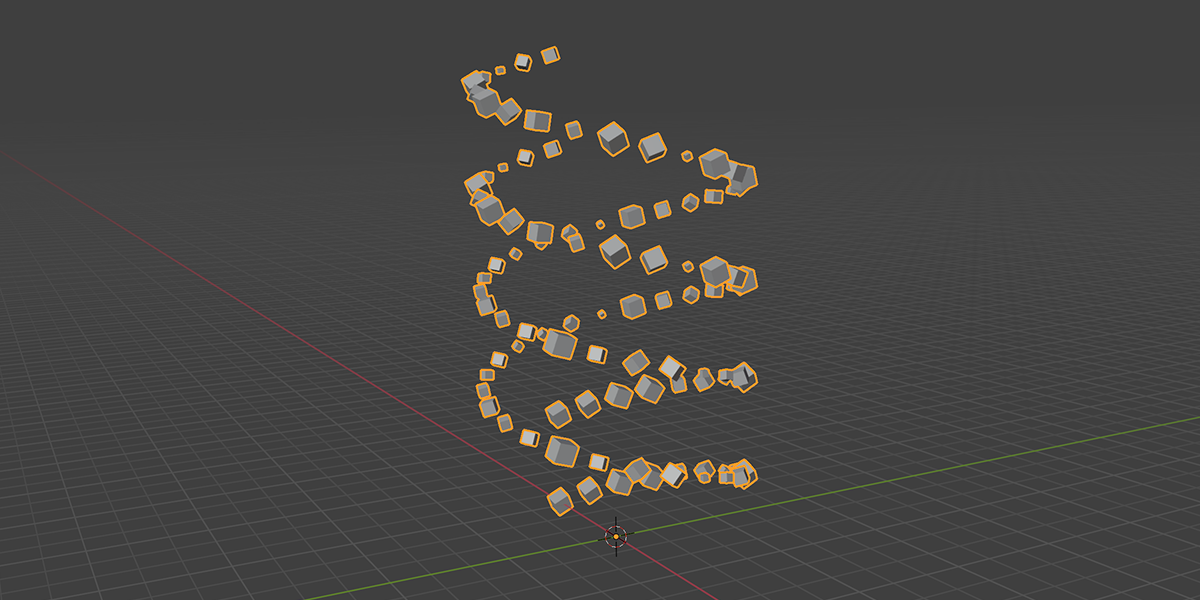
22) Double Helix
Uses curves to create a double helix structure with controls over length, column size, density, randomization.
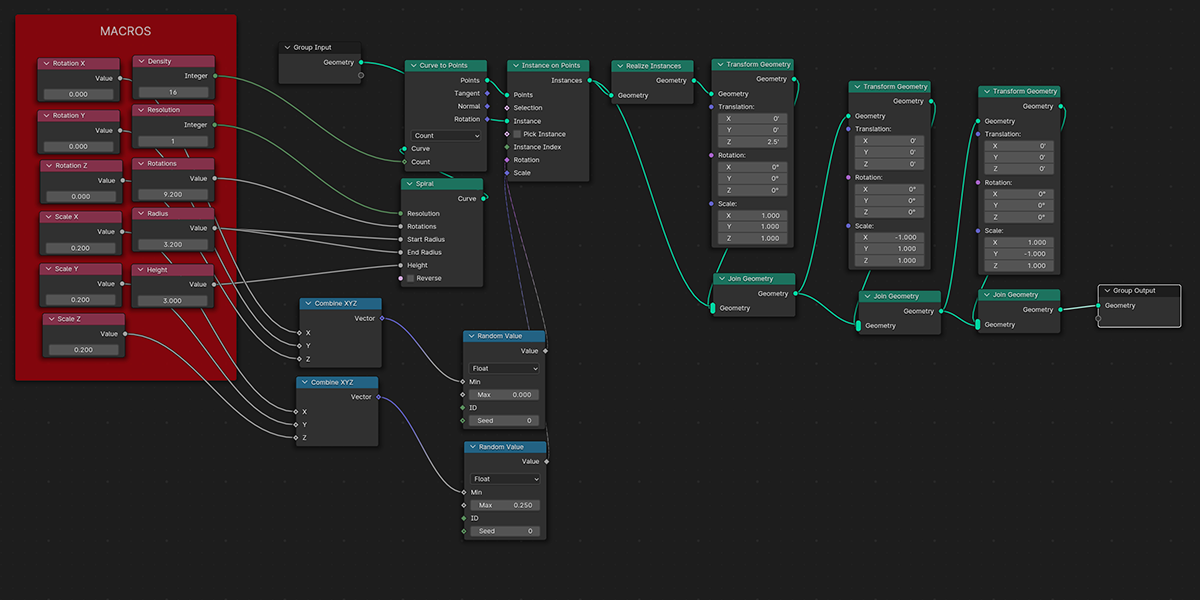
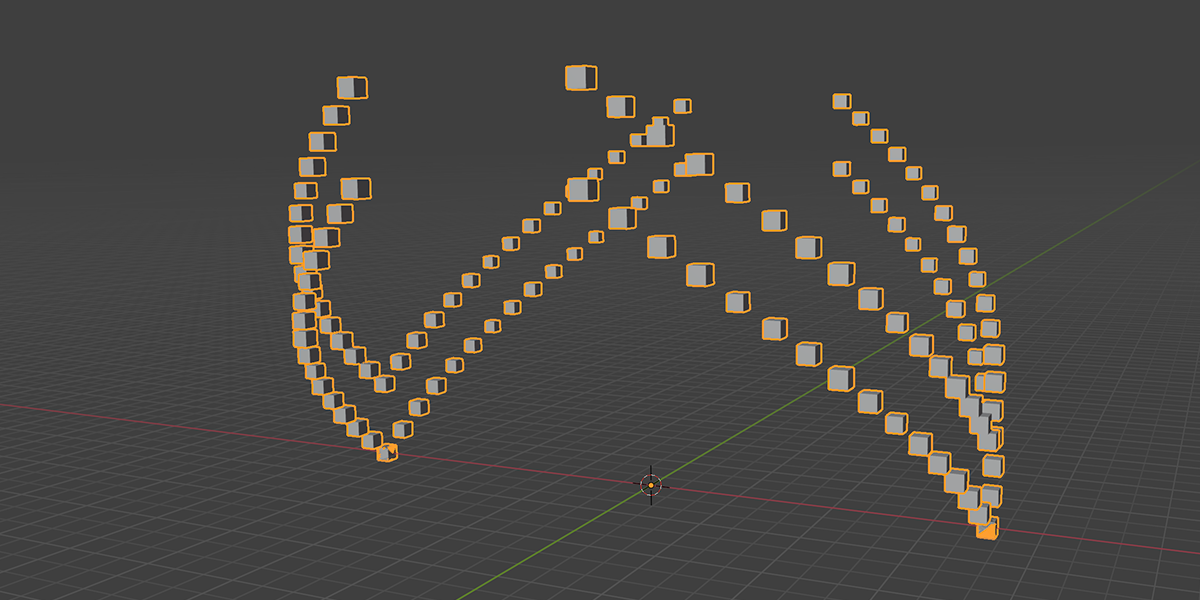
I plan on adding many more node setups in the future. This will be my only geometry-node based addon. New setups added will be included with free updates, and documentation added to this product page. Thanks for the support!
Want to see one added? Shoot me a message and I'll get it done!
Discover more products like this
presets scatter Geometry instance geometry nodes fractals Sacred fractal distribution



















